CompositeTasking: Understanding Images by Spatial Composition of Tasks
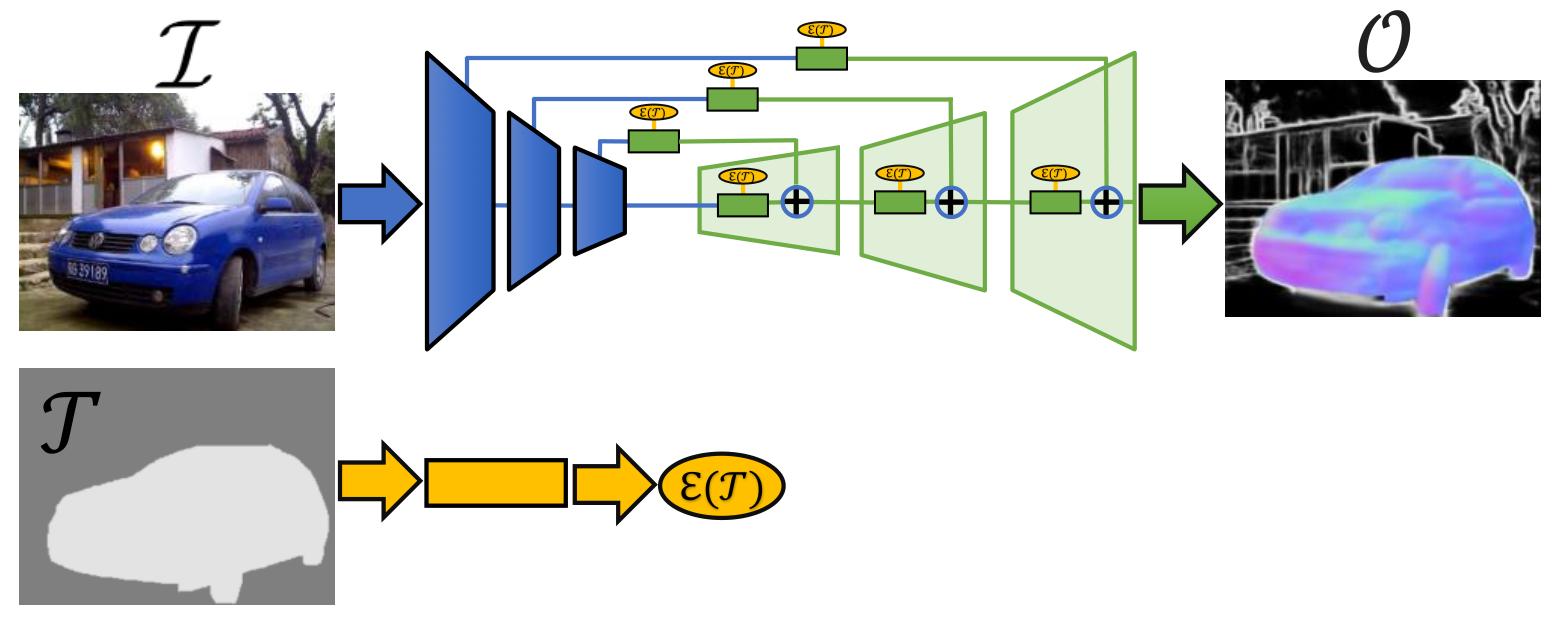
We define the concept of CompositeTasking as the fusion of multiple, spatially distributed tasks, for various aspects of image understanding. Learning to perform spatially distributed tasks is motivated by the frequent availability of only sparse labels across tasks, and the desire for a compact multi-tasking network. To facilitate CompositeTasking, we introduce a novel task conditioning model -- a single encoder-decoder network that performs multiple, spatially varying tasks at once. The proposed network takes an image and a set of pixel-wise dense task requests as inputs, and performs the requested prediction task for each pixel. Moreover, we also learn the composition of tasks that needs to be performed according to some CompositeTasking rules, which includes the decision of where to apply which task. It not only offers us a compact network for multi-tasking, but also allows for task-editing. Another strength of the proposed method is demonstrated by only having to supply sparse supervision per task. The obtained results are on par with our baselines that use dense supervision and a multi-headed multi-tasking design. The source code will be made publicly available at www.github.com/nikola3794/composite-tasking.
PDF Abstract CVPR 2021 PDF CVPR 2021 Abstract