Deep Weakly-Supervised Learning Methods for Classification and Localization in Histology Images: A Survey
Using deep learning models to diagnose cancer from histology data presents several challenges. Cancer grading and localization of regions of interest (ROIs) in these images normally relies on both image- and pixel-level labels, the latter requiring a costly annotation process. Deep weakly-supervised object localization (WSOL) methods provide different strategies for low-cost training of deep learning models. Using only image-class annotations, these methods can be trained to classify an image, and yield class activation maps (CAMs) for ROI localization. This paper provides a review of state-of-art DL methods for WSOL. We propose a taxonomy where these methods are divided into bottom-up and top-down methods according to the information flow in models. Although the latter have seen limited progress, recent bottom-up methods are currently driving much progress with deep WSOL methods. Early works focused on designing different spatial pooling functions. However, these methods reached limited localization accuracy, and unveiled a major limitation -- the under-activation of CAMs which leads to high false negative localization. Subsequent works aimed to alleviate this issue and recover complete object. Representative methods from our taxonomy are evaluated and compared in terms of classification and localization accuracy on two challenging histology datasets. Overall, the results indicate poor localization performance, particularly for generic methods that were initially designed to process natural images. Methods designed to address the challenges of histology data yielded good results. However, all methods suffer from high false positive/negative localization. Four key challenges are identified for the application of deep WSOL methods in histology -- under/over activation of CAMs, sensitivity to thresholding, and model selection.
PDF Abstract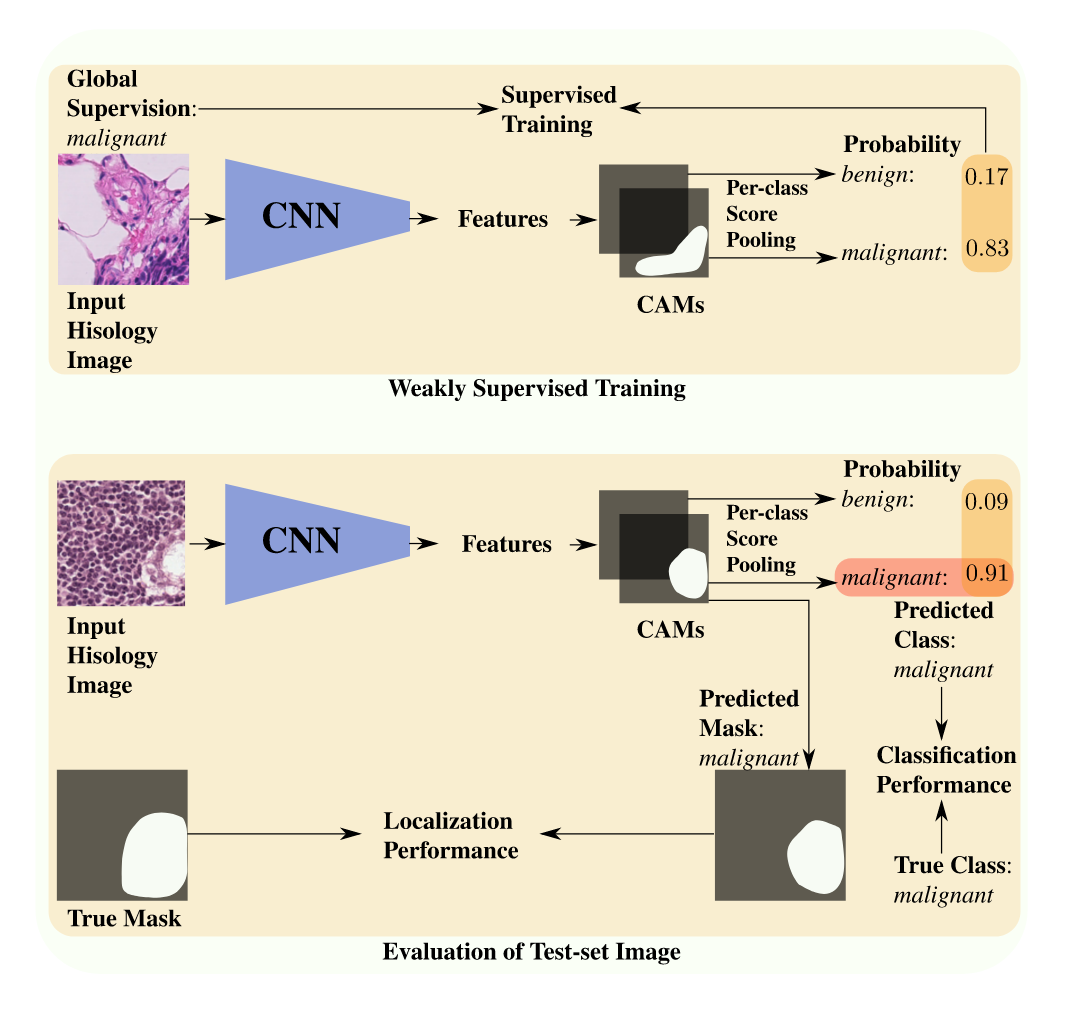



 GlaS
GlaS