A Deep Reinforcement Learning Approach for Global Routing
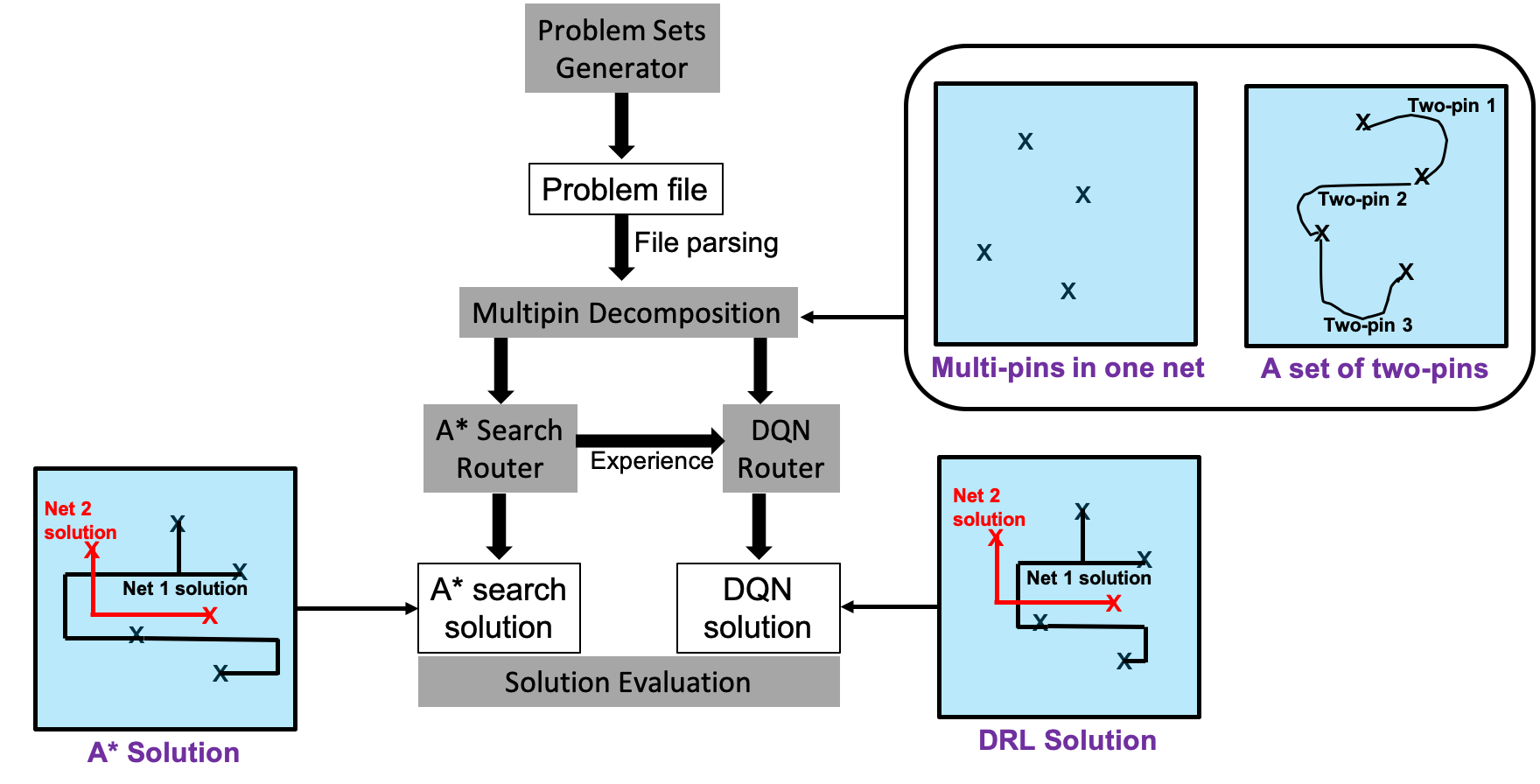
Global routing has been a historically challenging problem in electronic circuit design, where the challenge is to connect a large and arbitrary number of circuit components with wires without violating the design rules for the printed circuit boards or integrated circuits. Similar routing problems also exist in the design of complex hydraulic systems, pipe systems and logistic networks. Existing solutions typically consist of greedy algorithms and hard-coded heuristics. As such, existing approaches suffer from a lack of model flexibility and non-optimum solutions. As an alternative approach, this work presents a deep reinforcement learning method for solving the global routing problem in a simulated environment. At the heart of the proposed method is deep reinforcement learning that enables an agent to produce an optimal policy for routing based on the variety of problems it is presented with leveraging the conjoint optimization mechanism of deep reinforcement learning. Conjoint optimization mechanism is explained and demonstrated in details; the best network structure and the parameters of the learned model are explored. Based on the fine-tuned model, routing solutions and rewards are presented and analyzed. The results indicate that the approach can outperform the benchmark method of a sequential A* method, suggesting a promising potential for deep reinforcement learning for global routing and other routing or path planning problems in general. Another major contribution of this work is the development of a global routing problem sets generator with the ability to generate parameterized global routing problem sets with different size and constraints, enabling evaluation of different routing algorithms and the generation of training datasets for future data-driven routing approaches.
PDF Abstract