Sparse Overcomplete Word Vector Representations
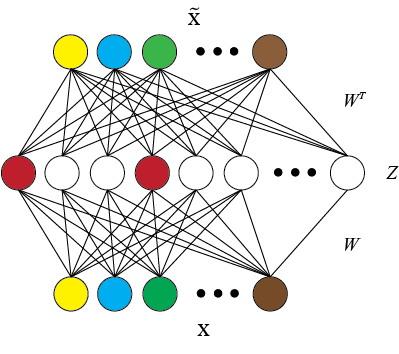
Current distributed representations of words show little resemblance to theories of lexical semantics. The former are dense and uninterpretable, the latter largely based on familiar, discrete classes (e.g., supersenses) and relations (e.g., synonymy and hypernymy). We propose methods that transform word vectors into sparse (and optionally binary) vectors. The resulting representations are more similar to the interpretable features typically used in NLP, though they are discovered automatically from raw corpora. Because the vectors are highly sparse, they are computationally easy to work with. Most importantly, we find that they outperform the original vectors on benchmark tasks.
PDF Abstract IJCNLP 2015 PDF IJCNLP 2015 Abstract