Counterpart Fairness -- Addressing Systematic between-group Differences in Fairness Evaluation
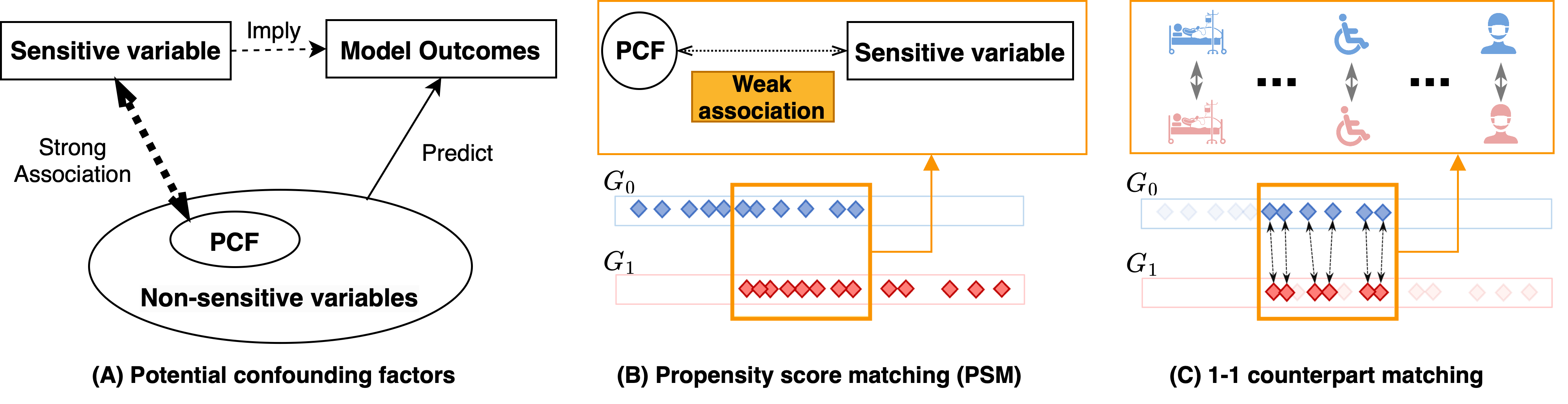
When using machine learning (ML) to aid decision-making, it is critical to ensure that an algorithmic decision is fair, i.e., it does not discriminate against specific individuals/groups, particularly those from underprivileged populations. Existing group fairness methods require equal group-wise measures, which however fails to consider systematic between-group differences. The confounding factors, which are non-sensitive variables but manifest systematic differences, can significantly affect fairness evaluation. To tackle this problem, we believe that a fairness measurement should be based on the comparison between counterparts (i.e., individuals who are similar to each other with respect to the task of interest) from different groups, whose group identities cannot be distinguished algorithmically by exploring confounding factors. We have developed a propensity-score-based method for identifying counterparts, which prevents fairness evaluation from comparing "oranges" with "apples". In addition, we propose a counterpart-based statistical fairness index, termed Counterpart-Fairness (CFair), to assess fairness of ML models. Various empirical studies were conducted to validate the effectiveness of CFair. We publish our code at \url{https://github.com/zhengyjo/CFair}.
PDF Abstract