Cross-Field Transformer for Diabetic Retinopathy Grading on Two-field Fundus Images
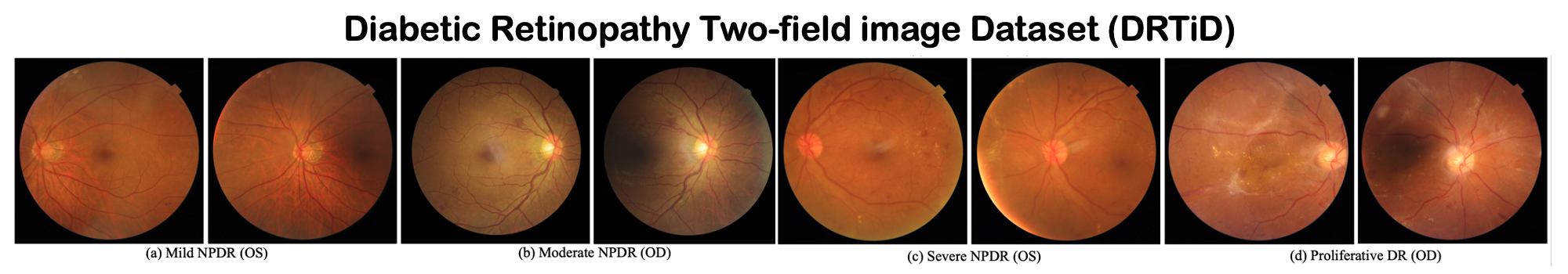
Automatic diabetic retinopathy (DR) grading based on fundus photography has been widely explored to benefit the routine screening and early treatment. Existing researches generally focus on single-field fundus images, which have limited field of view for precise eye examinations. In clinical applications, ophthalmologists adopt two-field fundus photography as the dominating tool, where the information from each field (i.e.,macula-centric and optic disc-centric) is highly correlated and complementary, and benefits comprehensive decisions. However, automatic DR grading based on two-field fundus photography remains a challenging task due to the lack of publicly available datasets and effective fusion strategies. In this work, we first construct a new benchmark dataset (DRTiD) for DR grading, consisting of 3,100 two-field fundus images. To the best of our knowledge, it is the largest public DR dataset with diverse and high-quality two-field images. Then, we propose a novel DR grading approach, namely Cross-Field Transformer (CrossFiT), to capture the correspondence between two fields as well as the long-range spatial correlations within each field. Considering the inherent two-field geometric constraints, we particularly define aligned position embeddings to preserve relative consistent position in fundus. Besides, we perform masked cross-field attention during interaction to flter the noisy relations between fields. Extensive experiments on our DRTiD dataset and a public DeepDRiD dataset demonstrate the effectiveness of our CrossFiT network. The new dataset and the source code of CrossFiT will be publicly available at https://github.com/FDU-VTS/DRTiD.
PDF AbstractCode
Datasets
Introduced in the Paper:
 DRTiD
DRTiD