CIRS: Bursting Filter Bubbles by Counterfactual Interactive Recommender System
While personalization increases the utility of recommender systems, it also brings the issue of filter bubbles. E.g., if the system keeps exposing and recommending the items that the user is interested in, it may also make the user feel bored and less satisfied. Existing work studies filter bubbles in static recommendation, where the effect of overexposure is hard to capture. In contrast, we believe it is more meaningful to study the issue in interactive recommendation and optimize long-term user satisfaction. Nevertheless, it is unrealistic to train the model online due to the high cost. As such, we have to leverage offline training data and disentangle the causal effect on user satisfaction. To achieve this goal, we propose a counterfactual interactive recommender system (CIRS) that augments offline reinforcement learning (offline RL) with causal inference. The basic idea is to first learn a causal user model on historical data to capture the overexposure effect of items on user satisfaction. It then uses the learned causal user model to help the planning of the RL policy. To conduct evaluation offline, we innovatively create an authentic RL environment (KuaiEnv) based on a real-world fully observed user rating dataset. The experiments show the effectiveness of CIRS in bursting filter bubbles and achieving long-term success in interactive recommendation. The implementation of CIRS is available via https://github.com/chongminggao/CIRS-codes.
PDF Abstract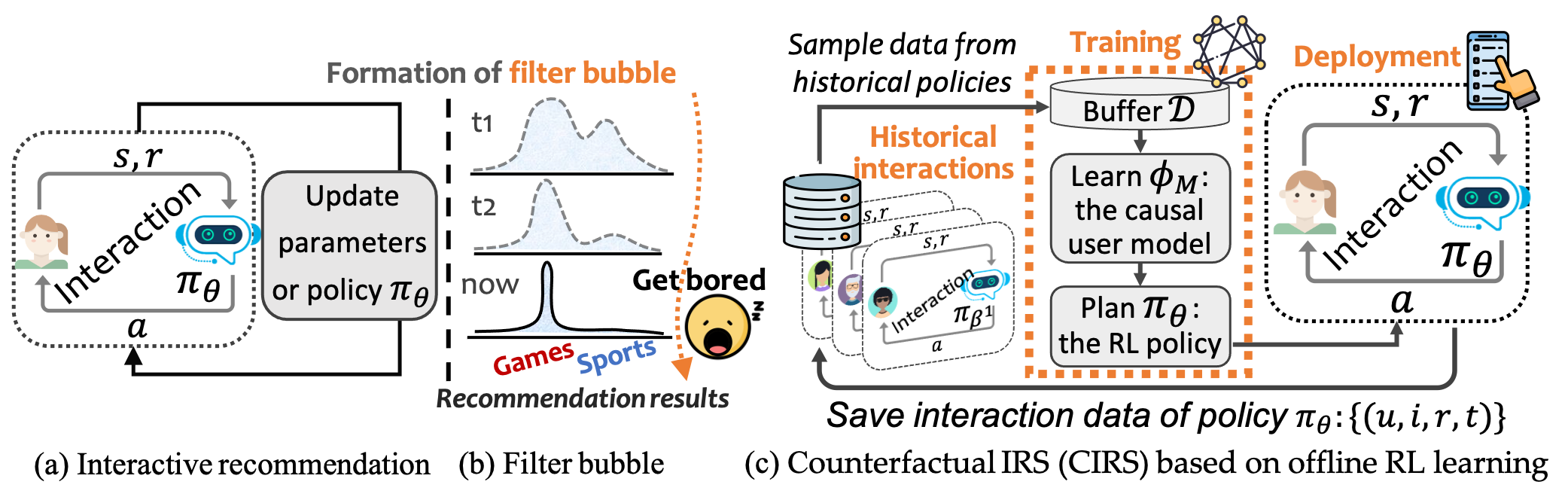




 KuaiRec
KuaiRec