Contextual Squeeze-and-Excitation for Efficient Few-Shot Image Classification
Recent years have seen a growth in user-centric applications that require effective knowledge transfer across tasks in the low-data regime. An example is personalization, where a pretrained system is adapted by learning on small amounts of labeled data belonging to a specific user. This setting requires high accuracy under low computational complexity, therefore the Pareto frontier of accuracy vs. adaptation cost plays a crucial role. In this paper we push this Pareto frontier in the few-shot image classification setting with a key contribution: a new adaptive block called Contextual Squeeze-and-Excitation (CaSE) that adjusts a pretrained neural network on a new task to significantly improve performance with a single forward pass of the user data (context). We use meta-trained CaSE blocks to conditionally adapt the body of a network and a fine-tuning routine to adapt a linear head, defining a method called UpperCaSE. UpperCaSE achieves a new state-of-the-art accuracy relative to meta-learners on the 26 datasets of VTAB+MD and on a challenging real-world personalization benchmark (ORBIT), narrowing the gap with leading fine-tuning methods with the benefit of orders of magnitude lower adaptation cost.
PDF Abstract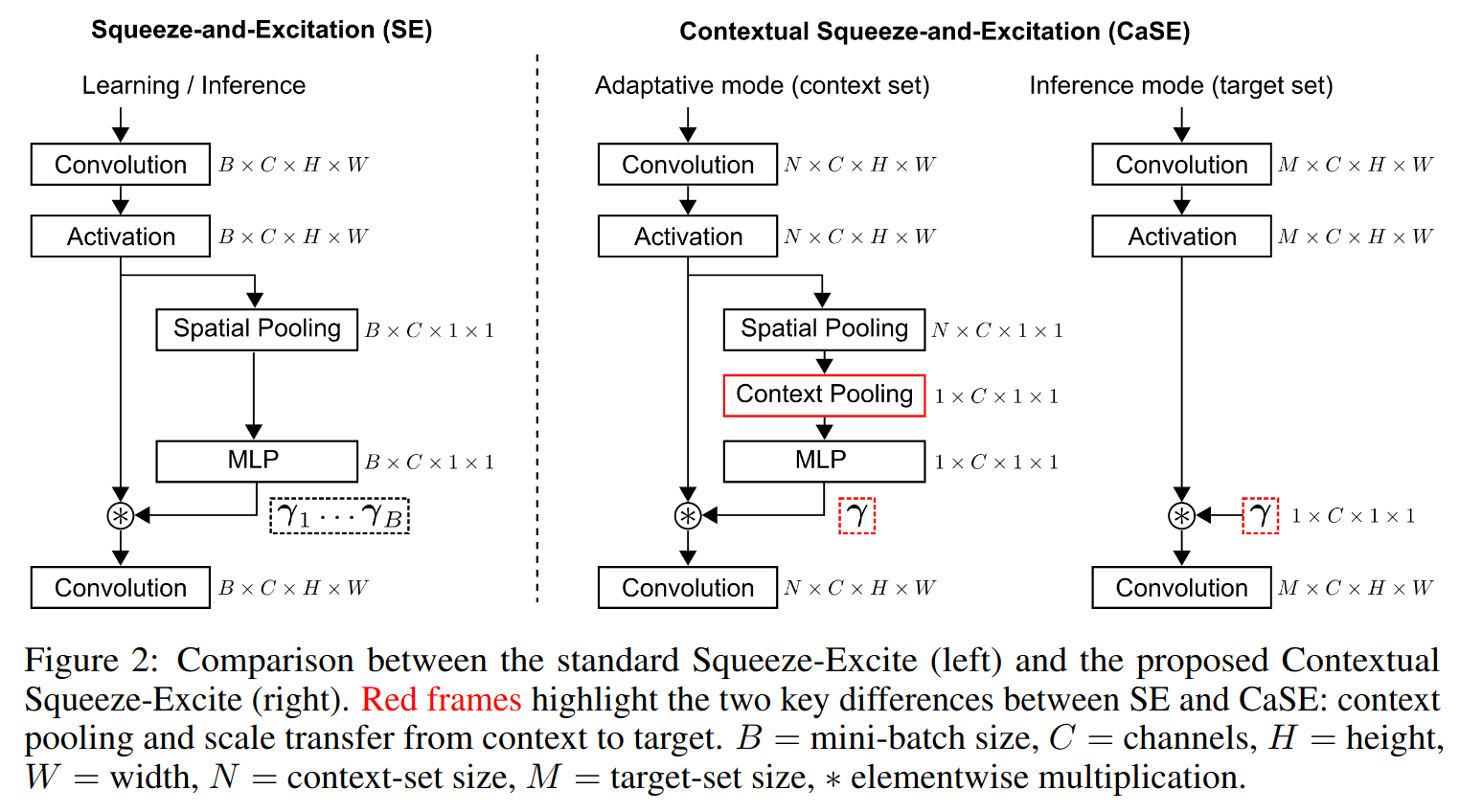







 Meta-Dataset
Meta-Dataset
 ORBIT
ORBIT
