Regularization
Regularization
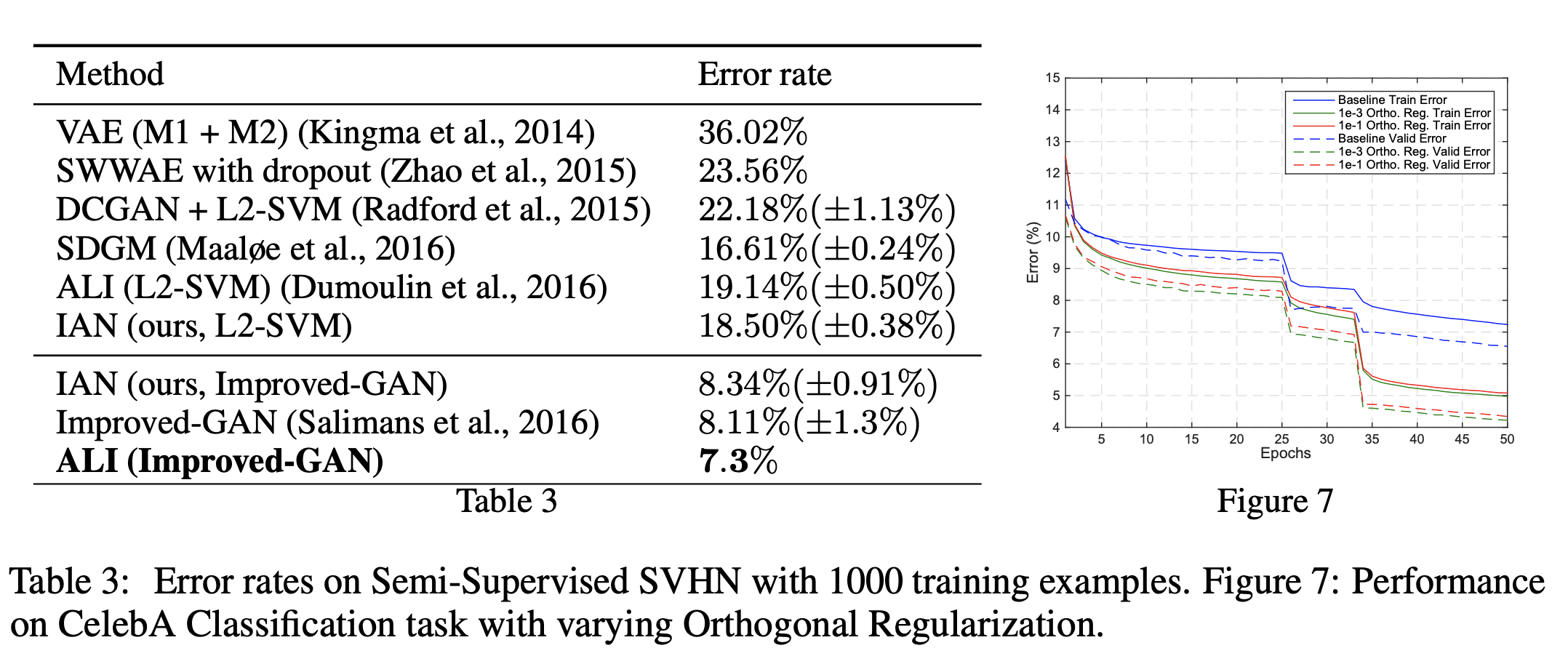
Orthogonal Regularization
Introduced by Brock et al. in Neural Photo Editing with Introspective Adversarial NetworksOrthogonal Regularization is a regularization technique for convolutional neural networks, introduced with generative modelling as the task in mind. Orthogonality is argued to be a desirable quality in ConvNet filters, partially because multiplication by an orthogonal matrix leaves the norm of the original matrix unchanged. This property is valuable in deep or recurrent networks, where repeated matrix multiplication can result in signals vanishing or exploding. To try to maintain orthogonality throughout training, Orthogonal Regularization encourages weights to be orthogonal by pushing them towards the nearest orthogonal manifold. The objective function is augmented with the cost:
$$ \mathcal{L}_{ortho} = \sum\left(|WW^{T} − I|\right) $$
Where $\sum$ indicates a sum across all filter banks, $W$ is a filter bank, and $I$ is the identity matrix
Source: Neural Photo Editing with Introspective Adversarial NetworksPapers
| Paper | Code | Results | Date | Stars |
|---|
Tasks
| Task | Papers | Share |
|---|---|---|
| Image Classification | 3 | 8.82% |
| Image Generation | 3 | 8.82% |
| Federated Learning | 2 | 5.88% |
| Sentence | 2 | 5.88% |
| Sentiment Analysis | 2 | 5.88% |
| Speech Synthesis | 2 | 5.88% |
| Video Generation | 2 | 5.88% |
| Video Prediction | 2 | 5.88% |
| General Classification | 2 | 5.88% |
Usage Over Time
Components
| Component | Type |
|
|---|---|---|
| 🤖 No Components Found | You can add them if they exist; e.g. Mask R-CNN uses RoIAlign |