An information-theoretic, all-scales approach to comparing networks
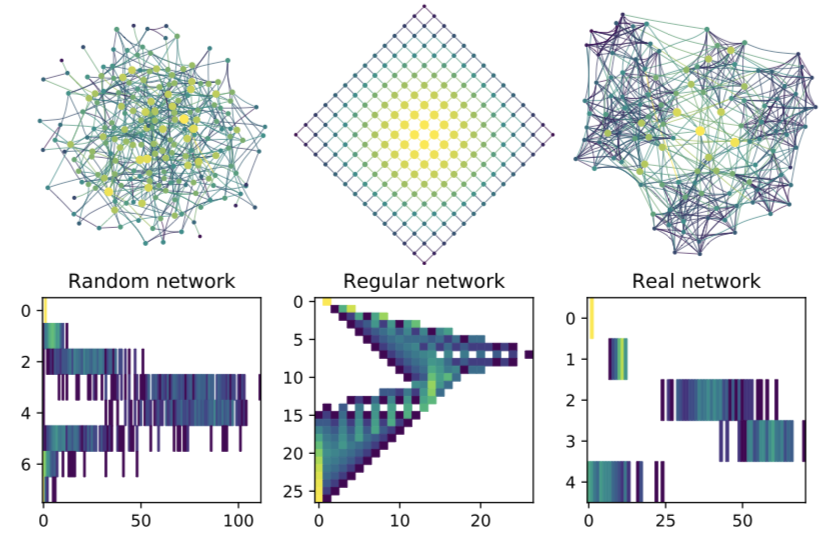
As network research becomes more sophisticated, it is more common than ever for researchers to find themselves not studying a single network but needing to analyze sets of networks. An important task when working with sets of networks is network comparison, developing a similarity or distance measure between networks so that meaningful comparisons can be drawn. The best means to accomplish this task remains an open area of research. Here we introduce a new measure to compare networks, the Portrait Divergence, that is mathematically principled, incorporates the topological characteristics of networks at all structural scales, and is general-purpose and applicable to all types of networks. An important feature of our measure that enables many of its useful properties is that it is based on a graph invariant, the network portrait. We test our measure on both synthetic graphs and real world networks taken from protein interaction data, neuroscience, and computational social science applications. The Portrait Divergence reveals important characteristics of multilayer and temporal networks extracted from data.
PDF Abstract