Discrepancy-Based Active Learning for Domain Adaptation
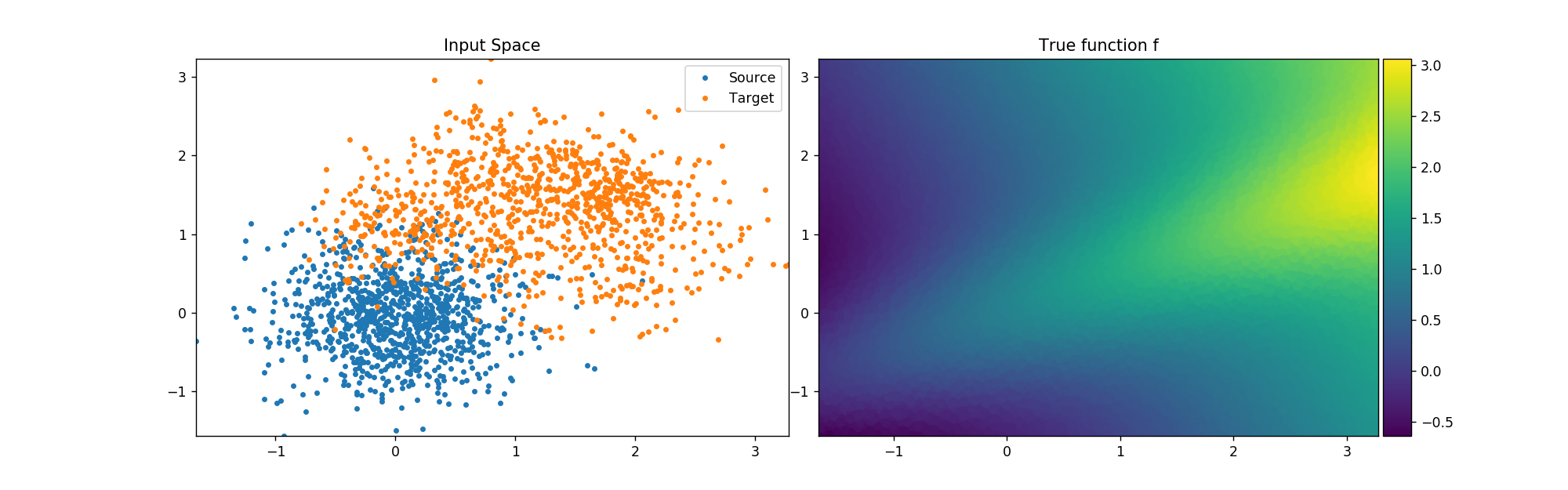
The goal of the paper is to design active learning strategies which lead to domain adaptation under an assumption of Lipschitz functions. Building on previous work by Mansour et al. (2009) we adapt the concept of discrepancy distance between source and target distributions to restrict the maximization over the hypothesis class to a localized class of functions which are performing accurate labeling on the source domain. We derive generalization error bounds for such active learning strategies in terms of Rademacher average and localized discrepancy for general loss functions which satisfy a regularity condition. A practical K-medoids algorithm that can address the case of large data set is inferred from the theoretical bounds. Our numerical experiments show that the proposed algorithm is competitive against other state-of-the-art active learning techniques in the context of domain adaptation, in particular on large data sets of around one hundred thousand images.
PDF Abstract ICLR 2022 PDF ICLR 2022 Abstract