An Inpainting Approach to Tackle the Kinematic and Thermal SZ Induced Biases in CMB-Cluster Lensing Estimators
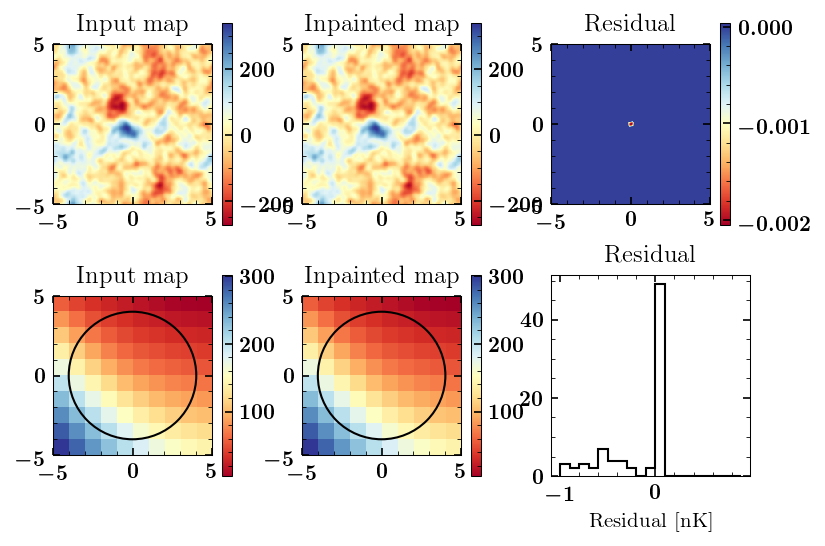
A galaxy cluster's own Sunyaev-Zel{'}dovich (SZ) signal is known to be a major contaminant when reconstructing the cluster's underlying lensing potential using cosmic microwave background (CMB) temperature maps. In this work, we develop a modified quadratic estimator (QE) that is designed to mitigate the lensing biases due to the kinematic and thermal SZ effects. The idea behind the approach is to use inpainting to eliminate the cluster's own emission from the large-scale CMB gradient map. In this inpainted gradient map, we fill the pixel values at the cluster location using a constrained Gaussian realization based on the information from surrounding regions. We show that the noise induced due to inpainting process is small compared to other noise sources for upcoming surveys and has minimal impact on the final lensing signal-to-noise. Without any foreground cleaning, we find a stacked mass uncertainty of 6.5% for the CMB-S4 experiment on a cluster sample containing 5000 clusters with $M_{200c} = 2 \times 10^{14}\ M_{\odot}$ at z = 0.7. In addition to the SZ-induced lensing biases, we also quantify the low mass bias arising due to the contamination of the CMB gradient by the cluster convergence. For the fiducial cluster sample considered in this work, we find that bias is negligible compared to the statistical uncertainties for both the standard and the modified QE even when modes up to $\sim 2700$ are used for the gradient estimation. With more gradient modes, we demonstrate that the sensitivity can be increased by 14% compared to the fiducial result above with gradient modes up to $2000$
PDF Abstract