Search Results for author: Jie Wen
Found 20 papers, 7 papers with code
CDIMC-net: Cognitive Deep Incomplete Multi-view Clustering Network
no code implementations • 28 Mar 2024 • Jie Wen, Zheng Zhang, Yong Xu, Bob Zhang, Lunke Fei, Guo-Sen Xie
In this paper, we propose a novel incomplete multi-view clustering network, called Cognitive Deep Incomplete Multi-view Clustering Network (CDIMC-net), to address these issues.
Information Recovery-Driven Deep Incomplete Multiview Clustering Network
2 code implementations • 2 Apr 2023 • Chengliang Liu, Jie Wen, Zhihao Wu, Xiaoling Luo, Chao Huang, Yong Xu
Concretely, a two-stage autoencoder network with the self-attention structure is built to synchronously extract high-level semantic representations of multiple views and recover the missing data.
Learning Reliable Representations for Incomplete Multi-View Partial Multi-Label Classification
no code implementations • 30 Mar 2023 • Chengliang Liu, Jie Wen, Yong Xu, Liqiang Nie, Min Zhang
The application of multi-view contrastive learning has further facilitated this process, however, the existing multi-view contrastive learning methods crudely separate the so-called negative pair, which largely results in the separation of samples belonging to the same category or similar ones.
Deep Double Incomplete Multi-view Multi-label Learning with Incomplete Labels and Missing Views
1 code implementation • IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems 2023 • Jie Wen, Chengliang Liu, Shijie Deng, Yicheng Liu, Lunke Fei, Ke Yan, Yong Xu
View missing and label missing are two challenging problems in the applications of multi-view multi-label classification scenery.
DICNet: Deep Instance-Level Contrastive Network for Double Incomplete Multi-View Multi-Label Classification
2 code implementations • 15 Mar 2023 • Chengliang Liu, Jie Wen, Xiaoling Luo, Chao Huang, Zhihao Wu, Yong Xu
To deal with the double incomplete multi-view multi-label classification problem, we propose a deep instance-level contrastive network, namely DICNet.
Incomplete Multi-View Multi-Label Learning via Label-Guided Masked View- and Category-Aware Transformers
1 code implementation • 13 Mar 2023 • Chengliang Liu, Jie Wen, Xiaoling Luo, Yong Xu
The former aggregates information from different views in the process of extracting view-specific features, and the latter learns subcategory embedding to improve classification performance.
Highly Confident Local Structure Based Consensus Graph Learning for Incomplete Multi-View Clustering
1 code implementation • CVPR 2023 • Jie Wen, Chengliang Liu, Gehui Xu, Zhihao Wu, Chao Huang, Lunke Fei, Yong Xu
Graph-based multi-view clustering has attracted extensive attention because of the powerful clustering-structure representation ability and noise robustness.
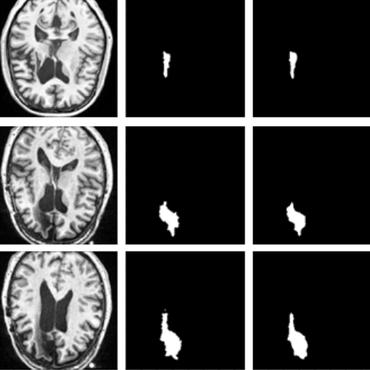
In vivo labeling and quantitative imaging of neurons using MRI
no code implementations • 13 Nov 2022 • Shana Li, Xiang Xu, Canjun Li, Ziyan Xu, Qiong Ye, Yan Zhang, Chunlei Cang, Jie Wen
Developing in vivo neuronal labeling and imaging techniques is crucial for studying the structure and function of neural circuits.
Cross-view Graph Contrastive Representation Learning on Partially Aligned Multi-view Data
no code implementations • 8 Nov 2022 • Yiming Wang, Dongxia Chang, Zhiqiang Fu, Jie Wen, Yao Zhao
Multi-view representation learning has developed rapidly over the past decades and has been applied in many fields.
A Survey on Incomplete Multi-view Clustering
1 code implementation • 17 Aug 2022 • Jie Wen, Zheng Zhang, Lunke Fei, Bob Zhang, Yong Xu, Zhao Zhang, Jinxing Li
However, in practical applications, such as disease diagnosis, multimedia analysis, and recommendation system, it is common to observe that not all views of samples are available in many cases, which leads to the failure of the conventional multi-view clustering methods.
Localized Sparse Incomplete Multi-view Clustering
1 code implementation • 5 Aug 2022 • Chengliang Liu, Zhihao Wu, Jie Wen, Chao Huang, Yong Xu
Moreover, a novel local graph embedding term is introduced to learn the structured consensus representation.
Global-Supervised Contrastive Loss and View-Aware-Based Post-Processing for Vehicle Re-Identification
no code implementations • 17 Apr 2022 • Zhijun Hu, Yong Xu, Jie Wen, Xianjing Cheng, Zaijun Zhang, Lilei Sun, YaoWei Wang
The proposed VABPP method is the first time that the view-aware-based method is used as a post-processing method in the field of vehicle re-identification.
ACTIVE:Augmentation-Free Graph Contrastive Learning for Partial Multi-View Clustering
no code implementations • 1 Mar 2022 • Yiming Wang, Dongxia Chang, Zhiqiang Fu, Jie Wen, Yao Zhao
In this paper, we propose an augmentation-free graph contrastive learning framework, namely ACTIVE, to solve the problem of partial multi-view clustering.
Automated assessment of disease severity of COVID-19 using artificial intelligence with synthetic chest CT
no code implementations • 11 Dec 2021 • Mengqiu Liu, Ying Liu, Yidong Yang, Aiping Liu, Shana Li, Changbing Qu, Xiaohui Qiu, Yang Li, Weifu Lv, Peng Zhang, Jie Wen
Correlations between imaging findings and clinical lab tests suggested the value of this system as a potential tool to assess disease severity of COVID-19.
Unsupervised COVID-19 Lesion Segmentation in CT Using Cycle Consistent Generative Adversarial Network
no code implementations • 23 Nov 2021 • Chengyijue Fang, Yingao Liu, Mengqiu Liu, Xiaohui Qiu, Ying Liu, Yang Li, Jie Wen, Yidong Yang
The lung volume volume was firstly delineated using a pre-trained U-net and worked as the input for the later network.
Vehicle Re-identification Based on Dual Distance Center Loss
no code implementations • 23 Dec 2020 • Zhijun Hu, Yong Xu, Jie Wen, Lilei Sun, Raja S P
Moreover, by designing a Euclidean distance threshold between all center pairs, which not only strengthens the inter-class separability of center loss, but also makes the center loss (or DDCL) works well without the combination of softmax loss.
Adaptive Locality Preserving Regression
no code implementations • 3 Jan 2019 • Jie Wen, Zuofeng Zhong, Zheng Zhang, Lunke Fei, Zhihui Lai, Runze Chen
This paper proposes a novel discriminative regression method, called adaptive locality preserving regression (ALPR) for classification.
Enhanced CNN for image denoising
no code implementations • 28 Oct 2018 • Chunwei Tian, Yong Xu, Lunke Fei, Junqian Wang, Jie Wen, Nan Luo
Owing to flexible architectures of deep convolutional neural networks (CNNs), CNNs are successfully used for image denoising.
Incomplete Multi-view Clustering via Graph Regularized Matrix Factorization
no code implementations • 17 Sep 2018 • Jie Wen, Zheng Zhang, Yong Xu, Zuofeng Zhong
Clustering with incomplete views is a challenge in multi-view clustering.
Local Multiple Directional Pattern of Palmprint Image
no code implementations • 21 Jul 2016 • Lunke Fei, Jie Wen, Zheng Zhang, Ke Yan, Zuofeng Zhong
Conventional methods usually capture the only one of the most dominant direction of palmprint images.