ADNet: Leveraging Error-Bias Towards Normal Direction in Face Alignment
The recent progress of CNN has dramatically improved face alignment performance. However, few works have paid attention to the error-bias with respect to error distribution of facial landmarks. In this paper, we investigate the error-bias issue in face alignment, where the distributions of landmark errors tend to spread along the tangent line to landmark curves. This error-bias is not trivial since it is closely connected to the ambiguous landmark labeling task. Inspired by this observation, we seek a way to leverage the error-bias property for better convergence of CNN model. To this end, we propose anisotropic direction loss (ADL) and anisotropic attention module (AAM) for coordinate and heatmap regression, respectively. ADL imposes strong binding force in normal direction for each landmark point on facial boundaries. On the other hand, AAM is an attention module which can get anisotropic attention mask focusing on the region of point and its local edge connected by adjacent points, it has a stronger response in tangent than in normal, which means relaxed constraints in the tangent. These two methods work in a complementary manner to learn both facial structures and texture details. Finally, we integrate them into an optimized end-to-end training pipeline named ADNet. Our ADNet achieves state-of-the-art results on 300W, WFLW and COFW datasets, which demonstrates the effectiveness and robustness.
PDF Abstract ICCV 2021 PDF ICCV 2021 Abstract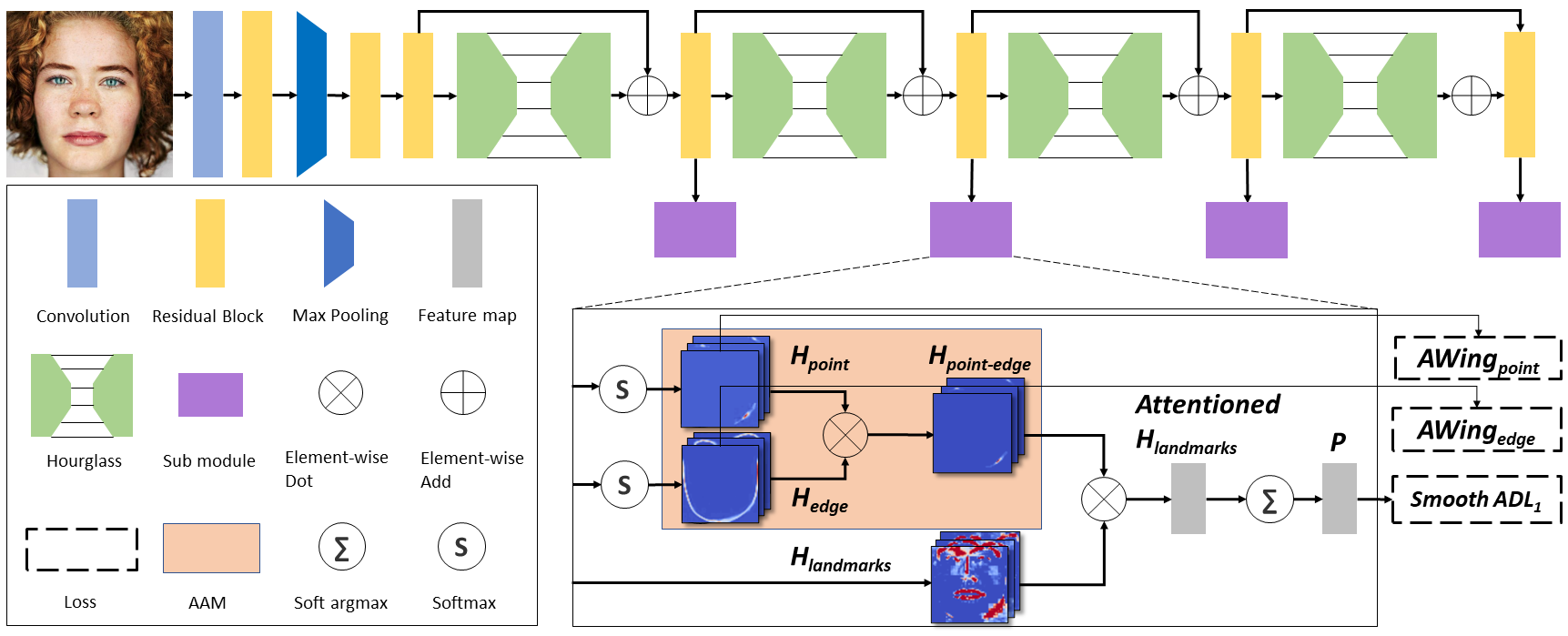




 300W
300W
 COFW
COFW
 WFLW
WFLW
