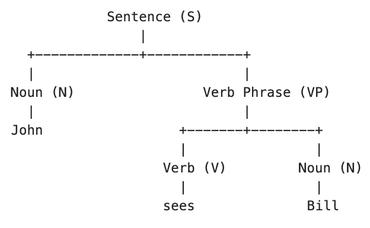
An Empirical Study of Building a Strong Baseline for Constituency Parsing
This paper investigates the construction of a strong baseline based on general purpose sequence-to-sequence models for constituency parsing. We incorporate several techniques that were mainly developed in natural language generation tasks, e.g., machine translation and summarization, and demonstrate that the sequence-to-sequence model achieves the current top-notch parsers{'} performance (almost) without requiring any explicit task-specific knowledge or architecture of constituent parsing.
PDF AbstractDatasets
| Task | Dataset | Model | Metric Name | Metric Value | Global Rank | Benchmark |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Constituency Parsing | Penn Treebank | LSTM Encoder-Decoder + LSTM-LM | F1 score | 94.32 | # 16 |






 Penn Treebank
Penn Treebank
