AutoSpeech: Neural Architecture Search for Speaker Recognition
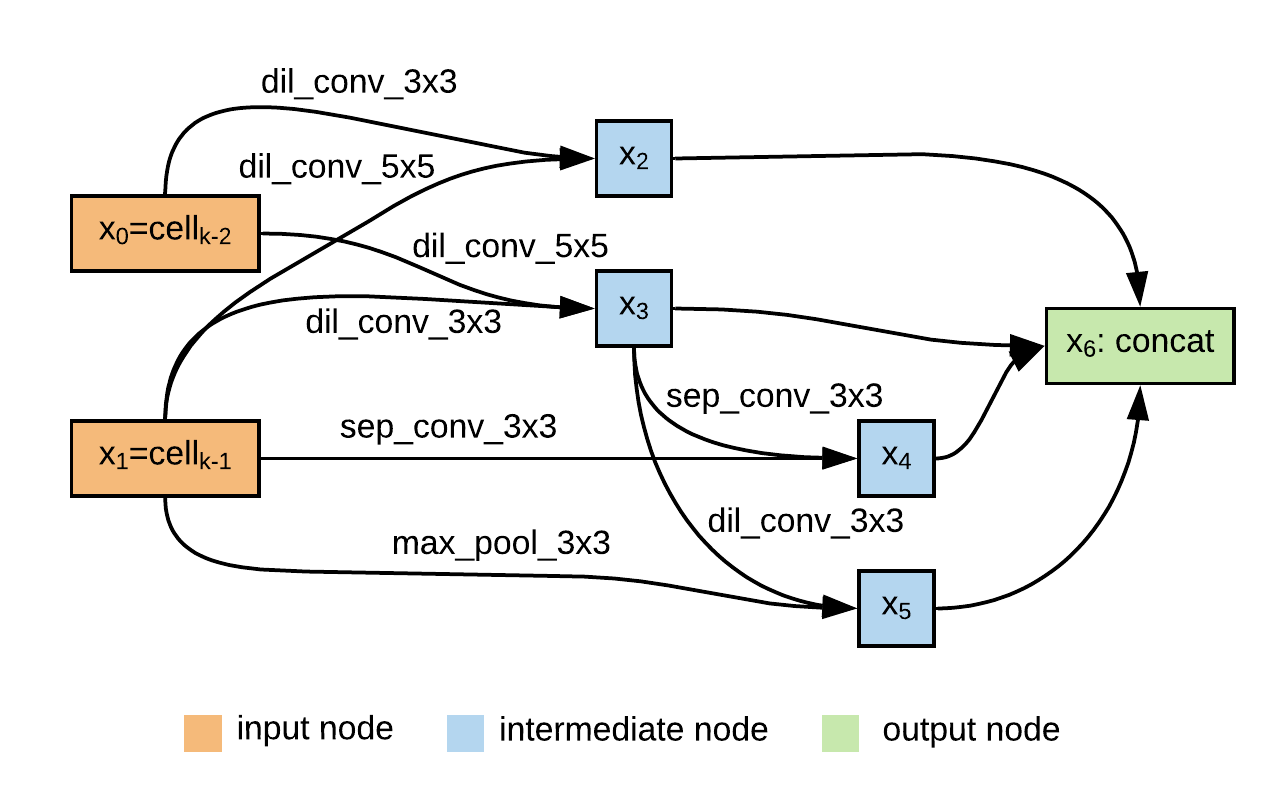
Speaker recognition systems based on Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) are often built with off-the-shelf backbones such as VGG-Net or ResNet. However, these backbones were originally proposed for image classification, and therefore may not be naturally fit for speaker recognition. Due to the prohibitive complexity of manually exploring the design space, we propose the first neural architecture search approach approach for the speaker recognition tasks, named as AutoSpeech. Our algorithm first identifies the optimal operation combination in a neural cell and then derives a CNN model by stacking the neural cell for multiple times. The final speaker recognition model can be obtained by training the derived CNN model through the standard scheme. To evaluate the proposed approach, we conduct experiments on both speaker identification and speaker verification tasks using the VoxCeleb1 dataset. Results demonstrate that the derived CNN architectures from the proposed approach significantly outperform current speaker recognition systems based on VGG-M, ResNet-18, and ResNet-34 back-bones, while enjoying lower model complexity.
PDF AbstractCode
Datasets
Results from the Paper
 Ranked #6 on
Speaker Identification
on VoxCeleb1
(using extra training data)
Ranked #6 on
Speaker Identification
on VoxCeleb1
(using extra training data)





 VoxCeleb1
VoxCeleb1