Search Results for author: Qingyao Wu
Found 33 papers, 15 papers with code
Human Interaction Learning on 3D Skeleton Point Clouds for Video Violence Recognition
no code implementations • ECCV 2020 • Yukun Su, Guosheng Lin, Jinhui Zhu, Qingyao Wu
This paper introduces a new method for recognizing violent behavior by learning contextual relationships between related people from human skeleton points.
 Ranked #5 on
Activity Recognition
on RWF-2000
Ranked #5 on
Activity Recognition
on RWF-2000
Spatial-Semantic Collaborative Cropping for User Generated Content
1 code implementation • 16 Jan 2024 • Yukun Su, Yiwen Cao, Jingliang Deng, Fengyun Rao, Qingyao Wu
A large amount of User Generated Content (UGC) is uploaded to the Internet daily and displayed to people world-widely through the client side (e. g., mobile and PC).
Variance-insensitive and Target-preserving Mask Refinement for Interactive Image Segmentation
no code implementations • 22 Dec 2023 • Chaowei Fang, Ziyin Zhou, Junye Chen, Hanjing Su, Qingyao Wu, Guanbin Li
We introduce a novel method, Variance-Insensitive and Target-Preserving Mask Refinement to enhance segmentation quality with fewer user inputs.
SARA: Controllable Makeup Transfer with Spatial Alignment and Region-Adaptive Normalization
no code implementations • 28 Nov 2023 • Xiaojing Zhong, Xinyi Huang, Zhonghua Wu, Guosheng Lin, Qingyao Wu
To address this problem, we propose a novel Spatial Alignment and Region-Adaptive normalization method (SARA) in this paper.
Typhoon Intensity Prediction with Vision Transformer
1 code implementation • 28 Nov 2023 • Huanxin Chen, Pengshuai Yin, Huichou Huang, Qingyao Wu, Ruirui Liu, Xiatian Zhu
Predicting typhoon intensity accurately across space and time is crucial for issuing timely disaster warnings and facilitating emergency response.
DI-Net : Decomposed Implicit Garment Transfer Network for Digital Clothed 3D Human
no code implementations • 28 Nov 2023 • Xiaojing Zhong, Yukun Su, Zhonghua Wu, Guosheng Lin, Qingyao Wu
3D virtual try-on enjoys many potential applications and hence has attracted wide attention.
Semantic-Constraint Matching Transformer for Weakly Supervised Object Localization
no code implementations • 4 Sep 2023 • Yiwen Cao, Yukun Su, Wenjun Wang, Yanxia Liu, Qingyao Wu
Weakly supervised object localization (WSOL) strives to learn to localize objects with only image-level supervision.
Occlusion-Aware Detection and Re-ID Calibrated Network for Multi-Object Tracking
no code implementations • 30 Aug 2023 • Yukun Su, Ruizhou Sun, Xin Shu, Yu Zhang, Qingyao Wu
Multi-Object Tracking (MOT) is a crucial computer vision task that aims to predict the bounding boxes and identities of objects simultaneously.
Improving Video Violence Recognition with Human Interaction Learning on 3D Skeleton Point Clouds
no code implementations • 26 Aug 2023 • Yukun Su, Guosheng Lin, Qingyao Wu
(ii) Global-SPIL: to better learn and refine the features of the unordered and unstructured skeleton points, Global-SPIL employs the self-attention layer that operates directly on the sampled points, which can help to make the output more permutation-invariant and well-suited for our task.
WMFormer++: Nested Transformer for Visible Watermark Removal via Implict Joint Learning
no code implementations • 20 Aug 2023 • Dongjian Huo, Zehong Zhang, Hanjing Su, Guanbin Li, Chaowei Fang, Qingyao Wu
Existing watermark removal methods mainly rely on UNet with task-specific decoder branches--one for watermark localization and the other for background image restoration.
Dual Progressive Transformations for Weakly Supervised Semantic Segmentation
1 code implementation • 30 Sep 2022 • Dongjian Huo, Yukun Su, Qingyao Wu
Weakly supervised semantic segmentation (WSSS), which aims to mine the object regions by merely using class-level labels, is a challenging task in computer vision.
A Unified Transformer Framework for Group-based Segmentation: Co-Segmentation, Co-Saliency Detection and Video Salient Object Detection
1 code implementation • 9 Mar 2022 • Yukun Su, Jingliang Deng, Ruizhou Sun, Guosheng Lin, Qingyao Wu
Besides, they fail to take full advantage of the cues among inter- and intra-feature within a group of images.
 Ranked #1 on
Video Salient Object Detection
on FBMS-59
Ranked #1 on
Video Salient Object Detection
on FBMS-59
Debiased Visual Question Answering from Feature and Sample Perspectives
1 code implementation • NeurIPS 2021 • Zhiquan Wen, Guanghui Xu, Mingkui Tan, Qingyao Wu, Qi Wu
From the sample perspective, we construct two types of negative samples to assist the training of the models, without introducing additional annotations.
Calibrating Class Activation Maps for Long-Tailed Visual Recognition
no code implementations • 29 Aug 2021 • Chi Zhang, Guosheng Lin, Lvlong Lai, Henghui Ding, Qingyao Wu
First, we present a Class Activation Map Calibration (CAMC) module to improve the learning and prediction of network classifiers, by enforcing network prediction based on important image regions.
MV-TON: Memory-based Video Virtual Try-on network
no code implementations • 17 Aug 2021 • Xiaojing Zhong, Zhonghua Wu, Taizhe Tan, Guosheng Lin, Qingyao Wu
With the development of Generative Adversarial Network, image-based virtual try-on methods have made great progress.
Context Decoupling Augmentation for Weakly Supervised Semantic Segmentation
1 code implementation • ICCV 2021 • Yukun Su, Ruizhou Sun, Guosheng Lin, Qingyao Wu
Data augmentation is vital for deep learning neural networks.
CycleSegNet: Object Co-segmentation with Cycle Refinement and Region Correspondence
no code implementations • 5 Jan 2021 • Chi Zhang, Guankai Li, Guosheng Lin, Qingyao Wu, Rui Yao
Image co-segmentation is an active computer vision task that aims to segment the common objects from a set of images.
Self-Supervised 3D Skeleton Action Representation Learning With Motion Consistency and Continuity
no code implementations • ICCV 2021 • Yukun Su, Guosheng Lin, Qingyao Wu
Recently, self-supervised learning (SSL) has been proved very effective and it can help boost the performance in learning representations from unlabeled data in the image domain.
StackRec: Efficient Training of Very Deep Sequential Recommender Models by Iterative Stacking
1 code implementation • 14 Dec 2020 • Jiachun Wang, Fajie Yuan, Jian Chen, Qingyao Wu, Min Yang, Yang Sun, Guoxiao Zhang
We validate the performance of StackRec by instantiating it with four state-of-the-art SR models in three practical scenarios with real-world datasets.
Double Forward Propagation for Memorized Batch Normalization
no code implementations • 10 Oct 2020 • Yong Guo, Qingyao Wu, Chaorui Deng, Jian Chen, Mingkui Tan
Although the standard BN can significantly accelerate the training of DNNs and improve the generalization performance, it has several underlying limitations which may hamper the performance in both training and inference.
Graph Edit Distance Reward: Learning to Edit Scene Graph
no code implementations • ECCV 2020 • Lichang Chen, Guosheng Lin, Shijie Wang, Qingyao Wu
Scene Graph, as a vital tool to bridge the gap between language domain and image domain, has been widely adopted in the cross-modality task like VQA.
Improving Generative Adversarial Networks with Local Coordinate Coding
1 code implementation • 28 Jul 2020 • Jiezhang Cao, Yong Guo, Qingyao Wu, Chunhua Shen, Junzhou Huang, Mingkui Tan
In this paper, rather than sampling from the predefined prior distribution, we propose an LCCGAN model with local coordinate coding (LCC) to improve the performance of generating data.
Collaborative Unsupervised Domain Adaptation for Medical Image Diagnosis
1 code implementation • 5 Jul 2020 • Yifan Zhang, Ying WEI, Qingyao Wu, Peilin Zhao, Shuaicheng Niu, Junzhou Huang, Mingkui Tan
Deep learning based medical image diagnosis has shown great potential in clinical medicine.
COVID-DA: Deep Domain Adaptation from Typical Pneumonia to COVID-19
1 code implementation • 30 Apr 2020 • Yifan Zhang, Shuaicheng Niu, Zhen Qiu, Ying WEI, Peilin Zhao, Jianhua Yao, Junzhou Huang, Qingyao Wu, Mingkui Tan
There are two main challenges: 1) the discrepancy of data distributions between domains; 2) the task difference between the diagnosis of typical pneumonia and COVID-19.
Cost-Sensitive Portfolio Selection via Deep Reinforcement Learning
no code implementations • 6 Mar 2020 • Yifan Zhang, Peilin Zhao, Qingyao Wu, Bin Li, Junzhou Huang, Mingkui Tan
This task, however, has two main difficulties: (i) the non-stationary price series and complex asset correlations make the learning of feature representation very hard; (ii) the practicality principle in financial markets requires controlling both transaction and risk costs.
Online Adaptive Asymmetric Active Learning with Limited Budgets
1 code implementation • 18 Nov 2019 • Yifan Zhang, Peilin Zhao, Shuaicheng Niu, Qingyao Wu, JieZhang Cao, Junzhou Huang, Mingkui Tan
In these problems, there are two key challenges: the query budget is often limited; the ratio between classes is highly imbalanced.
Collaborative Unsupervised Domain Adaptation for Medical Image Diagnosis
1 code implementation • 17 Nov 2019 • Yifan Zhang, Ying WEI, Peilin Zhao, Shuaicheng Niu, Qingyao Wu, Mingkui Tan, Junzhou Huang
In this paper, we seek to exploit rich labeled data from relevant domains to help the learning in the target task with unsupervised domain adaptation (UDA).
Attention Guided Network for Retinal Image Segmentation
2 code implementations • 25 Jul 2019 • Shihao Zhang, Huazhu Fu, Yuguang Yan, Yubing Zhang, Qingyao Wu, Ming Yang, Mingkui Tan, Yanwu Xu
Learning structural information is critical for producing an ideal result in retinal image segmentation.
Auto-Embedding Generative Adversarial Networks for High Resolution Image Synthesis
1 code implementation • 27 Mar 2019 • Yong Guo, Qi Chen, Jian Chen, Qingyao Wu, Qinfeng Shi, Mingkui Tan
To address this issue, we develop a novel GAN called Auto-Embedding Generative Adversarial Network (AEGAN), which simultaneously encodes the global structure features and captures the fine-grained details.
Discrimination-aware Channel Pruning for Deep Neural Networks
1 code implementation • NeurIPS 2018 • Zhuangwei Zhuang, Mingkui Tan, Bohan Zhuang, Jing Liu, Yong Guo, Qingyao Wu, Junzhou Huang, Jinhui Zhu
Channel pruning is one of the predominant approaches for deep model compression.
Adversarial Learning with Local Coordinate Coding
no code implementations • ICML 2018 • Jiezhang Cao, Yong Guo, Qingyao Wu, Chunhua Shen, Junzhou Huang, Mingkui Tan
Generative adversarial networks (GANs) aim to generate realistic data from some prior distribution (e. g., Gaussian noises).
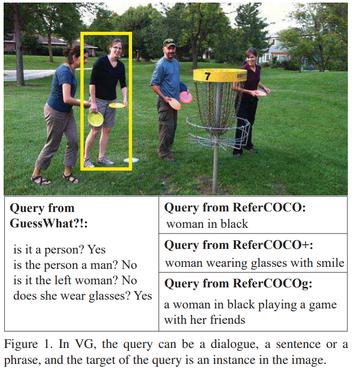
Visual Grounding via Accumulated Attention
no code implementations • CVPR 2018 • Chaorui Deng, Qi Wu, Qingyao Wu, Fuyuan Hu, Fan Lyu, Mingkui Tan
There are three main challenges in VG: 1) what is the main focus in a query; 2) how to understand an image; 3) how to locate an object.
A Self-Balanced Min-Cut Algorithm for Image Clustering
no code implementations • ICCV 2017 • Xiaojun Chen, Joshua Zhexue Haung, Feiping Nie, Renjie Chen, Qingyao Wu
In the new method, a self-balanced min-cut model is proposed in which the Exclusive Lasso is implicitly introduced as a balance regularizer in order to produce balanced partition.