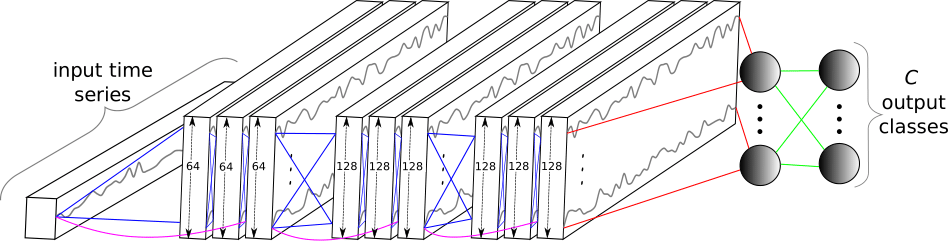
Data augmentation using synthetic data for time series classification with deep residual networks
Data augmentation in deep neural networks is the process of generating artificial data in order to reduce the variance of the classifier with the goal to reduce the number of errors. This idea has been shown to improve deep neural network's generalization capabilities in many computer vision tasks such as image recognition and object localization. Apart from these applications, deep Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) have also recently gained popularity in the Time Series Classification (TSC) community. However, unlike in image recognition problems, data augmentation techniques have not yet been investigated thoroughly for the TSC task. This is surprising as the accuracy of deep learning models for TSC could potentially be improved, especially for small datasets that exhibit overfitting, when a data augmentation method is adopted. In this paper, we fill this gap by investigating the application of a recently proposed data augmentation technique based on the Dynamic Time Warping distance, for a deep learning model for TSC. To evaluate the potential of augmenting the training set, we performed extensive experiments using the UCR TSC benchmark. Our preliminary experiments reveal that data augmentation can drastically increase deep CNN's accuracy on some datasets and significantly improve the deep model's accuracy when the method is used in an ensemble approach.
PDF Abstract