Collaborative Global-Local Networks for Memory-Efficient Segmentation of Ultra-High Resolution Images
Segmentation of ultra-high resolution images is increasingly demanded, yet poses significant challenges for algorithm efficiency, in particular considering the (GPU) memory limits. Current approaches either downsample an ultra-high resolution image or crop it into small patches for separate processing. In either way, the loss of local fine details or global contextual information results in limited segmentation accuracy. We propose collaborative Global-Local Networks (GLNet) to effectively preserve both global and local information in a highly memory-efficient manner. GLNet is composed of a global branch and a local branch, taking the downsampled entire image and its cropped local patches as respective inputs. For segmentation, GLNet deeply fuses feature maps from two branches, capturing both the high-resolution fine structures from zoomed-in local patches and the contextual dependency from the downsampled input. To further resolve the potential class imbalance problem between background and foreground regions, we present a coarse-to-fine variant of GLNet, also being memory-efficient. Extensive experiments and analyses have been performed on three real-world ultra-high aerial and medical image datasets (resolution up to 30 million pixels). With only one single 1080Ti GPU and less than 2GB memory used, our GLNet yields high-quality segmentation results and achieves much more competitive accuracy-memory usage trade-offs compared to state-of-the-arts.
PDF Abstract CVPR 2019 PDF CVPR 2019 Abstract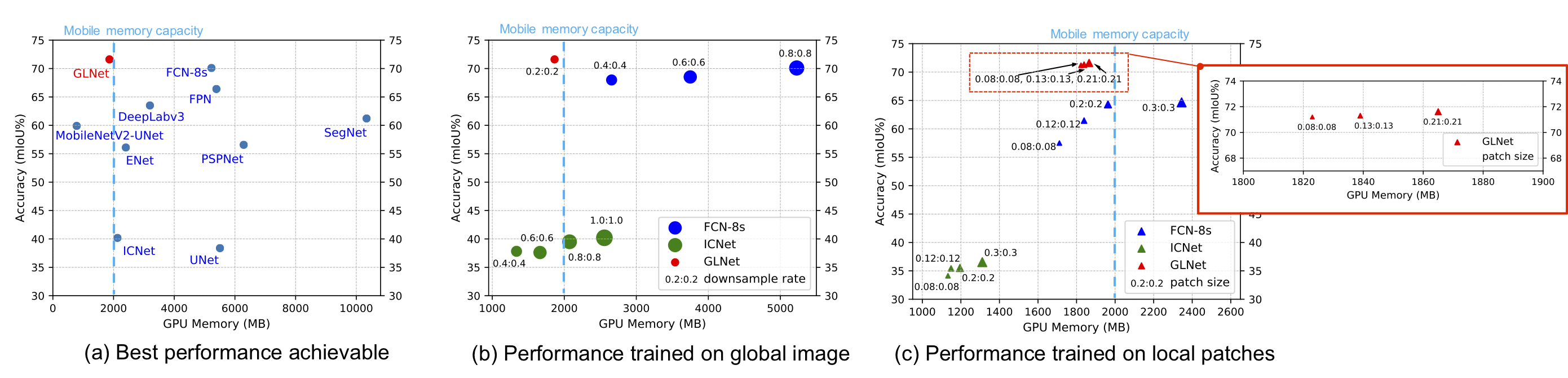




 DeepGlobe
DeepGlobe
