Enhanced LSTM for Natural Language Inference
Reasoning and inference are central to human and artificial intelligence. Modeling inference in human language is very challenging. With the availability of large annotated data (Bowman et al., 2015), it has recently become feasible to train neural network based inference models, which have shown to be very effective. In this paper, we present a new state-of-the-art result, achieving the accuracy of 88.6% on the Stanford Natural Language Inference Dataset. Unlike the previous top models that use very complicated network architectures, we first demonstrate that carefully designing sequential inference models based on chain LSTMs can outperform all previous models. Based on this, we further show that by explicitly considering recursive architectures in both local inference modeling and inference composition, we achieve additional improvement. Particularly, incorporating syntactic parsing information contributes to our best result---it further improves the performance even when added to the already very strong model.
PDF Abstract ACL 2017 PDF ACL 2017 Abstract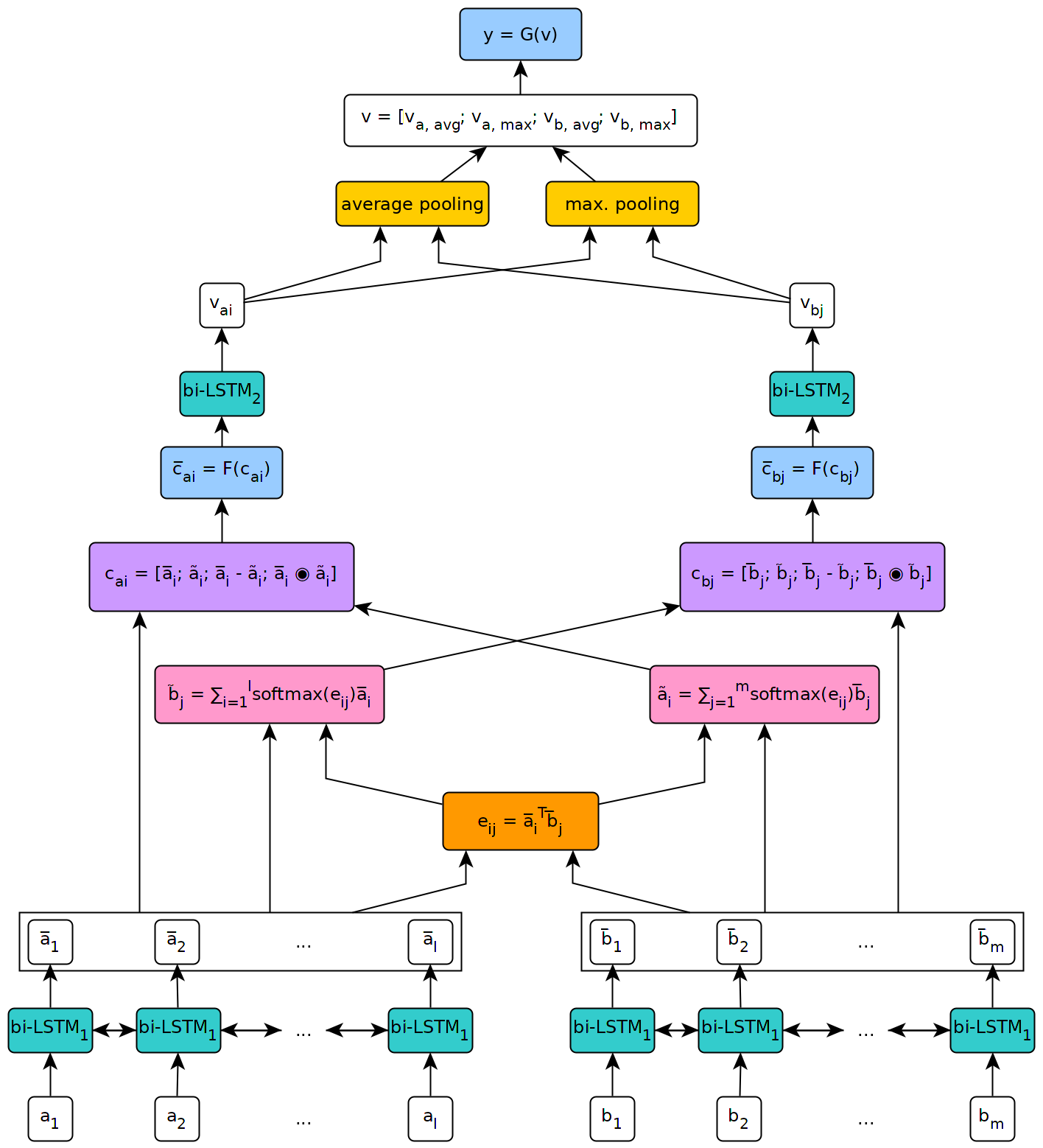



 SNLI
SNLI
