Breaking the Representation Bottleneck of Chinese Characters: Neural Machine Translation with Stroke Sequence Modeling
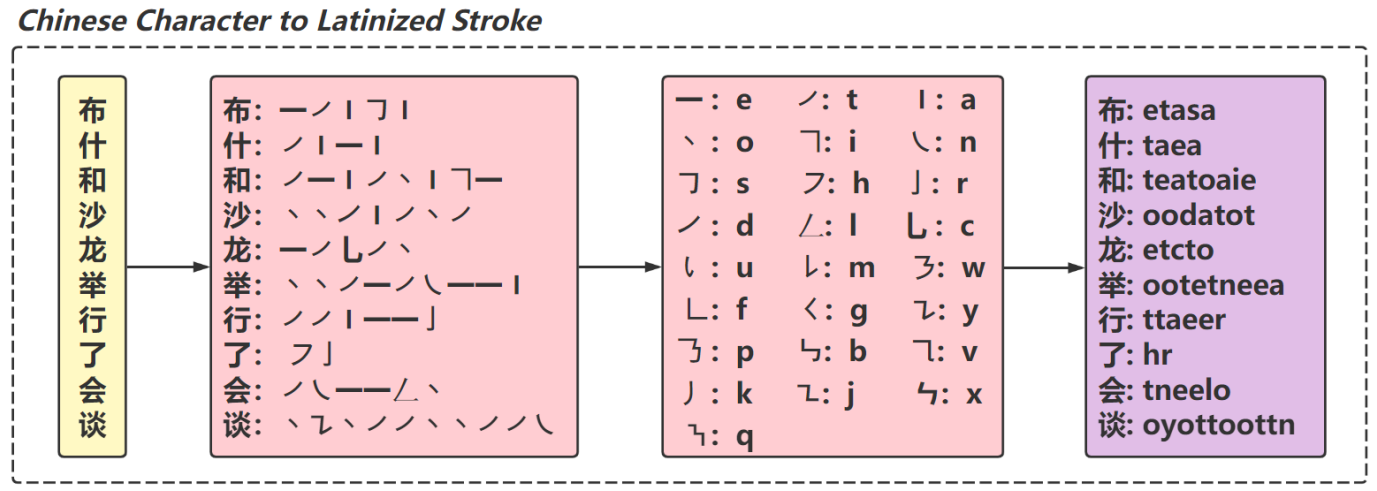
Existing research generally treats Chinese character as a minimum unit for representation. However, such Chinese character representation will suffer two bottlenecks: 1) Learning bottleneck, the learning cannot benefit from its rich internal features (e.g., radicals and strokes); and 2) Parameter bottleneck, each individual character has to be represented by a unique vector. In this paper, we introduce a novel representation method for Chinese characters to break the bottlenecks, namely StrokeNet, which represents a Chinese character by a Latinized stroke sequence (e.g., "ao1 (concave)" to "ajaie" and "tu1 (convex)" to "aeaqe"). Specifically, StrokeNet maps each stroke to a specific Latin character, thus allowing similar Chinese characters to have similar Latin representations. With the introduction of StrokeNet to neural machine translation (NMT), many powerful but not applicable techniques to non-Latin languages (e.g., shared subword vocabulary learning and ciphertext-based data augmentation) can now be perfectly implemented. Experiments on the widely-used NIST Chinese-English, WMT17 Chinese-English and IWSLT17 Japanese-English NMT tasks show that StrokeNet can provide a significant performance boost over the strong baselines with fewer model parameters, achieving 26.5 BLEU on the WMT17 Chinese-English task which is better than any previously reported results without using monolingual data. Code and scripts are freely available at https://github.com/zjwang21/StrokeNet.
PDF Abstract