A Physics-based Noise Formation Model for Extreme Low-light Raw Denoising
Lacking rich and realistic data, learned single image denoising algorithms generalize poorly to real raw images that do not resemble the data used for training. Although the problem can be alleviated by the heteroscedastic Gaussian model for noise synthesis, the noise sources caused by digital camera electronics are still largely overlooked, despite their significant effect on raw measurement, especially under extremely low-light condition. To address this issue, we present a highly accurate noise formation model based on the characteristics of CMOS photosensors, thereby enabling us to synthesize realistic samples that better match the physics of image formation process. Given the proposed noise model, we additionally propose a method to calibrate the noise parameters for available modern digital cameras, which is simple and reproducible for any new device. We systematically study the generalizability of a neural network trained with existing schemes, by introducing a new low-light denoising dataset that covers many modern digital cameras from diverse brands. Extensive empirical results collectively show that by utilizing our proposed noise formation model, a network can reach the capability as if it had been trained with rich real data, which demonstrates the effectiveness of our noise formation model.
PDF Abstract CVPR 2020 PDF CVPR 2020 Abstract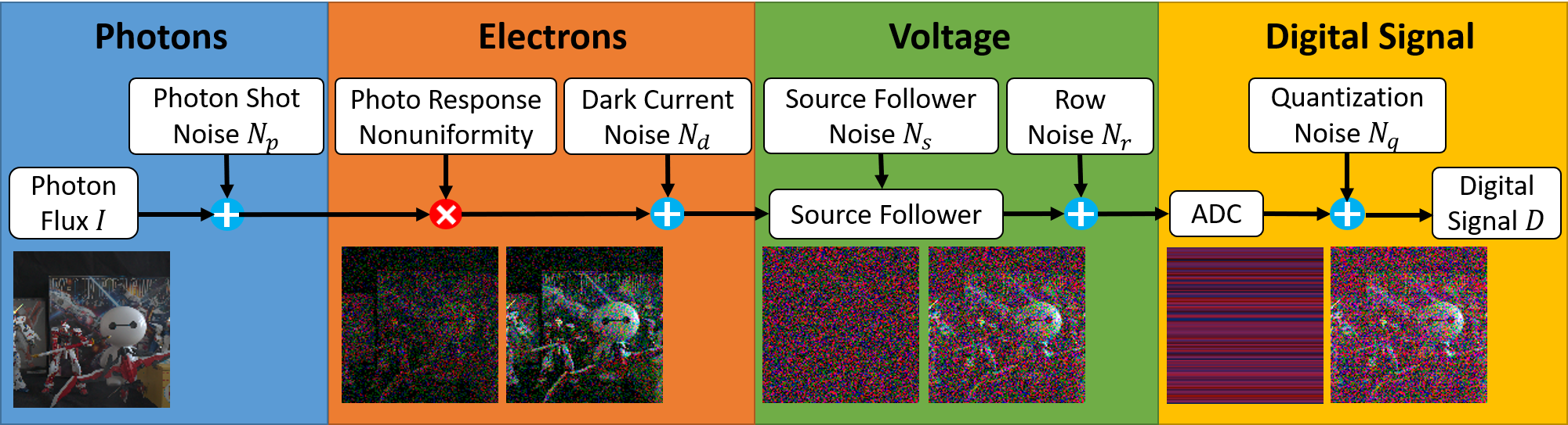





 ELD
ELD
 SID
SID
