Search Results for author: Federico Tombari
Found 168 papers, 57 papers with code
BRAVE: Broadening the visual encoding of vision-language models
no code implementations • 10 Apr 2024 • Oğuzhan Fatih Kar, Alessio Tonioni, Petra Poklukar, Achin Kulshrestha, Amir Zamir, Federico Tombari
Our results highlight the potential of incorporating different visual biases for a more broad and contextualized visual understanding of VLMs.
PhysAvatar: Learning the Physics of Dressed 3D Avatars from Visual Observations
no code implementations • 5 Apr 2024 • Yang Zheng, Qingqing Zhao, Guandao Yang, Wang Yifan, Donglai Xiang, Florian Dubost, Dmitry Lagun, Thabo Beeler, Federico Tombari, Leonidas Guibas, Gordon Wetzstein
This marks a significant advancement towards modeling photorealistic digital humans using physically based inverse rendering with physics in the loop.
OpenNeRF: Open Set 3D Neural Scene Segmentation with Pixel-Wise Features and Rendered Novel Views
no code implementations • 4 Apr 2024 • Francis Engelmann, Fabian Manhardt, Michael Niemeyer, Keisuke Tateno, Marc Pollefeys, Federico Tombari
Our OpenNeRF further leverages NeRF's ability to render novel views and extract open-set VLM features from areas that are not well observed in the initial posed images.
Know Your Neighbors: Improving Single-View Reconstruction via Spatial Vision-Language Reasoning
1 code implementation • 4 Apr 2024 • Rui Li, Tobias Fischer, Mattia Segu, Marc Pollefeys, Luc van Gool, Federico Tombari
We propose KYN, a novel method for single-view scene reconstruction that reasons about semantic and spatial context to predict each point's density.
CLoRA: A Contrastive Approach to Compose Multiple LoRA Models
no code implementations • 28 Mar 2024 • Tuna Han Salih Meral, Enis Simsar, Federico Tombari, Pinar Yanardag
Low-Rank Adaptations (LoRAs) have emerged as a powerful and popular technique in the field of image generation, offering a highly effective way to adapt and refine pre-trained deep learning models for specific tasks without the need for comprehensive retraining.
Zero123-6D: Zero-shot Novel View Synthesis for RGB Category-level 6D Pose Estimation
no code implementations • 21 Mar 2024 • Francesco Di Felice, Alberto Remus, Stefano Gasperini, Benjamin Busam, Lionel Ott, Federico Tombari, Roland Siegwart, Carlo Alberto Avizzano
Estimating the pose of objects through vision is essential to make robotic platforms interact with the environment.
RadSplat: Radiance Field-Informed Gaussian Splatting for Robust Real-Time Rendering with 900+ FPS
no code implementations • 20 Mar 2024 • Michael Niemeyer, Fabian Manhardt, Marie-Julie Rakotosaona, Michael Oechsle, Daniel Duckworth, Rama Gosula, Keisuke Tateno, John Bates, Dominik Kaeser, Federico Tombari
First, we use radiance fields as a prior and supervision signal for optimizing point-based scene representations, leading to improved quality and more robust optimization.
GeoGaussian: Geometry-aware Gaussian Splatting for Scene Rendering
no code implementations • 17 Mar 2024 • Yanyan Li, Chenyu Lyu, Yan Di, Guangyao Zhai, Gim Hee Lee, Federico Tombari
During the Gaussian Splatting optimization process, the scene's geometry can gradually deteriorate if its structure is not deliberately preserved, especially in non-textured regions such as walls, ceilings, and furniture surfaces.
KP-RED: Exploiting Semantic Keypoints for Joint 3D Shape Retrieval and Deformation
1 code implementation • 15 Mar 2024 • Ruida Zhang, Chenyangguang Zhang, Yan Di, Fabian Manhardt, Xingyu Liu, Federico Tombari, Xiangyang Ji
In this paper, we present KP-RED, a unified KeyPoint-driven REtrieval and Deformation framework that takes object scans as input and jointly retrieves and deforms the most geometrically similar CAD models from a pre-processed database to tightly match the target.
FocusCLIP: Multimodal Subject-Level Guidance for Zero-Shot Transfer in Human-Centric Tasks
no code implementations • 11 Mar 2024 • Muhammad Saif Ullah Khan, Muhammad Ferjad Naeem, Federico Tombari, Luc van Gool, Didier Stricker, Muhammad Zeshan Afzal
We propose FocusCLIP, integrating subject-level guidance--a specialized mechanism for target-specific supervision--into the CLIP framework for improved zero-shot transfer on human-centric tasks.
 Ranked #1 on
Emotion Recognition
on EMOTIC
Ranked #1 on
Emotion Recognition
on EMOTIC
HyperSDFusion: Bridging Hierarchical Structures in Language and Geometry for Enhanced 3D Text2Shape Generation
no code implementations • 1 Mar 2024 • Zhiying Leng, Tolga Birdal, Xiaohui Liang, Federico Tombari
First, we introduce a hyperbolic text-image encoder to learn the sequential and multi-modal hierarchical features of text in hyperbolic space.
OpenSUN3D: 1st Workshop Challenge on Open-Vocabulary 3D Scene Understanding
no code implementations • 23 Feb 2024 • Francis Engelmann, Ayca Takmaz, Jonas Schult, Elisabetta Fedele, Johanna Wald, Songyou Peng, Xi Wang, Or Litany, Siyu Tang, Federico Tombari, Marc Pollefeys, Leonidas Guibas, Hongbo Tian, Chunjie Wang, Xiaosheng Yan, Bingwen Wang, Xuanyang Zhang, Xiao Liu, Phuc Nguyen, Khoi Nguyen, Anh Tran, Cuong Pham, Zhening Huang, Xiaoyang Wu, Xi Chen, Hengshuang Zhao, Lei Zhu, Joan Lasenby
This report provides an overview of the challenge hosted at the OpenSUN3D Workshop on Open-Vocabulary 3D Scene Understanding held in conjunction with ICCV 2023.
Physics-Encoded Graph Neural Networks for Deformation Prediction under Contact
no code implementations • 5 Feb 2024 • Mahdi Saleh, Michael Sommersperger, Nassir Navab, Federico Tombari
We also incorporate cross-attention mechanisms to capture the interplay between the objects.
Denoising Diffusion via Image-Based Rendering
no code implementations • 5 Feb 2024 • Titas Anciukevičius, Fabian Manhardt, Federico Tombari, Paul Henderson
In this work, we introduce the first diffusion model able to perform fast, detailed reconstruction and generation of real-world 3D scenes.
InseRF: Text-Driven Generative Object Insertion in Neural 3D Scenes
no code implementations • 10 Jan 2024 • Mohamad Shahbazi, Liesbeth Claessens, Michael Niemeyer, Edo Collins, Alessio Tonioni, Luc van Gool, Federico Tombari
We introduce InseRF, a novel method for generative object insertion in the NeRF reconstructions of 3D scenes.
Learning to Prompt with Text Only Supervision for Vision-Language Models
1 code implementation • 4 Jan 2024 • Muhammad Uzair Khattak, Muhammad Ferjad Naeem, Muzammal Naseer, Luc van Gool, Federico Tombari
While effective, most of these works require labeled data which is not practical, and often struggle to generalize towards new datasets due to over-fitting on the source data.
Segment3D: Learning Fine-Grained Class-Agnostic 3D Segmentation without Manual Labels
no code implementations • 28 Dec 2023 • Rui Huang, Songyou Peng, Ayca Takmaz, Federico Tombari, Marc Pollefeys, Shiji Song, Gao Huang, Francis Engelmann
Therefore, we explore the use of image segmentation foundation models to automatically generate training labels for 3D segmentation.
UniSDF: Unifying Neural Representations for High-Fidelity 3D Reconstruction of Complex Scenes with Reflections
no code implementations • 20 Dec 2023 • Fangjinhua Wang, Marie-Julie Rakotosaona, Michael Niemeyer, Richard Szeliski, Marc Pollefeys, Federico Tombari
In this work, we propose UniSDF, a general purpose 3D reconstruction method that can reconstruct large complex scenes with reflections.
Text-Conditioned Resampler For Long Form Video Understanding
no code implementations • 19 Dec 2023 • Bruno Korbar, Yongqin Xian, Alessio Tonioni, Andrew Zisserman, Federico Tombari
In this paper we present a text-conditioned video resampler (TCR) module that uses a pre-trained and frozen visual encoder and large language model (LLM) to process long video sequences for a task.
 Ranked #5 on
Video Question Answering
on NExT-QA
Ranked #5 on
Video Question Answering
on NExT-QA
LIME: Localized Image Editing via Attention Regularization in Diffusion Models
no code implementations • 14 Dec 2023 • Enis Simsar, Alessio Tonioni, Yongqin Xian, Thomas Hofmann, Federico Tombari
Diffusion models (DMs) have gained prominence due to their ability to generate high-quality, varied images, with recent advancements in text-to-image generation.
CONFORM: Contrast is All You Need For High-Fidelity Text-to-Image Diffusion Models
no code implementations • 11 Dec 2023 • Tuna Han Salih Meral, Enis Simsar, Federico Tombari, Pinar Yanardag
Images produced by text-to-image diffusion models might not always faithfully represent the semantic intent of the provided text prompt, where the model might overlook or entirely fail to produce certain objects.
Re-Nerfing: Improving Novel Views Synthesis through Novel Views Synthesis
no code implementations • 4 Dec 2023 • Felix Tristram, Stefano Gasperini, Nassir Navab, Federico Tombari
With Re-Nerfing, we enhance the geometric consistency of novel views as follows: First, we train a NeRF with the available views.
DNS SLAM: Dense Neural Semantic-Informed SLAM
no code implementations • 30 Nov 2023 • Kunyi Li, Michael Niemeyer, Nassir Navab, Federico Tombari
In this work, we introduce DNS SLAM, a novel neural RGB-D semantic SLAM approach featuring a hybrid representation.
SemiVL: Semi-Supervised Semantic Segmentation with Vision-Language Guidance
1 code implementation • 27 Nov 2023 • Lukas Hoyer, David Joseph Tan, Muhammad Ferjad Naeem, Luc van Gool, Federico Tombari
In SemiVL, we propose to integrate rich priors from VLM pre-training into semi-supervised semantic segmentation to learn better semantic decision boundaries.
 Ranked #1 on
Semi-Supervised Semantic Segmentation
on PASCAL VOC 2012 732 labeled
(using extra training data)
Ranked #1 on
Semi-Supervised Semantic Segmentation
on PASCAL VOC 2012 732 labeled
(using extra training data)
D-SCo: Dual-Stream Conditional Diffusion for Monocular Hand-Held Object Reconstruction
no code implementations • 23 Nov 2023 • Bowen Fu, Gu Wang, Chenyangguang Zhang, Yan Di, Ziqin Huang, Zhiying Leng, Fabian Manhardt, Xiangyang Ji, Federico Tombari
Second, we introduce a dual-stream denoiser to semantically and geometrically model hand-object interactions with a novel unified hand-object semantic embedding, enhancing the reconstruction performance of the hand-occluded region of the object.
3D Compression Using Neural Fields
no code implementations • 21 Nov 2023 • Janis Postels, Yannick Strümpler, Klara Reichard, Luc van Gool, Federico Tombari
Neural Fields (NFs) have gained momentum as a tool for compressing various data modalities - e. g. images and videos.
SecondPose: SE(3)-Consistent Dual-Stream Feature Fusion for Category-Level Pose Estimation
1 code implementation • 18 Nov 2023 • Yamei Chen, Yan Di, Guangyao Zhai, Fabian Manhardt, Chenyangguang Zhang, Ruida Zhang, Federico Tombari, Nassir Navab, Benjamin Busam
Leveraging the advantage of DINOv2 in providing SE(3)-consistent semantic features, we hierarchically extract two types of SE(3)-invariant geometric features to further encapsulate local-to-global object-specific information.
SILC: Improving Vision Language Pretraining with Self-Distillation
no code implementations • 20 Oct 2023 • Muhammad Ferjad Naeem, Yongqin Xian, Xiaohua Zhai, Lukas Hoyer, Luc van Gool, Federico Tombari
However, the contrastive objective used by these models only focuses on image-text alignment and does not incentivise image feature learning for dense prediction tasks.
MOHO: Learning Single-view Hand-held Object Reconstruction with Multi-view Occlusion-Aware Supervision
no code implementations • 18 Oct 2023 • Chenyangguang Zhang, Guanlong Jiao, Yan Di, Gu Wang, Ziqin Huang, Ruida Zhang, Fabian Manhardt, Bowen Fu, Federico Tombari, Xiangyang Ji
Previous works concerning single-view hand-held object reconstruction typically rely on supervision from 3D ground-truth models, which are hard to collect in real world.
SG-Bot: Object Rearrangement via Coarse-to-Fine Robotic Imagination on Scene Graphs
no code implementations • 21 Sep 2023 • Guangyao Zhai, Xiaoni Cai, Dianye Huang, Yan Di, Fabian Manhardt, Federico Tombari, Nassir Navab, Benjamin Busam
In this paper, we present SG-Bot, a novel rearrangement framework that utilizes a coarse-to-fine scheme with a scene graph as the scene representation.
Dynamic Hyperbolic Attention Network for Fine Hand-object Reconstruction
no code implementations • ICCV 2023 • Zhiying Leng, Shun-Cheng Wu, Mahdi Saleh, Antonio Montanaro, Hao Yu, Yin Wang, Nassir Navab, Xiaohui Liang, Federico Tombari
In this work, we propose the first precise hand-object reconstruction method in hyperbolic space, namely Dynamic Hyperbolic Attention Network (DHANet), which leverages intrinsic properties of hyperbolic space to learn representative features.
Introducing Language Guidance in Prompt-based Continual Learning
1 code implementation • ICCV 2023 • Muhammad Gul Zain Ali Khan, Muhammad Ferjad Naeem, Luc van Gool, Didier Stricker, Federico Tombari, Muhammad Zeshan Afzal
While the model faces a disjoint set of classes in each task in this setting, we argue that these classes can be encoded to the same embedding space of a pre-trained language encoder.
3D Adversarial Augmentations for Robust Out-of-Domain Predictions
no code implementations • 29 Aug 2023 • Alexander Lehner, Stefano Gasperini, Alvaro Marcos-Ramiro, Michael Schmidt, Nassir Navab, Benjamin Busam, Federico Tombari
We conduct extensive experiments across a variety of scenarios on data from KITTI, Waymo, and CrashD for 3D object detection, and on data from SemanticKITTI, Waymo, and nuScenes for 3D semantic segmentation.
Robust Monocular Depth Estimation under Challenging Conditions
no code implementations • ICCV 2023 • Stefano Gasperini, Nils Morbitzer, HyunJun Jung, Nassir Navab, Federico Tombari
While state-of-the-art monocular depth estimation approaches achieve impressive results in ideal settings, they are highly unreliable under challenging illumination and weather conditions, such as at nighttime or in the presence of rain.
CCD-3DR: Consistent Conditioning in Diffusion for Single-Image 3D Reconstruction
no code implementations • 15 Aug 2023 • Yan Di, Chenyangguang Zhang, Pengyuan Wang, Guangyao Zhai, Ruida Zhang, Fabian Manhardt, Benjamin Busam, Xiangyang Ji, Federico Tombari
However, such strategies fail to consistently align the denoised point cloud with the given image, leading to unstable conditioning and inferior performance.
U-RED: Unsupervised 3D Shape Retrieval and Deformation for Partial Point Clouds
1 code implementation • ICCV 2023 • Yan Di, Chenyangguang Zhang, Ruida Zhang, Fabian Manhardt, Yongzhi Su, Jason Rambach, Didier Stricker, Xiangyang Ji, Federico Tombari
In this paper, we propose U-RED, an Unsupervised shape REtrieval and Deformation pipeline that takes an arbitrary object observation as input, typically captured by RGB images or scans, and jointly retrieves and deforms the geometrically similar CAD models from a pre-established database to tightly match the target.
View-to-Label: Multi-View Consistency for Self-Supervised 3D Object Detection
no code implementations • 29 May 2023 • Issa Mouawad, Nikolas Brasch, Fabian Manhardt, Federico Tombari, Francesca Odone
For autonomous vehicles, driving safely is highly dependent on the capability to correctly perceive the environment in 3D space, hence the task of 3D object detection represents a fundamental aspect of perception.
CommonScenes: Generating Commonsense 3D Indoor Scenes with Scene Graph Diffusion
1 code implementation • NeurIPS 2023 • Guangyao Zhai, Evin Pınar Örnek, Shun-Cheng Wu, Yan Di, Federico Tombari, Nassir Navab, Benjamin Busam
The generated scenes can be manipulated by editing the input scene graph and sampling the noise in the diffusion model.
Incremental 3D Semantic Scene Graph Prediction from RGB Sequences
no code implementations • CVPR 2023 • Shun-Cheng Wu, Keisuke Tateno, Nassir Navab, Federico Tombari
Our method consists of a novel incremental entity estimation pipeline and a scene graph prediction network.
SparseFusion: Fusing Multi-Modal Sparse Representations for Multi-Sensor 3D Object Detection
1 code implementation • ICCV 2023 • Yichen Xie, Chenfeng Xu, Marie-Julie Rakotosaona, Patrick Rim, Federico Tombari, Kurt Keutzer, Masayoshi Tomizuka, Wei Zhan
However, given that objects occupy only a small part of a scene, finding dense candidates and generating dense representations is noisy and inefficient.
TextMesh: Generation of Realistic 3D Meshes From Text Prompts
1 code implementation • 24 Apr 2023 • Christina Tsalicoglou, Fabian Manhardt, Alessio Tonioni, Michael Niemeyer, Federico Tombari
In addition, we propose a novel way to finetune the mesh texture, removing the effect of high saturation and improving the details of the output 3D mesh.
NEWTON: Neural View-Centric Mapping for On-the-Fly Large-Scale SLAM
no code implementations • 23 Mar 2023 • Hidenobu Matsuki, Keisuke Tateno, Michael Niemeyer, Federico Tombari
However, in real-time and on-the-fly scene capture applications, this prior knowledge cannot be assumed as fixed or static, since it dynamically changes and it is subject to significant updates based on run-time observations.
NeRFMeshing: Distilling Neural Radiance Fields into Geometrically-Accurate 3D Meshes
no code implementations • 16 Mar 2023 • Marie-Julie Rakotosaona, Fabian Manhardt, Diego Martin Arroyo, Michael Niemeyer, Abhijit Kundu, Federico Tombari
Obtaining 3D meshes from neural radiance fields still remains an open challenge since NeRFs are optimized for view synthesis, not enforcing an accurate underlying geometry on the radiance field.
Unsupervised Traffic Scene Generation with Synthetic 3D Scene Graphs
no code implementations • 15 Mar 2023 • Artem Savkin, Rachid Ellouze, Nassir Navab, Federico Tombari
Image synthesis driven by computer graphics achieved recently a remarkable realism, yet synthetic image data generated this way reveals a significant domain gap with respect to real-world data.
IPCC-TP: Utilizing Incremental Pearson Correlation Coefficient for Joint Multi-Agent Trajectory Prediction
no code implementations • CVPR 2023 • Dekai Zhu, Guangyao Zhai, Yan Di, Fabian Manhardt, Hendrik Berkemeyer, Tuan Tran, Nassir Navab, Federico Tombari, Benjamin Busam
Reliable multi-agent trajectory prediction is crucial for the safe planning and control of autonomous systems.
SupeRGB-D: Zero-shot Instance Segmentation in Cluttered Indoor Environments
1 code implementation • 22 Dec 2022 • Evin Pınar Örnek, Aravindhan K Krishnan, Shreekant Gayaka, Cheng-Hao Kuo, Arnie Sen, Nassir Navab, Federico Tombari
We introduce a zero-shot split for Tabletop Objects Dataset (TOD-Z) to enable this study and present a method that uses annotated objects to learn the ``objectness'' of pixels and generalize to unseen object categories in cluttered indoor environments.
SST: Real-time End-to-end Monocular 3D Reconstruction via Sparse Spatial-Temporal Guidance
no code implementations • 13 Dec 2022 • Chenyangguang Zhang, Zhiqiang Lou, Yan Di, Federico Tombari, Xiangyang Ji
Real-time monocular 3D reconstruction is a challenging problem that remains unsolved.
I2MVFormer: Large Language Model Generated Multi-View Document Supervision for Zero-Shot Image Classification
no code implementations • CVPR 2023 • Muhammad Ferjad Naeem, Muhammad Gul Zain Ali Khan, Yongqin Xian, Muhammad Zeshan Afzal, Didier Stricker, Luc van Gool, Federico Tombari
Our proposed model, I2MVFormer, learns multi-view semantic embeddings for zero-shot image classification with these class views.
LatentSwap3D: Semantic Edits on 3D Image GANs
no code implementations • 2 Dec 2022 • Enis Simsar, Alessio Tonioni, Evin Pınar Örnek, Federico Tombari
3D GANs have the ability to generate latent codes for entire 3D volumes rather than only 2D images.
Shape, Pose, and Appearance from a Single Image via Bootstrapped Radiance Field Inversion
1 code implementation • CVPR 2023 • Dario Pavllo, David Joseph Tan, Marie-Julie Rakotosaona, Federico Tombari
Neural Radiance Fields (NeRF) coupled with GANs represent a promising direction in the area of 3D reconstruction from a single view, owing to their ability to efficiently model arbitrary topologies.
SPARF: Neural Radiance Fields from Sparse and Noisy Poses
1 code implementation • CVPR 2023 • Prune Truong, Marie-Julie Rakotosaona, Fabian Manhardt, Federico Tombari
Neural Radiance Field (NeRF) has recently emerged as a powerful representation to synthesize photorealistic novel views.
DisPositioNet: Disentangled Pose and Identity in Semantic Image Manipulation
no code implementations • 10 Nov 2022 • Azade Farshad, Yousef Yeganeh, Helisa Dhamo, Federico Tombari, Nassir Navab
Graph representation of objects and their relations in a scene, known as a scene graph, provides a precise and discernible interface to manipulate a scene by modifying the nodes or the edges in the graph.
ParGAN: Learning Real Parametrizable Transformations
no code implementations • 9 Nov 2022 • Diego Martin Arroyo, Alessio Tonioni, Federico Tombari
Current methods for image-to-image translation produce compelling results, however, the applied transformation is difficult to control, since existing mechanisms are often limited and non-intuitive.
OPA-3D: Occlusion-Aware Pixel-Wise Aggregation for Monocular 3D Object Detection
no code implementations • 2 Nov 2022 • Yongzhi Su, Yan Di, Fabian Manhardt, Guangyao Zhai, Jason Rambach, Benjamin Busam, Didier Stricker, Federico Tombari
Despite monocular 3D object detection having recently made a significant leap forward thanks to the use of pre-trained depth estimators for pseudo-LiDAR recovery, such two-stage methods typically suffer from overfitting and are incapable of explicitly encapsulating the geometric relation between depth and object bounding box.
MonoGraspNet: 6-DoF Grasping with a Single RGB Image
no code implementations • 26 Sep 2022 • Guangyao Zhai, Dianye Huang, Shun-Cheng Wu, HyunJun Jung, Yan Di, Fabian Manhardt, Federico Tombari, Nassir Navab, Benjamin Busam
6-DoF robotic grasping is a long-lasting but unsolved problem.
Query-Guided Networks for Few-shot Fine-grained Classification and Person Search
no code implementations • 21 Sep 2022 • Bharti Munjal, Alessandro Flaborea, Sikandar Amin, Federico Tombari, Fabio Galasso
Few-shot fine-grained classification and person search appear as distinct tasks and literature has treated them separately.
I2DFormer: Learning Image to Document Attention for Zero-Shot Image Classification
no code implementations • 21 Sep 2022 • Muhammad Ferjad Naeem, Yongqin Xian, Luc van Gool, Federico Tombari
In order to distill discriminative visual words from noisy documents, we introduce a new cross-modal attention module that learns fine-grained interactions between image patches and document words.
Segmenting Known Objects and Unseen Unknowns without Prior Knowledge
no code implementations • ICCV 2023 • Stefano Gasperini, Alvaro Marcos-Ramiro, Michael Schmidt, Nassir Navab, Benjamin Busam, Federico Tombari
By doing so, for the first time in panoptic segmentation with unknown objects, our U3HS is trained without unknown categories, reducing assumptions and leaving the settings as unconstrained as in real-life scenarios.
ManiFlow: Implicitly Representing Manifolds with Normalizing Flows
no code implementations • 18 Aug 2022 • Janis Postels, Martin Danelljan, Luc van Gool, Federico Tombari
In contrast to prior work, we approach this problem by generating samples from the original data distribution given full knowledge about the perturbed distribution and the noise model.
SC-Explorer: Incremental 3D Scene Completion for Safe and Efficient Exploration Mapping and Planning
1 code implementation • 17 Aug 2022 • Lukas Schmid, Mansoor Nasir Cheema, Victor Reijgwart, Roland Siegwart, Federico Tombari, Cesar Cadena
We further present an informative path planning method, leveraging the capabilities of our mapping approach and a novel scene-completion-aware information gain.
SSP-Pose: Symmetry-Aware Shape Prior Deformation for Direct Category-Level Object Pose Estimation
no code implementations • 13 Aug 2022 • Ruida Zhang, Yan Di, Fabian Manhardt, Federico Tombari, Xiangyang Ji
In this paper, to handle these shortcomings, we propose an end-to-end trainable network SSP-Pose for category-level pose estimation, which integrates shape priors into a direct pose regression network.
CloudAttention: Efficient Multi-Scale Attention Scheme For 3D Point Cloud Learning
no code implementations • 31 Jul 2022 • Mahdi Saleh, Yige Wang, Nassir Navab, Benjamin Busam, Federico Tombari
The proposed hierarchical model achieves state-of-the-art shape classification in mean accuracy and yields results on par with the previous segmentation methods while requiring significantly fewer computations.
RBP-Pose: Residual Bounding Box Projection for Category-Level Pose Estimation
1 code implementation • 30 Jul 2022 • Ruida Zhang, Yan Di, Zhiqiang Lou, Fabian Manhardt, Federico Tombari, Xiangyang Ji
Category-level object pose estimation aims to predict the 6D pose as well as the 3D metric size of arbitrary objects from a known set of categories.
E-Graph: Minimal Solution for Rigid Rotation with Extensibility Graphs
no code implementations • 20 Jul 2022 • Yanyan Li, Federico Tombari
Minimal solutions for relative rotation and translation estimation tasks have been explored in different scenarios, typically relying on the so-called co-visibility graph.
GOCA: Guided Online Cluster Assignment for Self-Supervised Video Representation Learning
1 code implementation • 20 Jul 2022 • Huseyin Coskun, Alireza Zareian, Joshua L. Moore, Federico Tombari, Chen Wang
Specifically, we outperform the state of the art by 7% on UCF and 4% on HMDB for video retrieval, and 5% on UCF and 6% on HMDB for video classification
SHIFT: A Synthetic Driving Dataset for Continuous Multi-Task Domain Adaptation
1 code implementation • CVPR 2022 • Tao Sun, Mattia Segu, Janis Postels, Yuxuan Wang, Luc van Gool, Bernt Schiele, Federico Tombari, Fisher Yu
Adapting to a continuously evolving environment is a safety-critical challenge inevitably faced by all autonomous driving systems.
SoftPool++: An Encoder-Decoder Network for Point Cloud Completion
no code implementations • 8 May 2022 • Yida Wang, David Joseph Tan, Nassir Navab, Federico Tombari
We propose a novel convolutional operator for the task of point cloud completion.
Socratic Models: Composing Zero-Shot Multimodal Reasoning with Language
1 code implementation • 1 Apr 2022 • Andy Zeng, Maria Attarian, Brian Ichter, Krzysztof Choromanski, Adrian Wong, Stefan Welker, Federico Tombari, Aveek Purohit, Michael Ryoo, Vikas Sindhwani, Johnny Lee, Vincent Vanhoucke, Pete Florence
Large pretrained (e. g., "foundation") models exhibit distinct capabilities depending on the domain of data they are trained on.
 Ranked #21 on
Video Retrieval
on MSR-VTT-1kA
(video-to-text R@1 metric)
Ranked #21 on
Video Retrieval
on MSR-VTT-1kA
(video-to-text R@1 metric)
Learning Local Displacements for Point Cloud Completion
no code implementations • CVPR 2022 • Yida Wang, David Joseph Tan, Nassir Navab, Federico Tombari
To this aim, we introduce a second model that assembles our layers within a transformer architecture.
4D-OR: Semantic Scene Graphs for OR Domain Modeling
1 code implementation • 22 Mar 2022 • Ege Özsoy, Evin Pınar Örnek, Ulrich Eck, Tobias Czempiel, Federico Tombari, Nassir Navab
Towards this goal, for the first time, we propose using semantic scene graphs (SSG) to describe and summarize the surgical scene.
 Ranked #4 on
Scene Graph Generation
on 4D-OR
Ranked #4 on
Scene Graph Generation
on 4D-OR
Occlusion-Aware Self-Supervised Monocular 6D Object Pose Estimation
1 code implementation • 19 Mar 2022 • Gu Wang, Fabian Manhardt, Xingyu Liu, Xiangyang Ji, Federico Tombari
6D object pose estimation is a fundamental yet challenging problem in computer vision.
ZebraPose: Coarse to Fine Surface Encoding for 6DoF Object Pose Estimation
1 code implementation • CVPR 2022 • Yongzhi Su, Mahdi Saleh, Torben Fetzer, Jason Rambach, Nassir Navab, Benjamin Busam, Didier Stricker, Federico Tombari
Dense methods also improved pose estimation in the presence of occlusion.
From 2D to 3D: Re-thinking Benchmarking of Monocular Depth Prediction
no code implementations • 15 Mar 2022 • Evin Pınar Örnek, Shristi Mudgal, Johanna Wald, Yida Wang, Nassir Navab, Federico Tombari
There have been numerous recently proposed methods for monocular depth prediction (MDP) coupled with the equally rapid evolution of benchmarking tools.
GPV-Pose: Category-level Object Pose Estimation via Geometry-guided Point-wise Voting
3 code implementations • CVPR 2022 • Yan Di, Ruida Zhang, Zhiqiang Lou, Fabian Manhardt, Xiangyang Ji, Nassir Navab, Federico Tombari
While 6D object pose estimation has recently made a huge leap forward, most methods can still only handle a single or a handful of different objects, which limits their applications.
 Ranked #1 on
6D Pose Estimation
on LineMOD
(Mean ADD-S metric)
Ranked #1 on
6D Pose Estimation
on LineMOD
(Mean ADD-S metric)
Time-to-Label: Temporal Consistency for Self-Supervised Monocular 3D Object Detection
no code implementations • 4 Mar 2022 • Issa Mouawad, Nikolas Brasch, Fabian Manhardt, Federico Tombari, Francesca Odone
Monocular 3D object detection continues to attract attention due to the cost benefits and wider availability of RGB cameras.
Bending Graphs: Hierarchical Shape Matching using Gated Optimal Transport
no code implementations • CVPR 2022 • Mahdi Saleh, Shun-Cheng Wu, Luca Cosmo, Nassir Navab, Benjamin Busam, Federico Tombari
Shape matching has been a long-studied problem for the computer graphics and vision community.
Transformers in Action: Weakly Supervised Action Segmentation
no code implementations • 14 Jan 2022 • John Ridley, Huseyin Coskun, David Joseph Tan, Nassir Navab, Federico Tombari
The video action segmentation task is regularly explored under weaker forms of supervision, such as transcript supervision, where a list of actions is easier to obtain than dense frame-wise labels.
3D-VField: Adversarial Augmentation of Point Clouds for Domain Generalization in 3D Object Detection
no code implementations • CVPR 2022 • Alexander Lehner, Stefano Gasperini, Alvaro Marcos-Ramiro, Michael Schmidt, Mohammad-Ali Nikouei Mahani, Nassir Navab, Benjamin Busam, Federico Tombari
Despite training only on a standard dataset, such as KITTI, augmenting with our vector fields significantly improves the generalization to differently shaped objects and scenes.
Implicit Neural Representations for Image Compression
no code implementations • 8 Dec 2021 • Yannick Strümpler, Janis Postels, Ren Yang, Luc van Gool, Federico Tombari
Recently Implicit Neural Representations (INRs) gained attention as a novel and effective representation for various data types.
Object-aware Monocular Depth Prediction with Instance Convolutions
1 code implementation • 2 Dec 2021 • Enis Simsar, Evin Pınar Örnek, Fabian Manhardt, Helisa Dhamo, Nassir Navab, Federico Tombari
With the advent of deep learning, estimating depth from a single RGB image has recently received a lot of attention, being capable of empowering many different applications ranging from path planning for robotics to computational cinematography.
3D Compositional Zero-shot Learning with DeCompositional Consensus
no code implementations • 29 Nov 2021 • Muhammad Ferjad Naeem, Evin Pınar Örnek, Yongqin Xian, Luc van Gool, Federico Tombari
Parts represent a basic unit of geometric and semantic similarity across different objects.
Neural Fields in Visual Computing and Beyond
1 code implementation • 22 Nov 2021 • Yiheng Xie, Towaki Takikawa, Shunsuke Saito, Or Litany, Shiqin Yan, Numair Khan, Federico Tombari, James Tompkin, Vincent Sitzmann, Srinath Sridhar
Recent advances in machine learning have created increasing interest in solving visual computing problems using a class of coordinate-based neural networks that parametrize physical properties of scenes or objects across space and time.
Semantic Image Alignment for Vehicle Localization
no code implementations • 8 Oct 2021 • Markus Herb, Matthias Lemberger, Marcel M. Schmitt, Alexander Kurz, Tobias Weiherer, Nassir Navab, Federico Tombari
Accurate and reliable localization is a fundamental requirement for autonomous vehicles to use map information in higher-level tasks such as navigation or planning.
CertainNet: Sampling-free Uncertainty Estimation for Object Detection
no code implementations • 4 Oct 2021 • Stefano Gasperini, Jan Haug, Mohammad-Ali Nikouei Mahani, Alvaro Marcos-Ramiro, Nassir Navab, Benjamin Busam, Federico Tombari
Estimating the uncertainty of a neural network plays a fundamental role in safety-critical settings.
Semantic Dense Reconstruction with Consistent Scene Segments
no code implementations • 30 Sep 2021 • Yingcai Wan, Yanyan Li, Yingxuan You, Cheng Guo, Lijin Fang, Federico Tombari
In this paper, a method for dense semantic 3D scene reconstruction from an RGB-D sequence is proposed to solve high-level scene understanding tasks.
Adversarial Domain Feature Adaptation for Bronchoscopic Depth Estimation
no code implementations • 24 Sep 2021 • Mert Asim Karaoglu, Nikolas Brasch, Marijn Stollenga, Wolfgang Wein, Nassir Navab, Federico Tombari, Alexander Ladikos
The results of our experiments show that the proposed method improves the network's performance on real images by a considerable margin and can be employed in 3D reconstruction pipelines.
Graph-to-3D: End-to-End Generation and Manipulation of 3D Scenes Using Scene Graphs
1 code implementation • ICCV 2021 • Helisa Dhamo, Fabian Manhardt, Nassir Navab, Federico Tombari
Scene graphs are representations of a scene, composed of objects (nodes) and inter-object relationships (edges), proven to be particularly suited for this task, as they allow for semantic control on the generated content.
SO-Pose: Exploiting Self-Occlusion for Direct 6D Pose Estimation
2 code implementations • ICCV 2021 • Yan Di, Fabian Manhardt, Gu Wang, Xiangyang Ji, Nassir Navab, Federico Tombari
Directly regressing all 6 degrees-of-freedom (6DoF) for the object pose (e. g. the 3D rotation and translation) in a cluttered environment from a single RGB image is a challenging problem.
 Ranked #1 on
6D Pose Estimation using RGB
on Occlusion LineMOD
Ranked #1 on
6D Pose Estimation using RGB
on Occlusion LineMOD
Unconditional Scene Graph Generation
no code implementations • ICCV 2021 • Sarthak Garg, Helisa Dhamo, Azade Farshad, Sabrina Musatian, Nassir Navab, Federico Tombari
Scene graphs, composed of nodes as objects and directed-edges as relationships among objects, offer an alternative representation of a scene that is more semantically grounded than images.
R4Dyn: Exploring Radar for Self-Supervised Monocular Depth Estimation of Dynamic Scenes
no code implementations • 10 Aug 2021 • Stefano Gasperini, Patrick Koch, Vinzenz Dallabetta, Nassir Navab, Benjamin Busam, Federico Tombari
While self-supervised monocular depth estimation in driving scenarios has achieved comparable performance to supervised approaches, violations of the static world assumption can still lead to erroneous depth predictions of traffic participants, posing a potential safety issue.
Attention-based Adversarial Appearance Learning of Augmented Pedestrians
no code implementations • 6 Jul 2021 • Kevin Strauss, Artem Savkin, Federico Tombari
Synthetic data became already an essential component of machine learning-based perception in the field of autonomous driving.
On the Practicality of Deterministic Epistemic Uncertainty
2 code implementations • 1 Jul 2021 • Janis Postels, Mattia Segu, Tao Sun, Luca Sieber, Luc van Gool, Fisher Yu, Federico Tombari
We find that, while DUMs scale to realistic vision tasks and perform well on OOD detection, the practicality of current methods is undermined by poor calibration under distributional shifts.
 Out of Distribution (OOD) Detection
Out of Distribution (OOD) Detection
 Semantic Segmentation
+1
Semantic Segmentation
+1
LegoFormer: Transformers for Block-by-Block Multi-view 3D Reconstruction
1 code implementation • 23 Jun 2021 • Farid Yagubbayli, Yida Wang, Alessio Tonioni, Federico Tombari
Most modern deep learning-based multi-view 3D reconstruction techniques use RNNs or fusion modules to combine information from multiple images after independently encoding them.
Multimodal Semantic Scene Graphs for Holistic Modeling of Surgical Procedures
no code implementations • 9 Jun 2021 • Ege Özsoy, Evin Pınar Örnek, Ulrich Eck, Federico Tombari, Nassir Navab
We then use MSSG to introduce a dynamically generated graphical user interface tool for surgical procedure analysis which could be used for many applications including process optimization, OR design and automatic report generation.
Go with the Flows: Mixtures of Normalizing Flows for Point Cloud Generation and Reconstruction
no code implementations • 6 Jun 2021 • Janis Postels, Mengya Liu, Riccardo Spezialetti, Luc van Gool, Federico Tombari
Recently normalizing flows (NFs) have demonstrated state-of-the-art performance on modeling 3D point clouds while allowing sampling with arbitrary resolution at inference time.
KLIEP-based Density Ratio Estimation for Semantically Consistent Synthetic to Real Images Adaptation in Urban Traffic Scenes
no code implementations • 26 May 2021 • Artem Savkin, Federico Tombari
Synthetic data has been applied in many deep learning based computer vision tasks.
SRH-Net: Stacked Recurrent Hourglass Network for Stereo Matching
1 code implementation • 25 May 2021 • Hongzhi Du, Yanyan Li, Yanbiao Sun, Jigui Zhu, Federico Tombari
The cost aggregation strategy shows a crucial role in learning-based stereo matching tasks, where 3D convolutional filters obtain state of the art but require intensive computation resources, while 2D operations need less GPU memory but are sensitive to domain shift.
Content Disentanglement for Semantically Consistent Synthetic-to-Real Domain Adaptation
1 code implementation • 18 May 2021 • Mert Keser, Artem Savkin, Federico Tombari
Such performance drops are commonly attributed to the domain gap between real and synthetic data.
TSDF++: A Multi-Object Formulation for Dynamic Object Tracking and Reconstruction
1 code implementation • 16 May 2021 • Margarita Grinvald, Federico Tombari, Roland Siegwart, Juan Nieto
The ability to simultaneously track and reconstruct multiple objects moving in the scene is of the utmost importance for robotic tasks such as autonomous navigation and interaction.
Variational Transformer Networks for Layout Generation
no code implementations • CVPR 2021 • Diego Martin Arroyo, Janis Postels, Federico Tombari
Generative models able to synthesize layouts of different kinds (e. g. documents, user interfaces or furniture arrangements) are a useful tool to aid design processes and as a first step in the generation of synthetic data, among other tasks.
ManhattanSLAM: Robust Planar Tracking and Mapping Leveraging Mixture of Manhattan Frames
1 code implementation • 28 Mar 2021 • Raza Yunus, Yanyan Li, Federico Tombari
In this paper, a robust RGB-D SLAM system is proposed to utilize the structural information in indoor scenes, allowing for accurate tracking and efficient dense mapping on a CPU.
SceneGraphFusion: Incremental 3D Scene Graph Prediction from RGB-D Sequences
2 code implementations • CVPR 2021 • Shun-Cheng Wu, Johanna Wald, Keisuke Tateno, Nassir Navab, Federico Tombari
Scene graphs are a compact and explicit representation successfully used in a variety of 2D scene understanding tasks.
 Ranked #1 on
3D Object Classification
on 3R-Scan
Ranked #1 on
3D Object Classification
on 3R-Scan
GDR-Net: Geometry-Guided Direct Regression Network for Monocular 6D Object Pose Estimation
1 code implementation • CVPR 2021 • Gu Wang, Fabian Manhardt, Federico Tombari, Xiangyang Ji
In this work, we perform an in-depth investigation on both direct and indirect methods, and propose a simple yet effective Geometry-guided Direct Regression Network (GDR-Net) to learn the 6D pose in an end-to-end manner from dense correspondence-based intermediate geometric representations.
 Ranked #3 on
6D Pose Estimation using RGB
on Occlusion LineMOD
Ranked #3 on
6D Pose Estimation using RGB
on Occlusion LineMOD
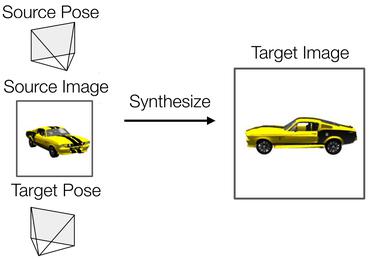
Unsupervised Novel View Synthesis from a Single Image
no code implementations • 5 Feb 2021 • Pierluigi Zama Ramirez, Alessio Tonioni, Federico Tombari
Novel view synthesis from a single image aims at generating novel views from a single input image of an object.
Learning Graph Embeddings for Compositional Zero-shot Learning
1 code implementation • CVPR 2021 • Muhammad Ferjad Naeem, Yongqin Xian, Federico Tombari, Zeynep Akata
In compositional zero-shot learning, the goal is to recognize unseen compositions (e. g. old dog) of observed visual primitives states (e. g. old, cute) and objects (e. g. car, dog) in the training set.
The Hidden Uncertainty in a Neural Networks Activations
no code implementations • 5 Dec 2020 • Janis Postels, Hermann Blum, Yannick Strümpler, Cesar Cadena, Roland Siegwart, Luc van Gool, Federico Tombari
We find that this leads to improved OOD detection of epistemic uncertainty at the cost of ambiguous calibration close to the data distribution.
3DSNet: Unsupervised Shape-to-Shape 3D Style Transfer
1 code implementation • 26 Nov 2020 • Mattia Segu, Margarita Grinvald, Roland Siegwart, Federico Tombari
Transferring the style from one image onto another is a popular and widely studied task in computer vision.
Batch Normalization Embeddings for Deep Domain Generalization
no code implementations • 25 Nov 2020 • Mattia Segu, Alessio Tonioni, Federico Tombari
Several recent methods use multiple datasets to train models to extract domain-invariant features, hoping to generalize to unseen domains.
 Ranked #63 on
Domain Generalization
on PACS
Ranked #63 on
Domain Generalization
on PACS
Deep Positional and Relational Feature Learning for Rotation-Invariant Point Cloud Analysis
no code implementations • ECCV 2020 • Ruixuan Yu, Xin Wei, Federico Tombari, Jian Sun
In this work, we propose a novel deep network for point clouds by incorporating positional information of points as inputs while yielding rotation-invariance.
A Divide et Impera Approach for 3D Shape Reconstruction from Multiple Views
no code implementations • 17 Nov 2020 • Riccardo Spezialetti, David Joseph Tan, Alessio Tonioni, Keisuke Tateno, Federico Tombari
Estimating the 3D shape of an object from a single or multiple images has gained popularity thanks to the recent breakthroughs powered by deep learning.
Panoster: End-to-end Panoptic Segmentation of LiDAR Point Clouds
no code implementations • 28 Oct 2020 • Stefano Gasperini, Mohammad-Ali Nikouei Mahani, Alvaro Marcos-Ramiro, Nassir Navab, Federico Tombari
Panoptic segmentation has recently unified semantic and instance segmentation, previously addressed separately, thus taking a step further towards creating more comprehensive and efficient perception systems.
SCFusion: Real-time Incremental Scene Reconstruction with Semantic Completion
2 code implementations • 26 Oct 2020 • Shun-Cheng Wu, Keisuke Tateno, Nassir Navab, Federico Tombari
We propose a framework that ameliorates this issue by performing scene reconstruction and semantic scene completion jointly in an incremental and real-time manner, based on an input sequence of depth maps.
Graphite: GRAPH-Induced feaTure Extraction for Point Cloud Registration
1 code implementation • 18 Oct 2020 • Mahdi Saleh, Shervin Dehghani, Benjamin Busam, Nassir Navab, Federico Tombari
3D Point clouds are a rich source of information that enjoy growing popularity in the vision community.
RGB-D SLAM with Structural Regularities
1 code implementation • 15 Oct 2020 • Yanyan Li, Raza Yunus, Nikolas Brasch, Nassir Navab, Federico Tombari
This work proposes a RGB-D SLAM system specifically designed for structured environments and aimed at improved tracking and mapping accuracy by relying on geometric features that are extracted from the surrounding.
Robotics
SoftPoolNet: Shape Descriptor for Point Cloud Completion and Classification
1 code implementation • ECCV 2020 • Yida Wang, David Joseph Tan, Nassir Navab, Federico Tombari
In this paper, we propose a method for 3D object completion and classification based on point clouds.
Beyond Controlled Environments: 3D Camera Re-Localization in Changing Indoor Scenes
1 code implementation • ECCV 2020 • Johanna Wald, Torsten Sattler, Stuart Golodetz, Tommaso Cavallari, Federico Tombari
In this paper, we adapt 3RScan - a recently introduced indoor RGB-D dataset designed for object instance re-localization - to create RIO10, a new long-term camera re-localization benchmark focused on indoor scenes.
Structure-SLAM: Low-Drift Monocular SLAM in Indoor Environments
1 code implementation • 5 Aug 2020 • Yanyan Li, Nikolas Brasch, Yida Wang, Nassir Navab, Federico Tombari
In this paper a low-drift monocular SLAM method is proposed targeting indoor scenarios, where monocular SLAM often fails due to the lack of textured surfaces.
Robotics
Binary DAD-Net: Binarized Driveable Area Detection Network for Autonomous Driving
no code implementations • 15 Jun 2020 • Alexander Frickenstein, Manoj Rohit Vemparala, Jakob Mayr, Naveen Shankar Nagaraja, Christian Unger, Federico Tombari, Walter Stechele
The driveable area detection, posed as a two class segmentation task, can be efficiently modeled with slim binary networks.
Joint Detection and Tracking in Videos with Identification Features
no code implementations • 21 May 2020 • Bharti Munjal, Abdul Rafey Aftab, Sikandar Amin, Meltem D. Brandlmaier, Federico Tombari, Fabio Galasso
Notably, our joint optimization maintains the detector performance, a typical multi-task challenge.
Explicit Domain Adaptation with Loosely Coupled Samples
no code implementations • 24 Apr 2020 • Oliver Scheel, Loren Schwarz, Nassir Navab, Federico Tombari
In this work we propose a transfer learning framework, core of which is learning an explicit mapping between domains.
Self6D: Self-Supervised Monocular 6D Object Pose Estimation
1 code implementation • ECCV 2020 • Gu Wang, Fabian Manhardt, Jianzhun Shao, Xiangyang Ji, Nassir Navab, Federico Tombari
6D object pose estimation is a fundamental problem in computer vision.
Learning 3D Semantic Scene Graphs from 3D Indoor Reconstructions
no code implementations • CVPR 2020 • Johanna Wald, Helisa Dhamo, Nassir Navab, Federico Tombari
In our work we focus on scene graphs, a data structure that organizes the entities of a scene in a graph, where objects are nodes and their relationships modeled as edges.
 Ranked #3 on
3d scene graph generation
on 3DSSG
Ranked #3 on
3d scene graph generation
on 3DSSG
Semantic Image Manipulation Using Scene Graphs
1 code implementation • CVPR 2020 • Helisa Dhamo, Azade Farshad, Iro Laina, Nassir Navab, Gregory D. Hager, Federico Tombari, Christian Rupprecht
In our work, we address the novel problem of image manipulation from scene graphs, in which a user can edit images by merely applying changes in the nodes or edges of a semantic graph that is generated from the image.
Ambiguity in Sequential Data: Predicting Uncertain Futures with Recurrent Models
no code implementations • 10 Mar 2020 • Alessandro Berlati, Oliver Scheel, Luigi Di Stefano, Federico Tombari
Ambiguity is inherently present in many machine learning tasks, but especially for sequential models seldom accounted for, as most only output a single prediction.
Restricting the Flow: Information Bottlenecks for Attribution
4 code implementations • ICLR 2020 • Karl Schulz, Leon Sixt, Federico Tombari, Tim Landgraf
Attribution methods provide insights into the decision-making of machine learning models like artificial neural networks.
Quaternion Equivariant Capsule Networks for 3D Point Clouds
2 code implementations • ECCV 2020 • Yongheng Zhao, Tolga Birdal, Jan Eric Lenssen, Emanuele Menegatti, Leonidas Guibas, Federico Tombari
We present a 3D capsule module for processing point clouds that is equivariant to 3D rotations and translations, as well as invariant to permutations of the input points.
Real-Time 3D Model Tracking in Color and Depth on a Single CPU Core
no code implementations • CVPR 2017 • Wadim Kehl, Federico Tombari, Slobodan Ilic, Nassir Navab
We present a novel method to track 3D models in color and depth data.
Unsupervised Monocular Depth Prediction for Indoor Continuous Video Streams
no code implementations • 20 Nov 2019 • Yinglong Feng, Shuncheng Wu, Okan Köpüklü, Xueyang Kang, Federico Tombari
This paper studies unsupervised monocular depth prediction problem.
ForkNet: Multi-branch Volumetric Semantic Completion from a Single Depth Image
no code implementations • ICCV 2019 • Yida Wang, David Joseph Tan, Nassir Navab, Federico Tombari
We propose a novel model for 3D semantic completion from a single depth image, based on a single encoder and three separate generators used to reconstruct different geometric and semantic representations of the original and completed scene, all sharing the same latent space.
 Ranked #7 on
3D Semantic Scene Completion
on NYUv2
(using extra training data)
Ranked #7 on
3D Semantic Scene Completion
on NYUv2
(using extra training data)
Object-Driven Multi-Layer Scene Decomposition From a Single Image
no code implementations • ICCV 2019 • Helisa Dhamo, Nassir Navab, Federico Tombari
Our approach aims at building up a Layered Depth Image (LDI) from a single RGB input, which is an efficient representation that arranges the scene in layers, including originally occluded regions.
RIO: 3D Object Instance Re-Localization in Changing Indoor Environments
1 code implementation • ICCV 2019 • Johanna Wald, Armen Avetisyan, Nassir Navab, Federico Tombari, Matthias Nießner
In this work, we introduce the task of 3D object instance re-localization (RIO): given one or multiple objects in an RGB-D scan, we want to estimate their corresponding 6DoF poses in another 3D scan of the same environment taken at a later point in time.
Grasp Type Estimation for Myoelectric Prostheses using Point Cloud Feature Learning
no code implementations • 7 Aug 2019 • Ghazal Ghazaei, Federico Tombari, Nassir Navab, Kianoush Nazarpour
Prosthetic hands can help people with limb difference to return to their life routines.
Sampling-free Epistemic Uncertainty Estimation Using Approximated Variance Propagation
1 code implementation • ICCV 2019 • Janis Postels, Francesco Ferroni, Huseyin Coskun, Nassir Navab, Federico Tombari
We present a sampling-free approach for computing the epistemic uncertainty of a neural network.
Domain-Specific Priors and Meta Learning for Few-Shot First-Person Action Recognition
no code implementations • 22 Jul 2019 • Huseyin Coskun, Zeeshan Zia, Bugra Tekin, Federica Bogo, Nassir Navab, Federico Tombari, Harpreet Sawhney
The lack of large-scale real datasets with annotations makes transfer learning a necessity for video activity understanding.
Query-guided End-to-End Person Search
1 code implementation • CVPR 2019 • Bharti Munjal, Sikandar Amin, Federico Tombari, Fabio Galasso
We extend this with i. a query-guided Siamese squeeze-and-excitation network (QSSE-Net) that uses global context from both the query and gallery images, ii.
Attention-based Lane Change Prediction
no code implementations • 4 Mar 2019 • Oliver Scheel, Naveen Shankar Nagaraja, Loren Schwarz, Nassir Navab, Federico Tombari
Lane change prediction of surrounding vehicles is a key building block of path planning.
3D Point Capsule Networks
2 code implementations • CVPR 2019 • Yongheng Zhao, Tolga Birdal, Haowen Deng, Federico Tombari
In this paper, we propose 3D point-capsule networks, an auto-encoder designed to process sparse 3D point clouds while preserving spatial arrangements of the input data.
 Ranked #5 on
3D Object Classification
on ModelNet40
Ranked #5 on
3D Object Classification
on ModelNet40
Explaining the Ambiguity of Object Detection and 6D Pose From Visual Data
no code implementations • ICCV 2019 • Fabian Manhardt, Diego Martin Arroyo, Christian Rupprecht, Benjamin Busam, Tolga Birdal, Nassir Navab, Federico Tombari
For each object instance we predict multiple pose and class outcomes to estimate the specific pose distribution generated by symmetries and repetitive textures.
Dealing with Ambiguity in Robotic Grasping via Multiple Predictions
no code implementations • 2 Nov 2018 • Ghazal Ghazaei, Iro Laina, Christian Rupprecht, Federico Tombari, Nassir Navab, Kianoush Nazarpour
Further, we reformulate the problem of robotic grasping by replacing conventional grasp rectangles with grasp belief maps, which hold more precise location information than a rectangle and account for the uncertainty inherent to the task.
Adversarial Semantic Scene Completion from a Single Depth Image
no code implementations • 25 Oct 2018 • Yida Wang, David Joseph Tan, Nassir Navab, Federico Tombari
We propose a method to reconstruct, complete and semantically label a 3D scene from a single input depth image.
A Summary of the 4th International Workshop on Recovering 6D Object Pose
no code implementations • 9 Oct 2018 • Tomas Hodan, Rigas Kouskouridas, Tae-Kyun Kim, Federico Tombari, Kostas Bekris, Bertram Drost, Thibault Groueix, Krzysztof Walas, Vincent Lepetit, Ales Leonardis, Carsten Steger, Frank Michel, Caner Sahin, Carsten Rother, Jiri Matas
The workshop featured four invited talks, oral and poster presentations of accepted workshop papers, and an introduction of the BOP benchmark for 6D object pose estimation.
Deep Model-Based 6D Pose Refinement in RGB
1 code implementation • ECCV 2018 • Fabian Manhardt, Wadim Kehl, Nassir Navab, Federico Tombari
We present a novel approach for model-based 6D pose refinement in color data.
Distortion-Aware Convolutional Filters for Dense Prediction in Panoramic Images
no code implementations • ECCV 2018 • Keisuke Tateno, Nassir Navab, Federico Tombari
There is a high demand of 3D data for 360° panoramic images and videos, pushed by the growing availability on the market of specialized hardware for both capturing (e. g., omnidirectional cameras) as well as visualizing in 3D (e. g., head mounted displays) panoramic images and videos.
 Ranked #10 on
Depth Estimation
on Stanford2D3D Panoramic
Ranked #10 on
Depth Estimation
on Stanford2D3D Panoramic
BOP: Benchmark for 6D Object Pose Estimation
1 code implementation • ECCV 2018 • Tomas Hodan, Frank Michel, Eric Brachmann, Wadim Kehl, Anders Glent Buch, Dirk Kraft, Bertram Drost, Joel Vidal, Stephan Ihrke, Xenophon Zabulis, Caner Sahin, Fabian Manhardt, Federico Tombari, Tae-Kyun Kim, Jiri Matas, Carsten Rother
We propose a benchmark for 6D pose estimation of a rigid object from a single RGB-D input image.
Fully-Convolutional Point Networks for Large-Scale Point Clouds
1 code implementation • ECCV 2018 • Dario Rethage, Johanna Wald, Jürgen Sturm, Nassir Navab, Federico Tombari
This work proposes a general-purpose, fully-convolutional network architecture for efficiently processing large-scale 3D data.
 Ranked #26 on
Semantic Segmentation
on ScanNet
Ranked #26 on
Semantic Segmentation
on ScanNet
Deep Learned Full-3D Object Completion from Single View
no code implementations • 21 Aug 2018 • Dario Rethage, Federico Tombari, Felix Achilles, Nassir Navab
3D geometry is a very informative cue when interacting with and navigating an environment.
Human Motion Analysis with Deep Metric Learning
2 code implementations • ECCV 2018 • Huseyin Coskun, David Joseph Tan, Sailesh Conjeti, Nassir Navab, Federico Tombari
Nevertheless, we believe that traditional approaches such as L2 distance or Dynamic Time Warping based on hand-crafted local pose metrics fail to appropriately capture the semantic relationship across motions and, as such, are not suitable for being employed as metrics within these tasks.
Peeking Behind Objects: Layered Depth Prediction from a Single Image
no code implementations • 23 Jul 2018 • Helisa Dhamo, Keisuke Tateno, Iro Laina, Nassir Navab, Federico Tombari
While conventional depth estimation can infer the geometry of a scene from a single RGB image, it fails to estimate scene regions that are occluded by foreground objects.
Situation Assessment for Planning Lane Changes: Combining Recurrent Models and Prediction
no code implementations • 17 May 2018 • Oliver Scheel, Loren Schwarz, Nassir Navab, Federico Tombari
One of the greatest challenges towards fully autonomous cars is the understanding of complex and dynamic scenes.
Webly Supervised Learning for Skin Lesion Classification
no code implementations • 31 Mar 2018 • Fernando Navarro, Sailesh Conjeti, Federico Tombari, Nassir Navab
Within medical imaging, manual curation of sufficient well-labeled samples is cost, time and scale-prohibitive.
Guide Me: Interacting with Deep Networks
no code implementations • CVPR 2018 • Christian Rupprecht, Iro Laina, Nassir Navab, Gregory D. Hager, Federico Tombari
Interaction and collaboration between humans and intelligent machines has become increasingly important as machine learning methods move into real-world applications that involve end users.
Fast and Accurate Semantic Mapping through Geometric-based Incremental Segmentation
no code implementations • 7 Mar 2018 • Yoshikatsu Nakajima, Keisuke Tateno, Federico Tombari, Hideo Saito
We propose an efficient and scalable method for incrementally building a dense, semantically annotated 3D map in real-time.
Predicting Multiple Actions for Stochastic Continuous Control
no code implementations • ICLR 2018 • Sanjeev Kumar, Christian Rupprecht, Federico Tombari, Gregory D. Hager
We introduce a new approach to estimate continuous actions using actor-critic algorithms for reinforcement learning problems.
SSD-6D: Making RGB-based 3D detection and 6D pose estimation great again
1 code implementation • ICCV 2017 • Wadim Kehl, Fabian Manhardt, Federico Tombari, Slobodan Ilic, Nassir Navab
We present a novel method for detecting 3D model instances and estimating their 6D poses from RGB data in a single shot.
 Ranked #1 on
6D Pose Estimation using RGBD
on Tejani
Ranked #1 on
6D Pose Estimation using RGBD
on Tejani
Long Short-Term Memory Kalman Filters: Recurrent Neural Estimators for Pose Regularization
no code implementations • ICCV 2017 • Huseyin Coskun, Felix Achilles, Robert DiPietro, Nassir Navab, Federico Tombari
One-shot pose estimation for tasks such as body joint localization, camera pose estimation, and object tracking are generally noisy, and temporal filters have been extensively used for regularization.
6D Object Pose Estimation with Depth Images: A Seamless Approach for Robotic Interaction and Augmented Reality
no code implementations • 5 Sep 2017 • David Joseph Tan, Nassir Navab, Federico Tombari
To determine the 3D orientation and 3D location of objects in the surroundings of a camera mounted on a robot or mobile device, we developed two powerful algorithms in object detection and temporal tracking that are combined seamlessly for robotic perception and interaction as well as Augmented Reality (AR).
Long Short-Term Memory Kalman Filters:Recurrent Neural Estimators for Pose Regularization
no code implementations • 6 Aug 2017 • Huseyin Coskun, Felix Achilles, Robert DiPietro, Nassir Navab, Federico Tombari
One-shot pose estimation for tasks such as body joint localization, camera pose estimation, and object tracking are generally noisy, and temporal filters have been extensively used for regularization.
Learning without Prejudice: Avoiding Bias in Webly-Supervised Action Recognition
no code implementations • 14 Jun 2017 • Christian Rupprecht, Ansh Kapil, Nan Liu, Lamberto Ballan, Federico Tombari
One of the main problems in webly-supervised learning is cleaning the noisy labeled data from the web.
CNN-SLAM: Real-time dense monocular SLAM with learned depth prediction
1 code implementation • CVPR 2017 • Keisuke Tateno, Federico Tombari, Iro Laina, Nassir Navab
Given the recent advances in depth prediction from Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs), this paper investigates how predicted depth maps from a deep neural network can be deployed for accurate and dense monocular reconstruction.
Concurrent Segmentation and Localization for Tracking of Surgical Instruments
no code implementations • 30 Mar 2017 • Iro Laina, Nicola Rieke, Christian Rupprecht, Josué Page Vizcaíno, Abouzar Eslami, Federico Tombari, Nassir Navab
Real-time instrument tracking is a crucial requirement for various computer-assisted interventions.
Learning in an Uncertain World: Representing Ambiguity Through Multiple Hypotheses
no code implementations • ICCV 2017 • Christian Rupprecht, Iro Laina, Robert DiPietro, Maximilian Baust, Federico Tombari, Nassir Navab, Gregory D. Hager
In future prediction, for example, many distinct outcomes are equally valid.
An Octree-Based Approach towards Efficient Variational Range Data Fusion
no code implementations • 26 Aug 2016 • Wadim Kehl, Tobias Holl, Federico Tombari, Slobodan Ilic, Nassir Navab
Volume-based reconstruction is usually expensive both in terms of memory consumption and runtime.
Hashmod: A Hashing Method for Scalable 3D Object Detection
no code implementations • 20 Jul 2016 • Wadim Kehl, Federico Tombari, Nassir Navab, Slobodan Ilic, Vincent Lepetit
We present a scalable method for detecting objects and estimating their 3D poses in RGB-D data.
Deep Learning of Local RGB-D Patches for 3D Object Detection and 6D Pose Estimation
no code implementations • 20 Jul 2016 • Wadim Kehl, Fausto Milletari, Federico Tombari, Slobodan Ilic, Nassir Navab
We present a 3D object detection method that uses regressed descriptors of locally-sampled RGB-D patches for 6D vote casting.
A Taxonomy and Library for Visualizing Learned Features in Convolutional Neural Networks
no code implementations • 24 Jun 2016 • Felix Grün, Christian Rupprecht, Nassir Navab, Federico Tombari
Over the last decade, Convolutional Neural Networks (CNN) saw a tremendous surge in performance.
Deeper Depth Prediction with Fully Convolutional Residual Networks
17 code implementations • 1 Jun 2016 • Iro Laina, Christian Rupprecht, Vasileios Belagiannis, Federico Tombari, Nassir Navab
This paper addresses the problem of estimating the depth map of a scene given a single RGB image.
A Versatile Learning-Based 3D Temporal Tracker: Scalable, Robust, Online
no code implementations • ICCV 2015 • David Joseph Tan, Federico Tombari, Slobodan Ilic, Nassir Navab
This paper proposes a temporal tracking algorithm based on Random Forest that uses depth images to estimate and track the 3D pose of a rigid object in real-time.
Learning a Descriptor-Specific 3D Keypoint Detector
no code implementations • ICCV 2015 • Samuele Salti, Federico Tombari, Riccardo Spezialetti, Luigi Di Stefano
Keypoint detection represents the first stage in the majority of modern computer vision pipelines based on automatically established correspondences between local descriptors.