Diverse Human Motion Prediction via Gumbel-Softmax Sampling from an Auxiliary Space
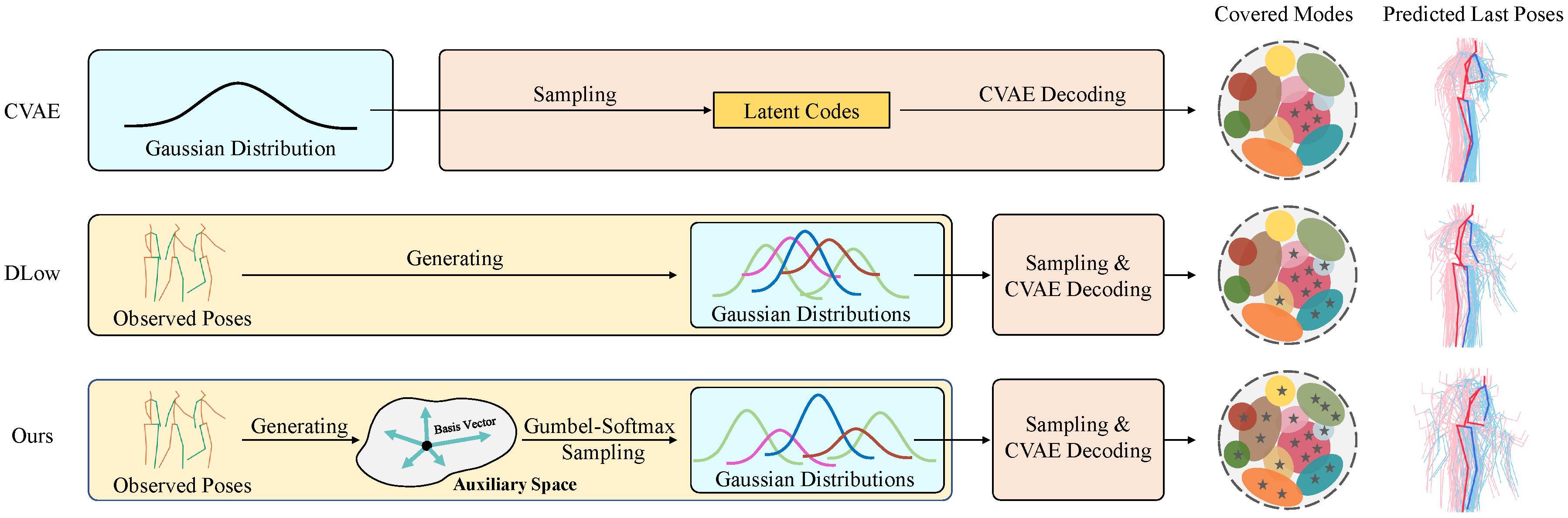
Diverse human motion prediction aims at predicting multiple possible future pose sequences from a sequence of observed poses. Previous approaches usually employ deep generative networks to model the conditional distribution of data, and then randomly sample outcomes from the distribution. While different results can be obtained, they are usually the most likely ones which are not diverse enough. Recent work explicitly learns multiple modes of the conditional distribution via a deterministic network, which however can only cover a fixed number of modes within a limited range. In this paper, we propose a novel sampling strategy for sampling very diverse results from an imbalanced multimodal distribution learned by a deep generative model. Our method works by generating an auxiliary space and smartly making randomly sampling from the auxiliary space equivalent to the diverse sampling from the target distribution. We propose a simple yet effective network architecture that implements this novel sampling strategy, which incorporates a Gumbel-Softmax coefficient matrix sampling method and an aggressive diversity promoting hinge loss function. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our method significantly improves both the diversity and accuracy of the samplings compared with previous state-of-the-art sampling approaches. Code and pre-trained models are available at https://github.com/Droliven/diverse_sampling.
PDF AbstractDatasets
| Task | Dataset | Model | Metric Name | Metric Value | Global Rank | Benchmark |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Human Pose Forecasting | Human3.6M | DiverseSampling | APD | 15310 | # 3 | |
| ADE | 370 | # 3 | ||||
| FDE | 485 | # 4 | ||||
| MMADE | 475 | # 4 | ||||
| MMFDE | 516 | # 4 | ||||
| CMD | 11.692 | # 4 | ||||
| FID | 2.083 | # 3 | ||||
| Human Pose Forecasting | HumanEva-I | DHMP | APD@2000ms | 6109 | # 2 | |
| ADE@2000ms | 220 | # 3 | ||||
| FDE@2000ms | 234 | # 2 | ||||
| MMADE@2000ms | 342 | # 2 | ||||
| MMFDE@2000ms | 316 | # 1 |





 Human3.6M
Human3.6M
