DiffusionNet: Discretization Agnostic Learning on Surfaces
We introduce a new general-purpose approach to deep learning on 3D surfaces, based on the insight that a simple diffusion layer is highly effective for spatial communication. The resulting networks are automatically robust to changes in resolution and sampling of a surface -- a basic property which is crucial for practical applications. Our networks can be discretized on various geometric representations such as triangle meshes or point clouds, and can even be trained on one representation then applied to another. We optimize the spatial support of diffusion as a continuous network parameter ranging from purely local to totally global, removing the burden of manually choosing neighborhood sizes. The only other ingredients in the method are a multi-layer perceptron applied independently at each point, and spatial gradient features to support directional filters. The resulting networks are simple, robust, and efficient. Here, we focus primarily on triangle mesh surfaces, and demonstrate state-of-the-art results for a variety of tasks including surface classification, segmentation, and non-rigid correspondence.
PDF Abstract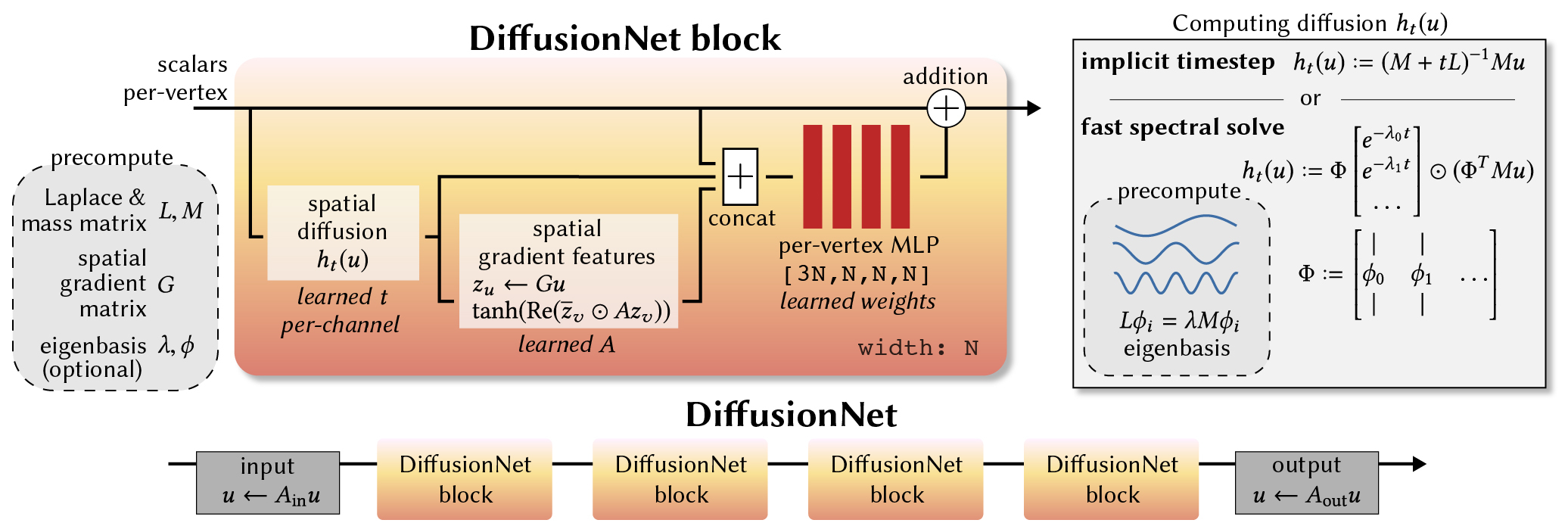

 FAUST
FAUST