Coarse-to-Fine Q-attention with Learned Path Ranking
We propose Learned Path Ranking (LPR), a method that accepts an end-effector goal pose, and learns to rank a set of goal-reaching paths generated from an array of path generating methods, including: path planning, Bezier curve sampling, and a learned policy. The core idea being that each of the path generation modules will be useful in different tasks, or at different stages in a task. When LPR is added as an extension to C2F-ARM, our new system, C2F-ARM+LPR, retains the sample efficiency of its predecessor, while also being able to accomplish a larger set of tasks; in particular, tasks that require very specific motions (e.g. opening toilet seat) that need to be inferred from both demonstrations and exploration data. In addition to benchmarking our approach across 16 RLBench tasks, we also learn real-world tasks, tabula rasa, in 10-15 minutes, with only 3 demonstrations.
PDF Abstract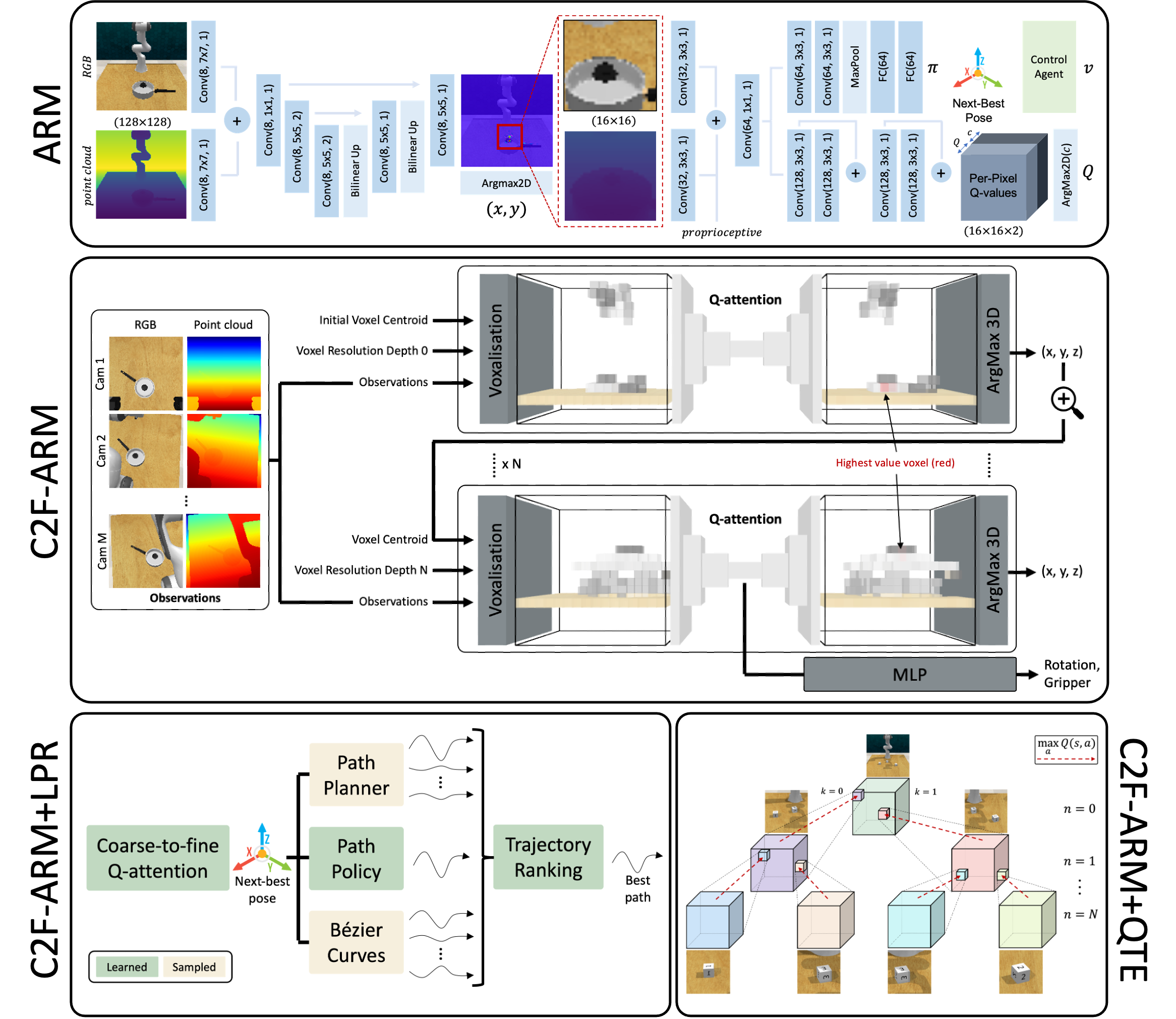


 RLBench
RLBench