BERT and PALs: Projected Attention Layers for Efficient Adaptation in Multi-Task Learning
Multi-task learning shares information between related tasks, sometimes reducing the number of parameters required. State-of-the-art results across multiple natural language understanding tasks in the GLUE benchmark have previously used transfer from a single large task: unsupervised pre-training with BERT, where a separate BERT model was fine-tuned for each task. We explore multi-task approaches that share a single BERT model with a small number of additional task-specific parameters. Using new adaptation modules, PALs or `projected attention layers', we match the performance of separately fine-tuned models on the GLUE benchmark with roughly 7 times fewer parameters, and obtain state-of-the-art results on the Recognizing Textual Entailment dataset.
PDF Abstract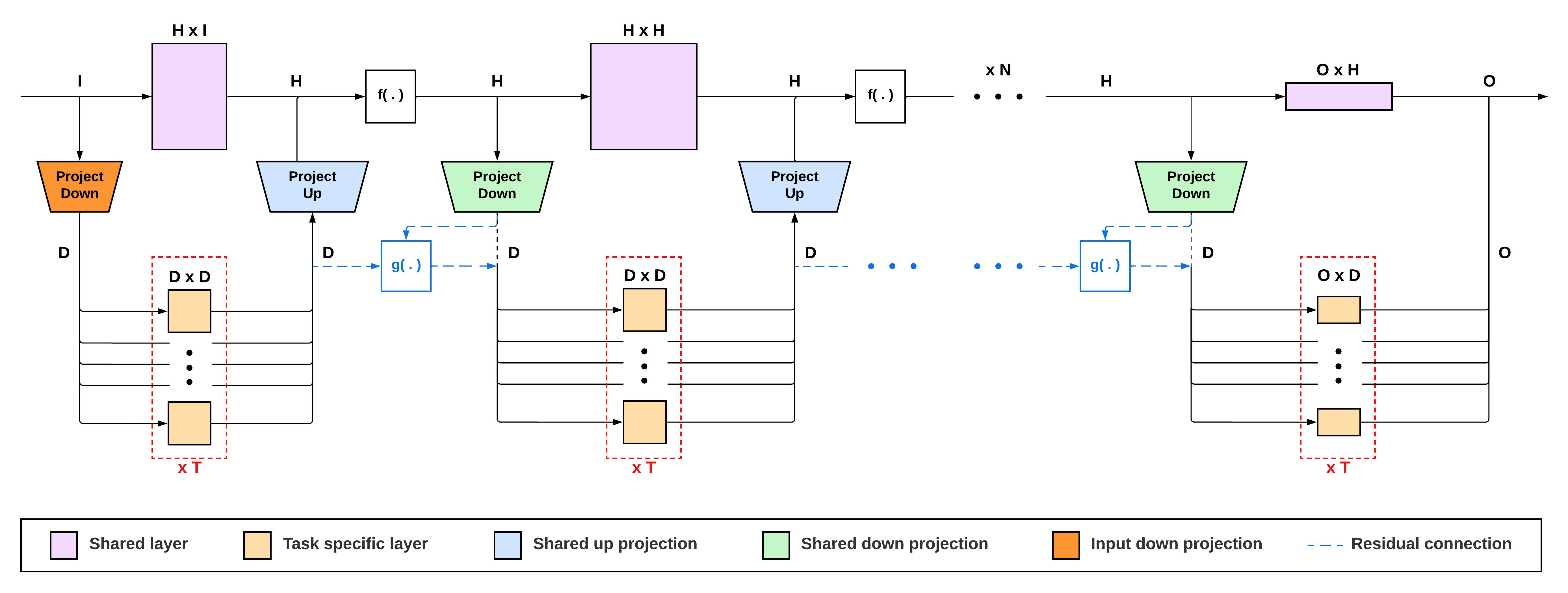




 GLUE
GLUE
 SST
SST
 QNLI
QNLI
 MRPC
MRPC
 CoLA
CoLA