Search Results for author: Rudolf Mester
Found 19 papers, 4 papers with code
Removing Adverse Volumetric Effects From Trained Neural Radiance Fields
no code implementations • 17 Nov 2023 • Andreas L. Teigen, Mauhing Yip, Victor P. Hamran, Vegard Skui, Annette Stahl, Rudolf Mester
While the use of neural radiance fields (NeRFs) in different challenging settings has been explored, only very recently have there been any contributions that focus on the use of NeRF in foggy environments.
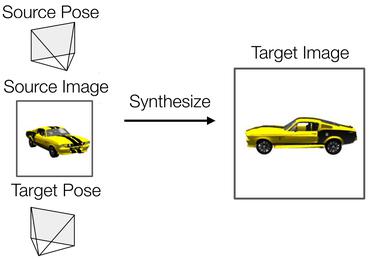
RGB-D Mapping and Tracking in a Plenoxel Radiance Field
1 code implementation • 7 Jul 2023 • Andreas L. Teigen, Yeonsoo Park, Annette Stahl, Rudolf Mester
In this paper, we present the vital differences between view synthesis models and 3D reconstruction models.
Realistic Full-Body Anonymization with Surface-Guided GANs
1 code implementation • 6 Jan 2022 • Håkon Hukkelås, Morten Smebye, Rudolf Mester, Frank Lindseth
Recent work on image anonymization has shown that generative adversarial networks (GANs) can generate near-photorealistic faces to anonymize individuals.
Model-Based Parameter Optimization for Ground Texture Based Localization Methods
no code implementations • 3 Sep 2021 • Jan Fabian Schmid, Stephan F. Simon, Rudolf Mester
A promising approach to accurate positioning of robots is ground texture based localization.
Urban Traffic Surveillance (UTS): A fully probabilistic 3D tracking approach based on 2D detections
no code implementations • 31 May 2021 • Henry Bradler, Adrian Kretz, Rudolf Mester
We quantitatively evaluate UTS using self generated synthetic data and ground truth from the CARLA simulator, due to the non-existence of datasets with an urban vehicle surveillance setting and labeled 3D bounding boxes.
Image Inpainting with Learnable Feature Imputation
1 code implementation • 2 Nov 2020 • Håkon Hukkelås, Frank Lindseth, Rudolf Mester
We propose (layer-wise) feature imputation of the missing input values to a convolution.
Features for Ground Texture Based Localization -- A Survey
no code implementations • 27 Feb 2020 • Jan Fabian Schmid, Stephan F. Simon, Rudolf Mester
Ground texture based vehicle localization using feature-based methods is a promising approach to achieve infrastructure-free high-accuracy localization.
Ground Texture Based Localization Using Compact Binary Descriptors
no code implementations • 25 Feb 2020 • Jan Fabian Schmid, Stephan F. Simon, Rudolf Mester
Ground texture based localization is a promising approach to achieve high-accuracy positioning of vehicles.
DeepPrivacy: A Generative Adversarial Network for Face Anonymization
2 code implementations • 10 Sep 2019 • Håkon Hukkelås, Rudolf Mester, Frank Lindseth
Our model is based on a conditional generative adversarial network, generating images considering the original pose and image background.
 Ranked #1 on
Face Anonymization
on 2019_test set
(using extra training data)
Ranked #1 on
Face Anonymization
on 2019_test set
(using extra training data)
Mono-SF: Multi-View Geometry Meets Single-View Depth for Monocular Scene Flow Estimation of Dynamic Traffic Scenes
no code implementations • ICCV 2019 • Fabian Brickwedde, Steffen Abraham, Rudolf Mester
Existing 3D scene flow estimation methods provide the 3D geometry and 3D motion of a scene and gain a lot of interest, for example in the context of autonomous driving.
Mono-Stixels: Monocular depth reconstruction of dynamic street scenes
no code implementations • 7 Aug 2019 • Fabian Brickwedde, Steffen Abraham, Rudolf Mester
In our experiments we use the public available DeepFlow for optical flow estimation and FCN8s for the semantic information as inputs and show on the KITTI 2015 dataset that mono-stixels provide a compact and reliable depth reconstruction of both the static and moving parts of the scene.
SDNet: Semantically Guided Depth Estimation Network
no code implementations • 24 Jul 2019 • Matthias Ochs, Adrian Kretz, Rudolf Mester
Autonomous vehicles and robots require a full scene understanding of the environment to interact with it.
DistanceNet: Estimating Traveled Distance from Monocular Images using a Recurrent Convolutional Neural Network
no code implementations • 17 Apr 2019 • Robin Kreuzig, Matthias Ochs, Rudolf Mester
Thus, our DistanceNet can be used as a component to solve the scale problem and help improve current and future classical mono vSLAM/VO methods.
Simulated Autonomous Driving in a Realistic Driving Environment using Deep Reinforcement Learning and a Deterministic Finite State Machine
no code implementations • 19 Nov 2018 • Patrick Klose, Rudolf Mester
In the field of Autonomous Driving, the system controlling the vehicle can be seen as an agent acting in a complex environment and thus naturally fits into the modern framework of Reinforcement Learning.
Simulated Autonomous Driving on Realistic Road Networks using Deep Reinforcement Learning
no code implementations • 12 Dec 2017 • Patrick Klose, Rudolf Mester
Using Deep Reinforcement Learning (DRL) can be a promising approach to handle various tasks in the field of (simulated) autonomous driving.
Joint Epipolar Tracking (JET): Simultaneous optimization of epipolar geometry and feature correspondences
no code implementations • 15 Mar 2017 • Henry Bradler, Matthias Ochs, Rudolf Mester
In this paper, we propose a sparse direct method which introduces a loss function that allows to simultaneously optimize the unscaled relative pose, as well as the set of feature correspondences directly considering the image intensity values.
Learning Rank Reduced Interpolation with Principal Component Analysis
no code implementations • 15 Mar 2017 • Matthias Ochs, Henry Bradler, Rudolf Mester
When facing situations with only very sparse measurements, typically the number of principal components is further reduced which results in a loss of expressiveness of the basis.
Lost and Found: Detecting Small Road Hazards for Self-Driving Vehicles
no code implementations • 15 Sep 2016 • Peter Pinggera, Sebastian Ramos, Stefan Gehrig, Uwe Franke, Carsten Rother, Rudolf Mester
The proposed approach outperforms all considered baselines in our evaluations on both pixel and object level and runs at frame rates of up to 20 Hz on 2 mega-pixel stereo imagery.
Discriminative Subspace Clustering
no code implementations • CVPR 2013 • Vasileios Zografos, Liam Ellis, Rudolf Mester
We present a novel method for clustering data drawn from a union of arbitrary dimensional subspaces, called Discriminative Subspace Clustering (DiSC).