Comprehensive Comparison of Deep Learning Models for Lung and COVID-19 Lesion Segmentation in CT scans
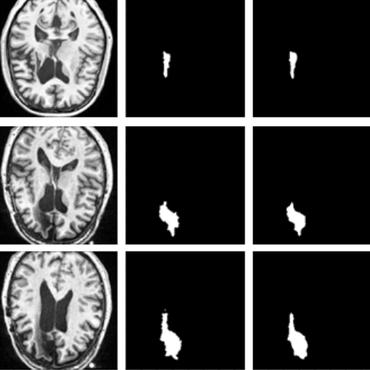
Recently there has been an explosion in the use of Deep Learning (DL) methods for medical image segmentation. However the field's reliability is hindered by the lack of a common base of reference for accuracy/performance evaluation and the fact that previous research uses different datasets for evaluation. In this paper, an extensive comparison of DL models for lung and COVID-19 lesion segmentation in Computerized Tomography (CT) scans is presented, which can also be used as a benchmark for testing medical image segmentation models. Four DL architectures (Unet, Linknet, FPN, PSPNet) are combined with 25 randomly initialized and pretrained encoders (variations of VGG, DenseNet, ResNet, ResNext, DPN, MobileNet, Xception, Inception-v4, EfficientNet), to construct 200 tested models. Three experimental setups are conducted for lung segmentation, lesion segmentation and lesion segmentation using the original lung masks. A public COVID-19 dataset with 100 CT scan images (80 for train, 20 for validation) is used for training/validation and a different public dataset consisting of 829 images from 9 CT scan volumes for testing. Multiple findings are provided including the best architecture-encoder models for each experiment as well as mean Dice results for each experiment, architecture and encoder independently. Finally, the upper bounds improvements when using lung masks as a preprocessing step or when using pretrained models are quantified. The source code and 600 pretrained models for the three experiments are provided, suitable for fine-tuning in experimental setups without GPU capabilities.
PDF Abstract