Assessing the Use of Prosody in Constituency Parsing of Imperfect Transcripts
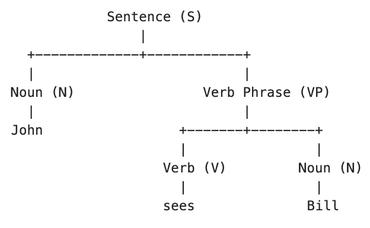
This work explores constituency parsing on automatically recognized transcripts of conversational speech. The neural parser is based on a sentence encoder that leverages word vectors contextualized with prosodic features, jointly learning prosodic feature extraction with parsing. We assess the utility of the prosody in parsing on imperfect transcripts, i.e. transcripts with automatic speech recognition (ASR) errors, by applying the parser in an N-best reranking framework. In experiments on Switchboard, we obtain 13-15% of the oracle N-best gain relative to parsing the 1-best ASR output, with insignificant impact on word recognition error rate. Prosody provides a significant part of the gain, and analyses suggest that it leads to more grammatical utterances via recovering function words.
PDF Abstract