Search Results for author: Wolfgang Minker
Found 52 papers, 1 papers with code
From Argument Search to Argumentative Dialogue: A Topic-independent Approach to Argument Acquisition for Dialogue Systems
1 code implementation • SIGDIAL (ACL) 2021 • Niklas Rach, Carolin Schindler, Isabel Feustel, Johannes Daxenberger, Wolfgang Minker, Stefan Ultes
Despite the remarkable progress in the field of computational argumentation, dialogue systems concerned with argumentative tasks often rely on structured knowledge about arguments and their relations.
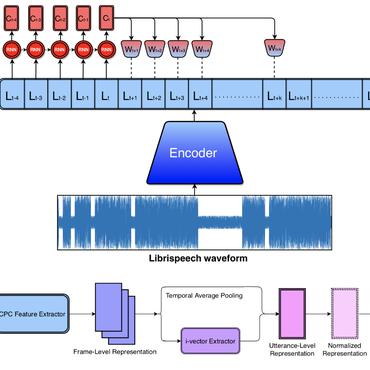
Towards Speech-only Opinion-level Sentiment Analysis
no code implementations • LREC 2022 • Annalena Aicher, Alisa Gazizullina, Aleksei Gusev, Yuri Matveev, Wolfgang Minker
The growing popularity of various forms of Spoken Dialogue Systems (SDS) raises the demand for their capability of implicitly assessing the speaker’s sentiment from speech only.
Towards Building a Spoken Dialogue System for Argument Exploration
no code implementations • LREC 2022 • Annalena Aicher, Nadine Gerstenlauer, Isabel Feustel, Wolfgang Minker, Stefan Ultes
We evaluate the likeability and motivation of users to interact with the new system in a user study.
User Interest Modelling in Argumentative Dialogue Systems
no code implementations • LREC 2022 • Annalena Aicher, Nadine Gerstenlauer, Wolfgang Minker, Stefan Ultes
Most systems helping to provide structured information and support opinion building, discuss with users without considering their individual interest.
Towards Modelling Self-imposed Filter Bubbles in Argumentative Dialogue Systems
no code implementations • LREC 2022 • Annalena Aicher, Wolfgang Minker, Stefan Ultes
To build a well-founded opinion it is natural for humans to gather and exchange new arguments.
ProDial – An Annotated Proactive Dialogue Act Corpus for Conversational Assistants using Crowdsourcing
no code implementations • LREC 2022 • Matthias Kraus, Nicolas Wagner, Wolfgang Minker
For creating a sound interactive personalization, we have developed an empathy-augmented dialogue strategy.
System-Initiated Transitions from Chit-Chat to Task-Oriented Dialogues with Transition Info Extractor and Transition Sentence Generator
no code implementations • 6 Aug 2023 • Ye Liu, Stefan Ultes, Wolfgang Minker, Wolfgang Maier
In this work, we study dialogue scenarios that start from chit-chat but eventually switch to task-related services, and investigate how a unified dialogue model, which can engage in both chit-chat and task-oriented dialogues, takes the initiative during the dialogue mode transition from chit-chat to task-oriented in a coherent and cooperative manner.
Unified Conversational Models with System-Initiated Transitions between Chit-Chat and Task-Oriented Dialogues
no code implementations • 4 Jul 2023 • Ye Liu, Stefan Ultes, Wolfgang Minker, Wolfgang Maier
We contribute two efficient prompt models which can proactively generate a transition sentence to trigger system-initiated transitions in a unified dialogue model.
Development of a Trust-Aware User Simulator for Statistical Proactive Dialog Modeling in Human-AI Teams
no code implementations • 24 Apr 2023 • Matthias Kraus, Ron Riekenbrauck, Wolfgang Minker
In this paper, we present the development of a corpus-based user simulator for training and testing proactive dialog policies.
Does It Affect You? Social and Learning Implications of Using Cognitive-Affective State Recognition for Proactive Human-Robot Tutoring
no code implementations • 20 Dec 2022 • Matthias Kraus, Diana Betancourt, Wolfgang Minker
For this reason, a concept learning task scenario was observed where a robotic assistant proactively helped when negative user states were detected.
Improving Proactive Dialog Agents Using Socially-Aware Reinforcement Learning
no code implementations • 25 Nov 2022 • Matthias Kraus, Nicolas Wagner, Ron Riekenbrauck, Wolfgang Minker
The next step for intelligent dialog agents is to escape their role as silent bystanders and become proactive.
ConceptNet infused DialoGPT for Underlying Commonsense Understanding and Reasoning in Dialogue Response Generation
no code implementations • 29 Sep 2022 • Ye Liu, Wolfgang Maier, Wolfgang Minker, Stefan Ultes
The pre-trained conversational models still fail to capture the implicit commonsense (CS) knowledge hidden in the dialogue interaction, even though they were pre-trained with an enormous dataset.
Context Matters in Semantically Controlled Language Generation for Task-oriented Dialogue Systems
no code implementations • ICON 2021 • Ye Liu, Wolfgang Maier, Wolfgang Minker, Stefan Ultes
We utilize the pre-trained multi-context ConveRT model for context representation in a model trained from scratch; and leverage the immediate preceding user utterance for context generation in a model adapted from the pre-trained GPT-2.
Empathetic Dialogue Generation with Pre-trained RoBERTa-GPT2 and External Knowledge
no code implementations • 7 Sep 2021 • Ye Liu, Wolfgang Maier, Wolfgang Minker, Stefan Ultes
One challenge for dialogue agents is to recognize feelings of the conversation partner and respond accordingly.
Naturalness Evaluation of Natural Language Generation in Task-oriented Dialogues using BERT
no code implementations • RANLP 2021 • Ye Liu, Wolfgang Maier, Wolfgang Minker, Stefan Ultes
This paper presents an automatic method to evaluate the naturalness of natural language generation in dialogue systems.
Natural Language Understanding for Argumentative Dialogue Systems in the Opinion Building Domain
no code implementations • 3 Mar 2021 • Waheed Ahmed Abro, Annalena Aicher, Niklas Rach, Stefan Ultes, Wolfgang Minker, Guilin Qi
Intent classifier model stacks BiLSTM with attention mechanism on top of the pre-trained BERT model and fine-tune the model for recognizing the user intent, whereas the argument similarity model employs BERT+BiLSTM for identifying system arguments the user refers to in his or her natural language utterances.
An Audio-Video Deep and Transfer Learning Framework for Multimodal Emotion Recognition in the wild
no code implementations • 7 Oct 2020 • Denis Dresvyanskiy, Elena Ryumina, Heysem Kaya, Maxim Markitantov, Alexey Karpov, Wolfgang Minker
In this paper, we present our contribution to ABAW facial expression challenge.
A Comparison of Explicit and Implicit Proactive Dialogue Strategies for Conversational Recommendation
no code implementations • LREC 2020 • Matthias Kraus, Fabian Fischbach, Pascal Jansen, Wolfgang Minker
Depending on the way a recommendation is communicated influences the user{'}s perception of the system.
Estimating User Communication Styles for Spoken Dialogue Systems
no code implementations • LREC 2020 • Juliana Miehle, Isabel Feustel, Julia Hornauer, Wolfgang Minker, Stefan Ultes
We use this corpus to estimate the elaborateness and the directness of each utterance.
How Users React to Proactive Voice Assistant Behavior While Driving
no code implementations • LREC 2020 • Maria Schmidt, Wolfgang Minker, Steffen Werner
Finally, the users reacted significantly faster to proactive PA actions, which we interpret as less cognitive load compared to non-proactive behavior.
Evaluation of Argument Search Approaches in the Context of Argumentative Dialogue Systems
no code implementations • LREC 2020 • Niklas Rach, Yuki Matsuda, Johannes Daxenberger, Stefan Ultes, Keiichi Yasumoto, Wolfgang Minker
We present an approach to evaluate argument search techniques in view of their use in argumentative dialogue systems by assessing quality aspects of the retrieved arguments.
Comparative Study of Sentence Embeddings for Contextual Paraphrasing
no code implementations • LREC 2020 • Louisa Pragst, Wolfgang Minker, Stefan Ultes
Paraphrasing is an important aspect of natural-language generation that can produce more variety in the way specific content is presented.
Cross-Corpus Data Augmentation for Acoustic Addressee Detection
no code implementations • WS 2019 • Oleg Akhtiamov, Ingo Siegert, Alexey Karpov, Wolfgang Minker
Mixup is shown to be beneficial for merging acoustic data (extracted features but not raw waveforms) from different domains that allows us to reach a higher classification performance on human-machine AD and also for training a multipurpose neural network that is capable of solving both human-machine and adult-child AD problems.
Acquisition and Assessment of Semantic Content for the Generation of Elaborateness and Indirectness in Spoken Dialogue Systems
no code implementations • IJCNLP 2017 • Louisa Pragst, Koichiro Yoshino, Wolfgang Minker, Satoshi Nakamura, Stefan Ultes
Defining all possible system actions in a dialogue system by hand is a tedious work.
 Cultural Vocal Bursts Intensity Prediction
Cultural Vocal Bursts Intensity Prediction
 Spoken Dialogue Systems
Spoken Dialogue Systems
Interaction Quality Estimation Using Long Short-Term Memories
no code implementations • WS 2017 • Niklas Rach, Wolfgang Minker, Stefan Ultes
For estimating the Interaction Quality (IQ) in Spoken Dialogue Systems (SDS), the dialogue history is of significant importance.
A Comparative Study of Text Preprocessing Approaches for Topic Detection of User Utterances
no code implementations • LREC 2016 • Roman Sergienko, Muhammad Shan, Wolfgang Minker
The numerical experiments have shown that the simultaneous use of the novel proposed approaches (collectives of term weighting methods and the novel feature transformation method) allows reaching the high classification results with very small number of features.
Could Speaker, Gender or Age Awareness be beneficial in Speech-based Emotion Recognition?
no code implementations • LREC 2016 • Maxim Sidorov, Alex Schmitt, er, Eugene Semenkin, Wolfgang Minker
Emotion Recognition (ER) is an important part of dialogue analysis which can be used in order to improve the quality of Spoken Dialogue Systems (SDSs).
First Insight into Quality-Adaptive Dialogue
no code implementations • LREC 2014 • Stefan Ultes, H{\"u}seyin Dikme, Wolfgang Minker
While Spoken Dialogue Systems have gained in importance in recent years, most systems applied in the real world are still static and error-prone.
Speech-Based Emotion Recognition: Feature Selection by Self-Adaptive Multi-Criteria Genetic Algorithm
no code implementations • LREC 2014 • Maxim Sidorov, Christina Brester, Wolfgang Minker, Eugene Semenkin
Automated emotion recognition has a number of applications in Interactive Voice Response systems, call centers, etc.
A Parameterized and Annotated Spoken Dialog Corpus of the CMU Let's Go Bus Information System
no code implementations • LREC 2012 • Alex Schmitt, er, Stefan Ultes, Wolfgang Minker
Standardized corpora are the foundation for spoken language research.
 Automatic Speech Recognition
Automatic Speech Recognition
 Automatic Speech Recognition (ASR)
+3
Automatic Speech Recognition (ASR)
+3
Using multimodal resources for explanation approaches in intelligent systems
no code implementations • LREC 2012 • Florian Nothdurft, Wolfgang Minker
We propose that not only creating multimodal output for the user is important, but to take multimodal input resources into account for the decision when and how to interact.
Adaptive Speech Understanding for Intuitive Model-based Spoken Dialogues
no code implementations • LREC 2012 • Tobias Heinroth, Maximilian Grotz, Florian Nothdurft, Wolfgang Minker
Thus we present three enhancements towards a more sophisticated use of the ontology-based dialogue models and show how grammars may dynamically be adapted in order to understand intuitive user utterances.
Speech and Language Resources for LVCSR of Russian
no code implementations • LREC 2012 • Sergey Zablotskiy, Alex Shvets, er, Maxim Sidorov, Eugene Semenkin, Wolfgang Minker
In this paper a method for the syllable concatenation and error correction is suggested and tested.
Investigating Verbal Intelligence Using the TF-IDF Approach
no code implementations • LREC 2012 • Kseniya Zablotskaya, Fern Mart{\'\i}nez, o Fern{\'a}ndez, Wolfgang Minker
In this paper we also checked a hypothesis that differences in vocabulary of speakers yielding different verbal intelligence are sufficient enough for good classification results.
Relating Dominance of Dialogue Participants with their Verbal Intelligence Scores
no code implementations • LREC 2012 • Kseniya Zablotskaya, Umair Rahim, Fern Mart{\'\i}nez, o Fern{\'a}ndez, Wolfgang Minker
All the dialogues were divided into three groups: H-H is a group of dialogues between higher verbal intelligence participants, L-L is a group of dialogues between lower verbal intelligence participant and L-H is a group of all the other dialogues.