DCASE 2021 Task 3: Spectrotemporally-aligned Features for Polyphonic Sound Event Localization and Detection
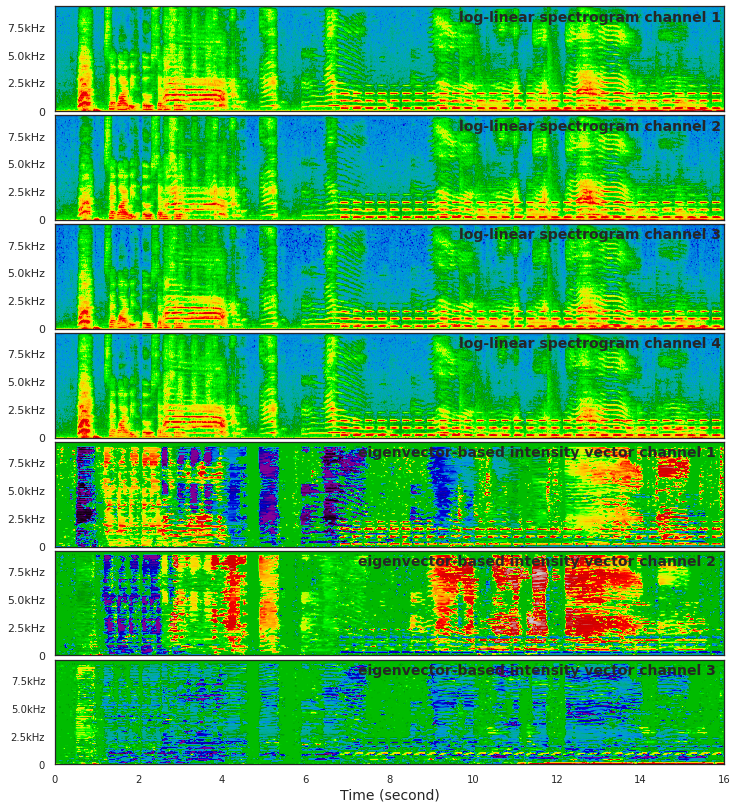
Sound event localization and detection consists of two subtasks which are sound event detection and direction-of-arrival estimation. While sound event detection mainly relies on time-frequency patterns to distinguish different sound classes, direction-of-arrival estimation uses magnitude or phase differences between microphones to estimate source directions. Therefore, it is often difficult to jointly train these two subtasks simultaneously. We propose a novel feature called spatial cue-augmented log-spectrogram (SALSA) with exact time-frequency mapping between the signal power and the source direction-of-arrival. The feature includes multichannel log-spectrograms stacked along with the estimated direct-to-reverberant ratio and a normalized version of the principal eigenvector of the spatial covariance matrix at each time-frequency bin on the spectrograms. Experimental results on the DCASE 2021 dataset for sound event localization and detection with directional interference showed that the deep learning-based models trained on this new feature outperformed the DCASE challenge baseline by a large margin. We combined several models with slightly different architectures that were trained on the new feature to further improve the system performances for the DCASE sound event localization and detection challenge.
PDF Abstract