CODA-19: Using a Non-Expert Crowd to Annotate Research Aspects on 10,000+ Abstracts in the COVID-19 Open Research Dataset
This paper introduces CODA-19, a human-annotated dataset that codes the Background, Purpose, Method, Finding/Contribution, and Other sections of 10,966 English abstracts in the COVID-19 Open Research Dataset. CODA-19 was created by 248 crowd workers from Amazon Mechanical Turk within 10 days, and achieved labeling quality comparable to that of experts. Each abstract was annotated by nine different workers, and the final labels were acquired by majority vote. The inter-annotator agreement (Cohen's kappa) between the crowd and the biomedical expert (0.741) is comparable to inter-expert agreement (0.788). CODA-19's labels have an accuracy of 82.2% when compared to the biomedical expert's labels, while the accuracy between experts was 85.0%. Reliable human annotations help scientists access and integrate the rapidly accelerating coronavirus literature, and also serve as the battery of AI/NLP research, but obtaining expert annotations can be slow. We demonstrated that a non-expert crowd can be rapidly employed at scale to join the fight against COVID-19.
PDF Abstract ACL 2020 PDF ACL 2020 Abstract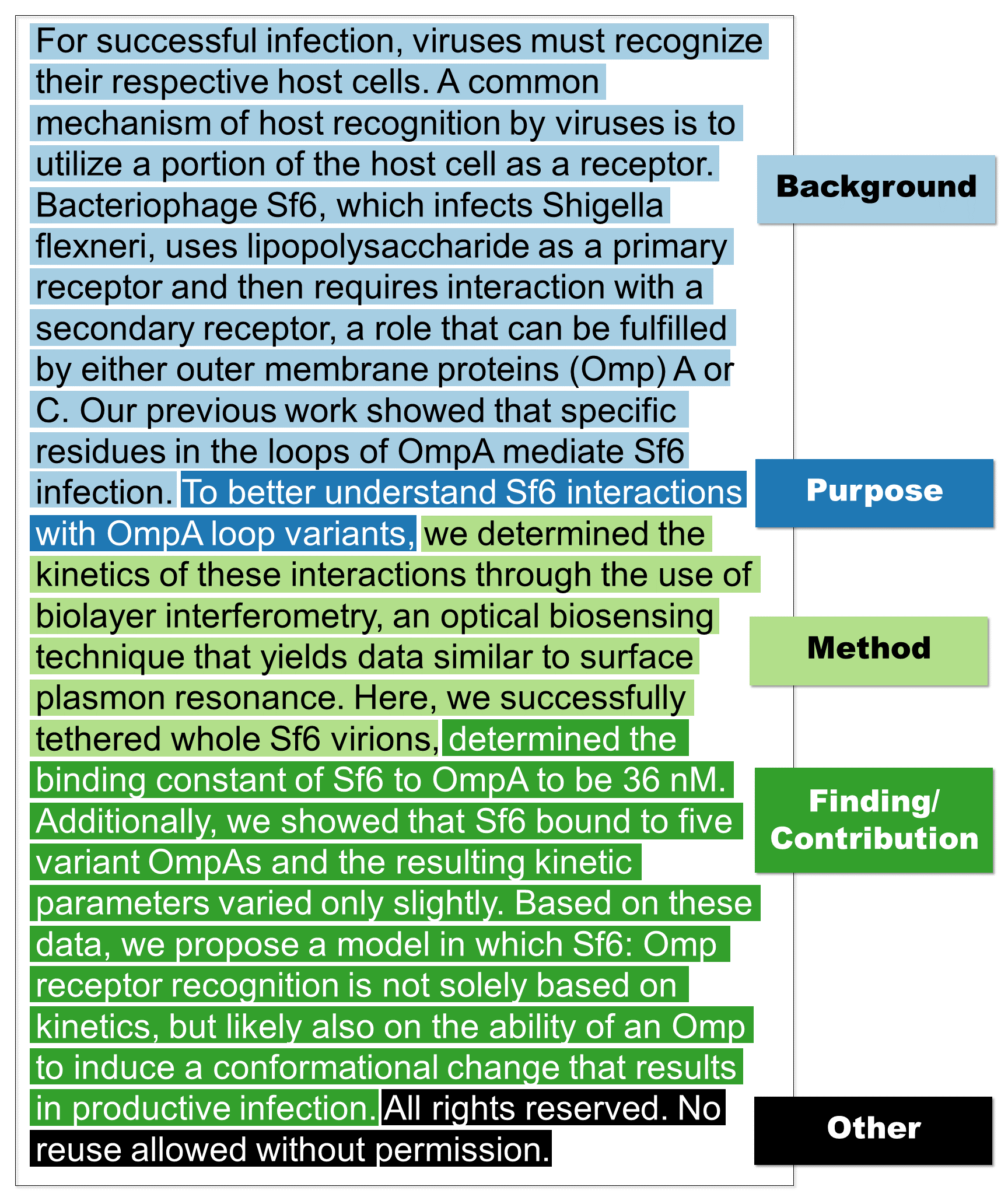

 CODA-19
CODA-19
 CORD-19
CORD-19