Context Modeling in 3D Human Pose Estimation: A Unified Perspective
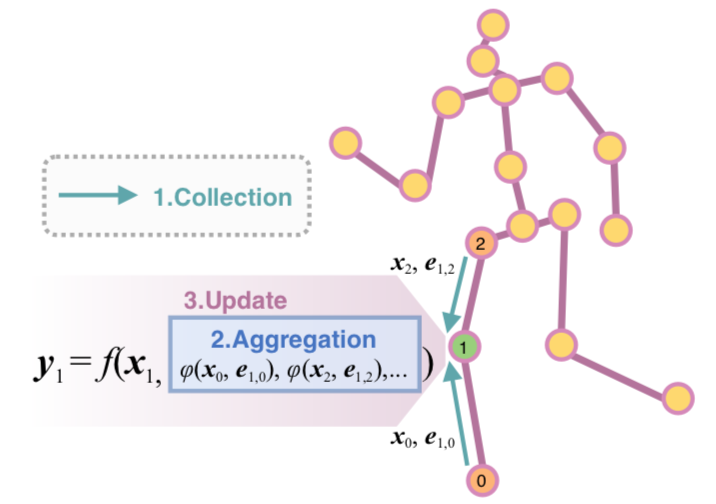
Estimating 3D human pose from a single image suffers from severe ambiguity since multiple 3D joint configurations may have the same 2D projection. The state-of-the-art methods often rely on context modeling methods such as pictorial structure model (PSM) or graph neural network (GNN) to reduce ambiguity. However, there is no study that rigorously compares them side by side. So we first present a general formula for context modeling in which both PSM and GNN are its special cases. By comparing the two methods, we found that the end-to-end training scheme in GNN and the limb length constraints in PSM are two complementary factors to improve results. To combine their advantages, we propose ContextPose based on attention mechanism that allows enforcing soft limb length constraints in a deep network. The approach effectively reduces the chance of getting absurd 3D pose estimates with incorrect limb lengths and achieves state-of-the-art results on two benchmark datasets. More importantly, the introduction of limb length constraints into deep networks enables the approach to achieve much better generalization performance.
PDF Abstract CVPR 2021 PDF CVPR 2021 AbstractDatasets
Results from the Paper
 Ranked #60 on
3D Human Pose Estimation
on MPI-INF-3DHP
(AUC metric)
Ranked #60 on
3D Human Pose Estimation
on MPI-INF-3DHP
(AUC metric)





 Human3.6M
Human3.6M
 MPII
MPII
 MPI-INF-3DHP
MPI-INF-3DHP