A Novel Speech Intelligibility Enhancement Model based on CanonicalCorrelation and Deep Learning
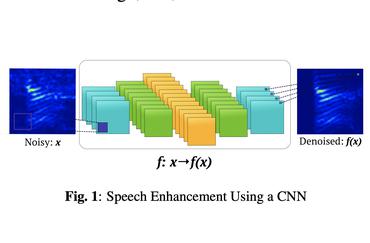
Current deep learning (DL) based approaches to speech intelligibility enhancement in noisy environments are often trained to minimise the feature distance between noise-free speech and enhanced speech signals. Despite improving the speech quality, such approaches do not deliver required levels of speech intelligibility in everyday noisy environments . Intelligibility-oriented (I-O) loss functions have recently been developed to train DL approaches for robust speech enhancement. Here, we formulate, for the first time, a novel canonical correlation based I-O loss function to more effectively train DL algorithms. Specifically, we present a canonical-correlation based short-time objective intelligibility (CC-STOI) cost function to train a fully convolutional neural network (FCN) model. We carry out comparative simulation experiments to show that our CC-STOI based speech enhancement framework outperforms state-of-the-art DL models trained with conventional distance-based and STOI-based loss functions, using objective and subjective evaluation measures for case of both unseen speakers and noises. Ongoing future work is evaluating the proposed approach for design of robust hearing-assistive technology.
PDF Abstract