Watch out! Motion is Blurring the Vision of Your Deep Neural Networks
The state-of-the-art deep neural networks (DNNs) are vulnerable against adversarial examples with additive random-like noise perturbations. While such examples are hardly found in the physical world, the image blurring effect caused by object motion, on the other hand, commonly occurs in practice, making the study of which greatly important especially for the widely adopted real-time image processing tasks (e.g., object detection, tracking). In this paper, we initiate the first step to comprehensively investigate the potential hazards of the blur effect for DNN, caused by object motion. We propose a novel adversarial attack method that can generate visually natural motion-blurred adversarial examples, named motion-based adversarial blur attack (ABBA). To this end, we first formulate the kernel-prediction-based attack where an input image is convolved with kernels in a pixel-wise way, and the misclassification capability is achieved by tuning the kernel weights. To generate visually more natural and plausible examples, we further propose the saliency-regularized adversarial kernel prediction, where the salient region serves as a moving object, and the predicted kernel is regularized to achieve naturally visual effects. Besides, the attack is further enhanced by adaptively tuning the translations of object and background. A comprehensive evaluation on the NeurIPS'17 adversarial competition dataset demonstrates the effectiveness of ABBA by considering various kernel sizes, translations, and regions. The in-depth study further confirms that our method shows more effective penetrating capability to the state-of-the-art GAN-based deblurring mechanisms compared with other blurring methods. We release the code to https://github.com/tsingqguo/ABBA.
PDF Abstract NeurIPS 2020 PDF NeurIPS 2020 Abstract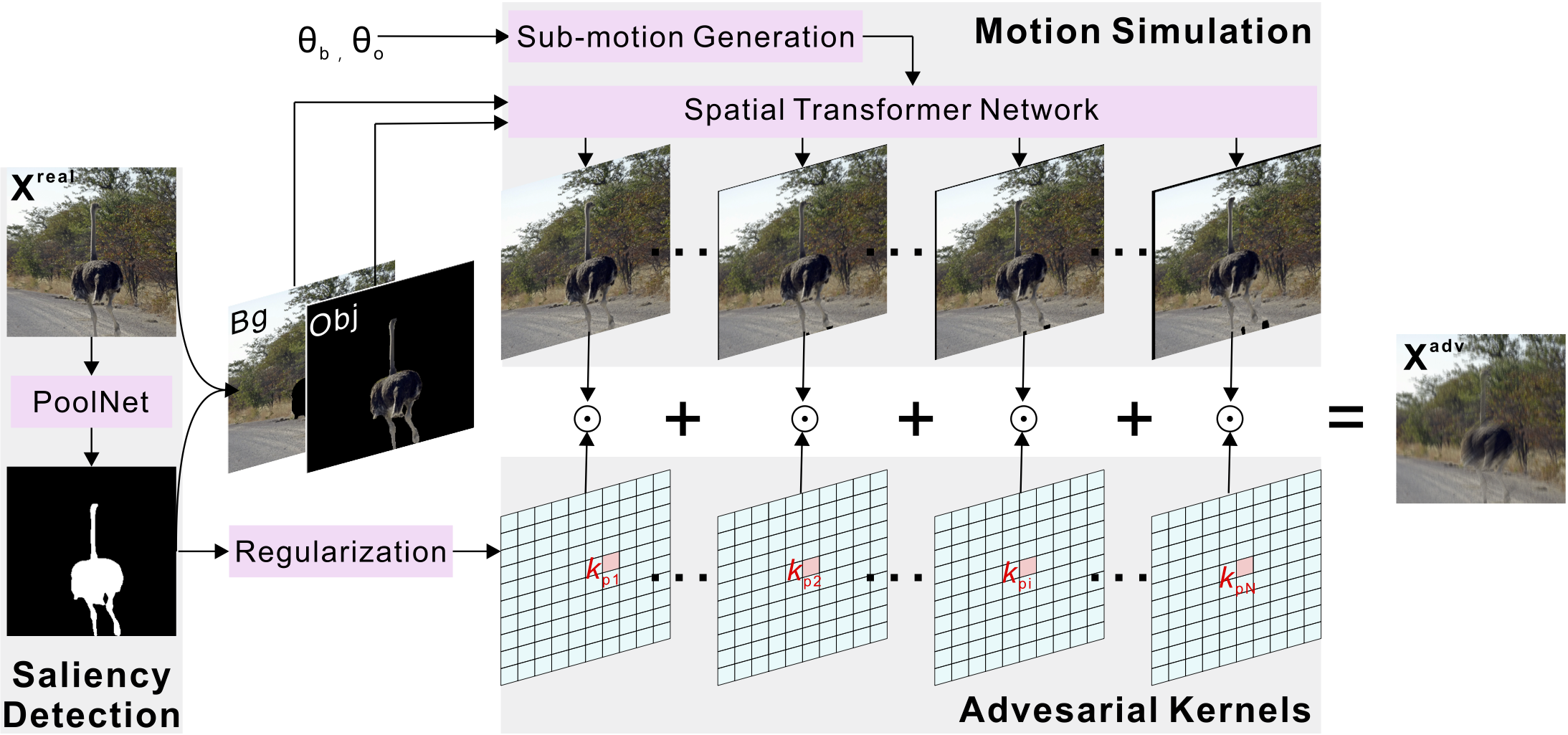




 ImageNet-C
ImageNet-C
 AirSim
AirSim