Designing Neural Speaker Embeddings with Meta Learning
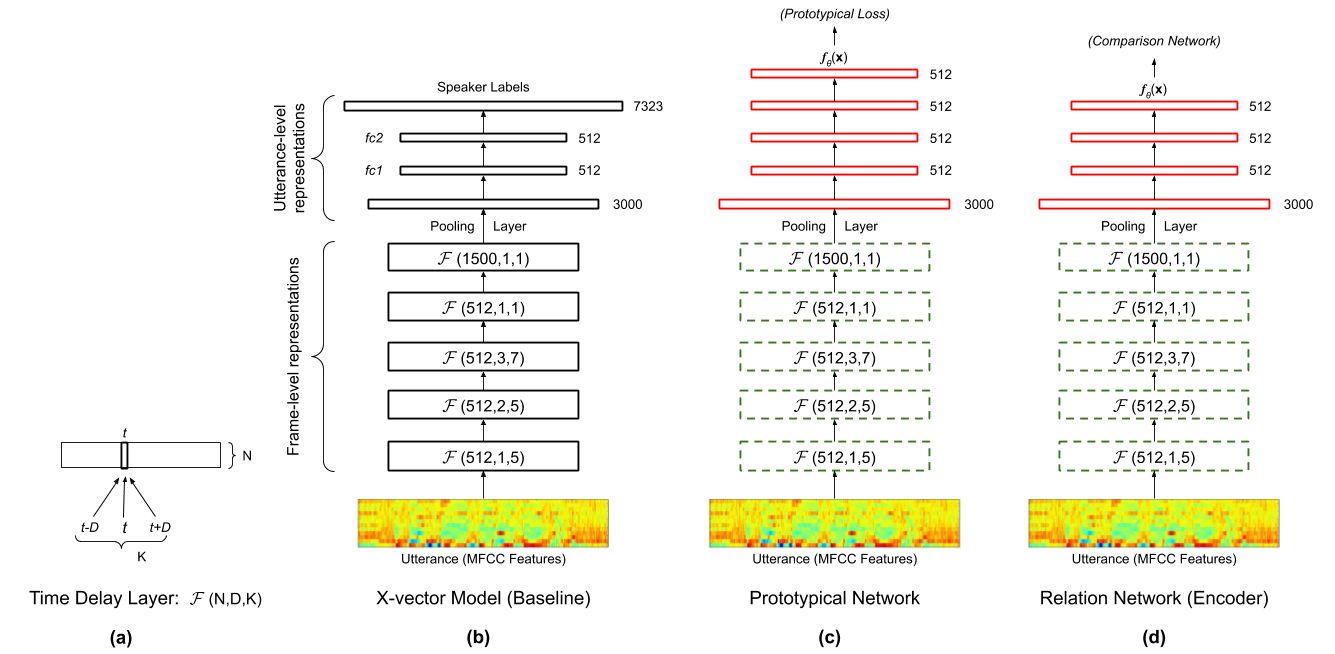
Neural speaker embeddings trained using classification objectives have demonstrated state-of-the-art performance in multiple applications. Typically, such embeddings are trained on an out-of-domain corpus on a single task e.g., speaker classification, albeit with a large number of classes (speakers). In this work, we reformulate embedding training under the meta-learning paradigm. We redistribute the training corpus as an ensemble of multiple related speaker classification tasks, and learn a representation that generalizes better to unseen speakers. First, we develop an open source toolkit to train x-vectors that is matched in performance with pre-trained Kaldi models for speaker diarization and speaker verification applications. We find that different bottleneck layers in the architecture variedly favor different applications. Next, we use two meta-learning strategies, namely prototypical networks and relation networks, to improve over the x-vector embeddings. Our best performing model achieves a relative improvement of 12.37% and 7.11% in speaker error on the DIHARD II development corpus and the AMI meeting corpus, respectively. We analyze improvements across different domains in the DIHARD corpus. Notably, on the challenging child speech domain, we study the relation between child age and the diarization performance. Further, we show reductions in equal error rate for speaker verification on the SITW corpus (7.68%) and the VOiCES challenge corpus (8.78%). We observe that meta-learning particularly offers benefits in challenging acoustic conditions and recording setups encountered in these corpora. Our experiments illustrate the applicability of meta-learning as a generalized learning paradigm for training deep neural speaker embeddings.
PDF Abstract