Search Results for author: Khiem Vuong
Found 6 papers, 4 papers with code
WALT3D: Generating Realistic Training Data from Time-Lapse Imagery for Reconstructing Dynamic Objects under Occlusion
no code implementations • 27 Mar 2024 • Khiem Vuong, N. Dinesh Reddy, Robert Tamburo, Srinivasa G. Narasimhan
Current methods for 2D and 3D object understanding struggle with severe occlusions in busy urban environments, partly due to the lack of large-scale labeled ground-truth annotations for learning occlusion.
Toward Planet-Wide Traffic Camera Calibration
no code implementations • 6 Nov 2023 • Khiem Vuong, Robert Tamburo, Srinivasa G. Narasimhan
Despite the widespread deployment of outdoor cameras, their potential for automated analysis remains largely untapped due, in part, to calibration challenges.
Egocentric Scene Understanding via Multimodal Spatial Rectifier
1 code implementation • CVPR 2022 • Tien Do, Khiem Vuong, Hyun Soo Park
We present a multimodal spatial rectifier that stabilizes the egocentric images to a set of reference directions, which allows learning a coherent visual representation.
Deep Multi-view Depth Estimation with Predicted Uncertainty
1 code implementation • 19 Nov 2020 • Tong Ke, Tien Do, Khiem Vuong, Kourosh Sartipi, Stergios I. Roumeliotis
In this paper, we address the problem of estimating dense depth from a sequence of images using deep neural networks.
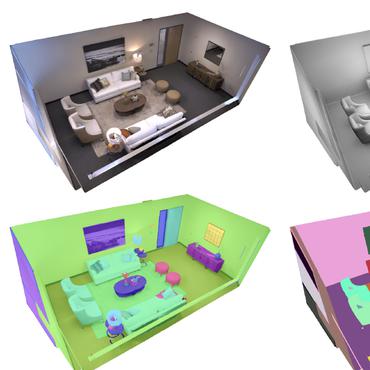
Deep Depth Estimation from Visual-Inertial SLAM
1 code implementation • 31 Jul 2020 • Kourosh Sartipi, Tien Do, Tong Ke, Khiem Vuong, Stergios I. Roumeliotis
This paper addresses the problem of learning to complete a scene's depth from sparse depth points and images of indoor scenes.
Surface Normal Estimation of Tilted Images via Spatial Rectifier
1 code implementation • ECCV 2020 • Tien Do, Khiem Vuong, Stergios I. Roumeliotis, Hyun Soo Park
Our two main hypotheses are: (1) visual scene layout is indicative of the gravity direction; and (2) not all surfaces are equally represented by a learned estimator due to the structured distribution of the training data, thus, there exists a transformation for each tilted image that is more responsive to the learned estimator than others.