Decoupling Makes Weakly Supervised Local Feature Better
Weakly supervised learning can help local feature methods to overcome the obstacle of acquiring a large-scale dataset with densely labeled correspondences. However, since weak supervision cannot distinguish the losses caused by the detection and description steps, directly conducting weakly supervised learning within a joint describe-then-detect pipeline suffers limited performance. In this paper, we propose a decoupled describe-then-detect pipeline tailored for weakly supervised local feature learning. Within our pipeline, the detection step is decoupled from the description step and postponed until discriminative and robust descriptors are learned. In addition, we introduce a line-to-window search strategy to explicitly use the camera pose information for better descriptor learning. Extensive experiments show that our method, namely PoSFeat (Camera Pose Supervised Feature), outperforms previous fully and weakly supervised methods and achieves state-of-the-art performance on a wide range of downstream tasks.
PDF Abstract CVPR 2022 PDF CVPR 2022 Abstract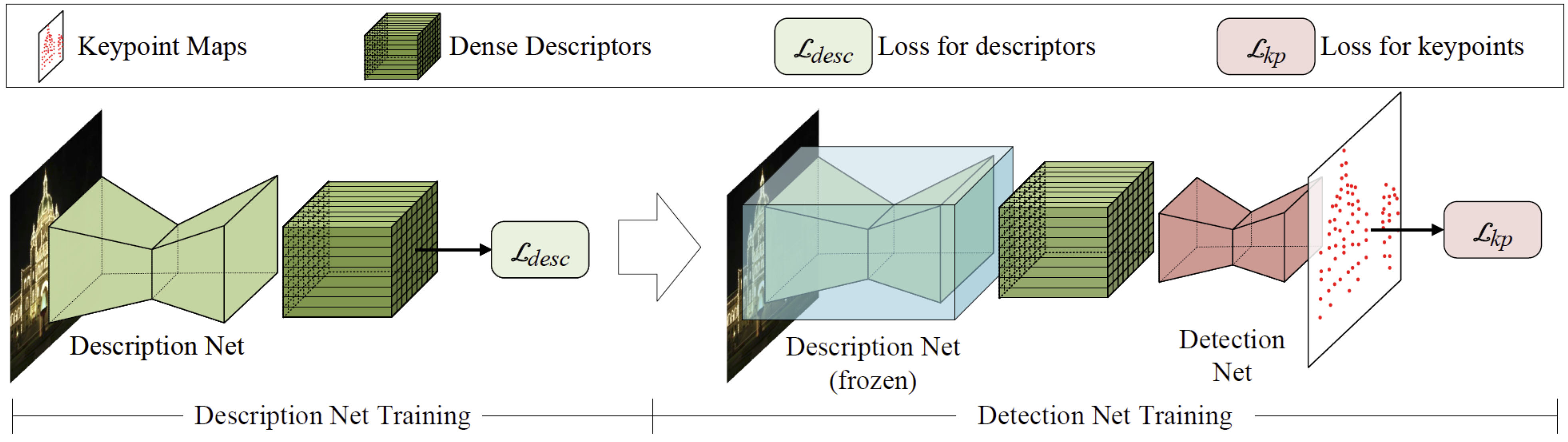




 HPatches
HPatches
 Aachen Day-Night
Aachen Day-Night
 ETH SfM
ETH SfM
