DADA: Depth-aware Domain Adaptation in Semantic Segmentation
Unsupervised domain adaptation (UDA) is important for applications where large scale annotation of representative data is challenging. For semantic segmentation in particular, it helps deploy on real "target domain" data models that are trained on annotated images from a different "source domain", notably a virtual environment. To this end, most previous works consider semantic segmentation as the only mode of supervision for source domain data, while ignoring other, possibly available, information like depth. In this work, we aim at exploiting at best such a privileged information while training the UDA model. We propose a unified depth-aware UDA framework that leverages in several complementary ways the knowledge of dense depth in the source domain. As a result, the performance of the trained semantic segmentation model on the target domain is boosted. Our novel approach indeed achieves state-of-the-art performance on different challenging synthetic-2-real benchmarks.
PDF Abstract ICCV 2019 PDF ICCV 2019 Abstract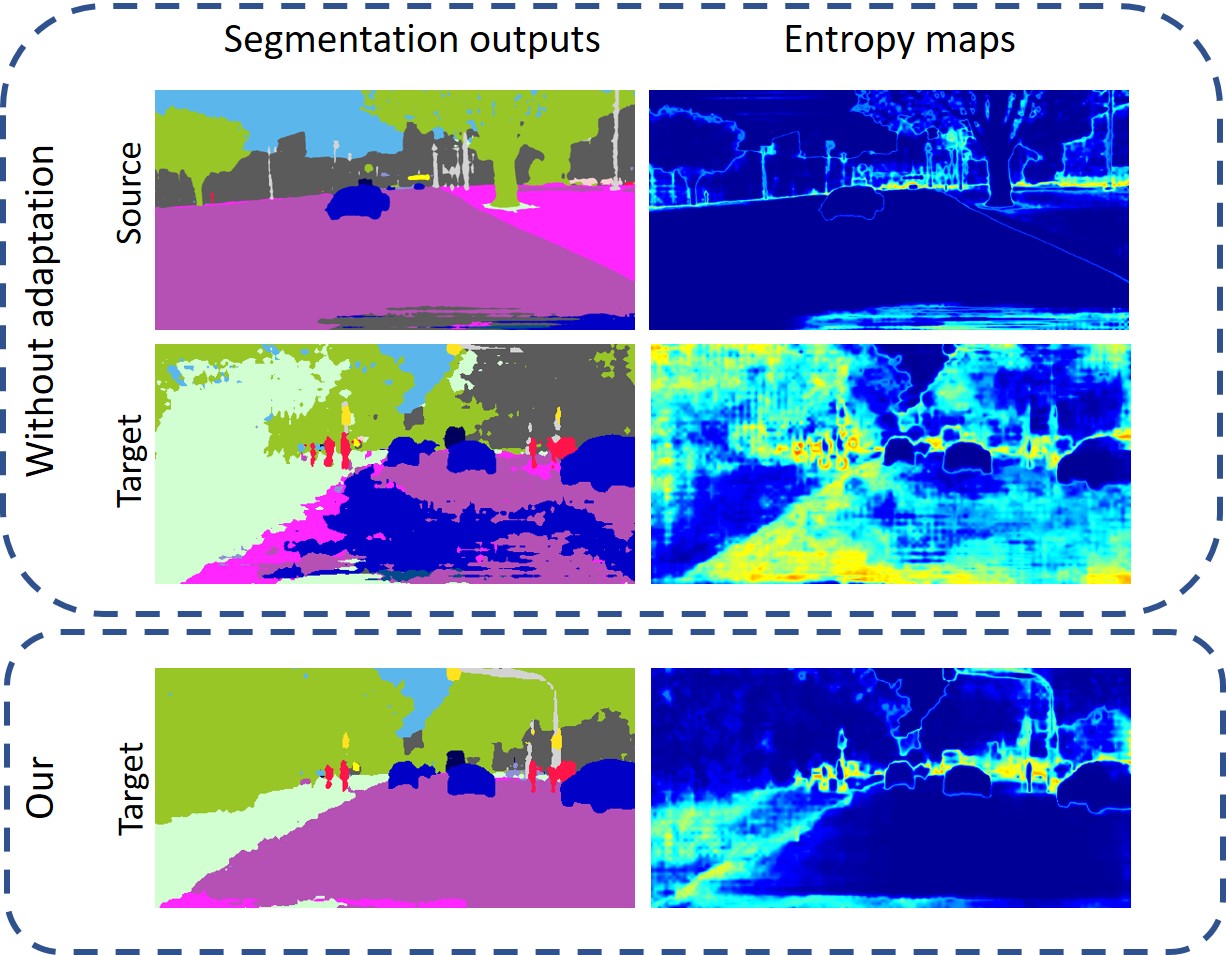






 Cityscapes
Cityscapes
 SYNTHIA
SYNTHIA
