Confidence Propagation through CNNs for Guided Sparse Depth Regression
Generally, convolutional neural networks (CNNs) process data on a regular grid, e.g. data generated by ordinary cameras. Designing CNNs for sparse and irregularly spaced input data is still an open research problem with numerous applications in autonomous driving, robotics, and surveillance. In this paper, we propose an algebraically-constrained normalized convolution layer for CNNs with highly sparse input that has a smaller number of network parameters compared to related work. We propose novel strategies for determining the confidence from the convolution operation and propagating it to consecutive layers. We also propose an objective function that simultaneously minimizes the data error while maximizing the output confidence. To integrate structural information, we also investigate fusion strategies to combine depth and RGB information in our normalized convolution network framework. In addition, we introduce the use of output confidence as an auxiliary information to improve the results. The capabilities of our normalized convolution network framework are demonstrated for the problem of scene depth completion. Comprehensive experiments are performed on the KITTI-Depth and the NYU-Depth-v2 datasets. The results clearly demonstrate that the proposed approach achieves superior performance while requiring only about 1-5% of the number of parameters compared to the state-of-the-art methods.
PDF Abstract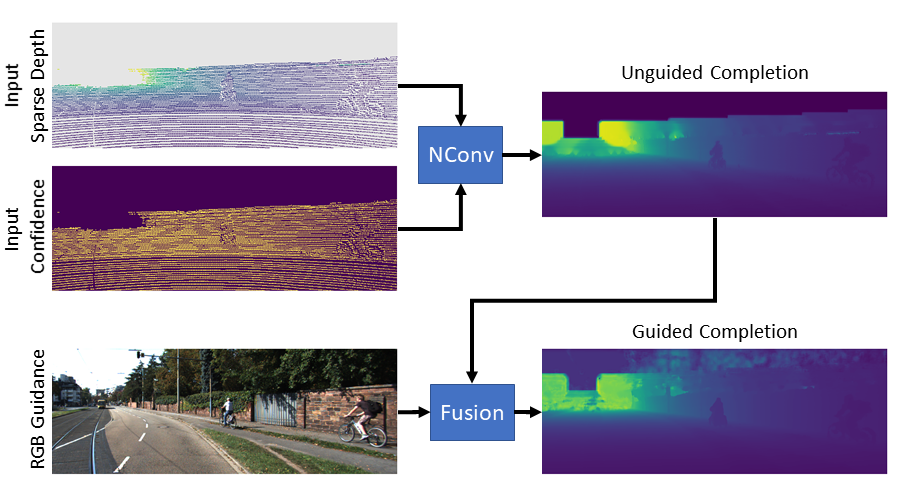





 KITTI-Depth
KITTI-Depth
