BALANCE: Bayesian Linear Attribution for Root Cause Localization
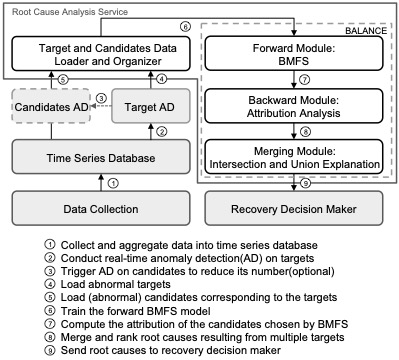
Root Cause Analysis (RCA) plays an indispensable role in distributed data system maintenance and operations, as it bridges the gap between fault detection and system recovery. Existing works mainly study multidimensional localization or graph-based root cause localization. This paper opens up the possibilities of exploiting the recently developed framework of explainable AI (XAI) for the purpose of RCA. In particular, we propose BALANCE (BAyesian Linear AttributioN for root CausE localization), which formulates the problem of RCA through the lens of attribution in XAI and seeks to explain the anomalies in the target KPIs by the behavior of the candidate root causes. BALANCE consists of three innovative components. First, we propose a Bayesian multicollinear feature selection (BMFS) model to predict the target KPIs given the candidate root causes in a forward manner while promoting sparsity and concurrently paying attention to the correlation between the candidate root causes. Second, we introduce attribution analysis to compute the attribution score for each candidate in a backward manner. Third, we merge the estimated root causes related to each KPI if there are multiple KPIs. We extensively evaluate the proposed BALANCE method on one synthesis dataset as well as three real-world RCA tasks, that is, bad SQL localization, container fault localization, and fault type diagnosis for Exathlon. Results show that BALANCE outperforms the state-of-the-art (SOTA) methods in terms of accuracy with the least amount of running time, and achieves at least $6\%$ notably higher accuracy than SOTA methods for real tasks. BALANCE has been deployed to production to tackle real-world RCA problems, and the online results further advocate its usage for real-time diagnosis in distributed data systems.
PDF Abstract