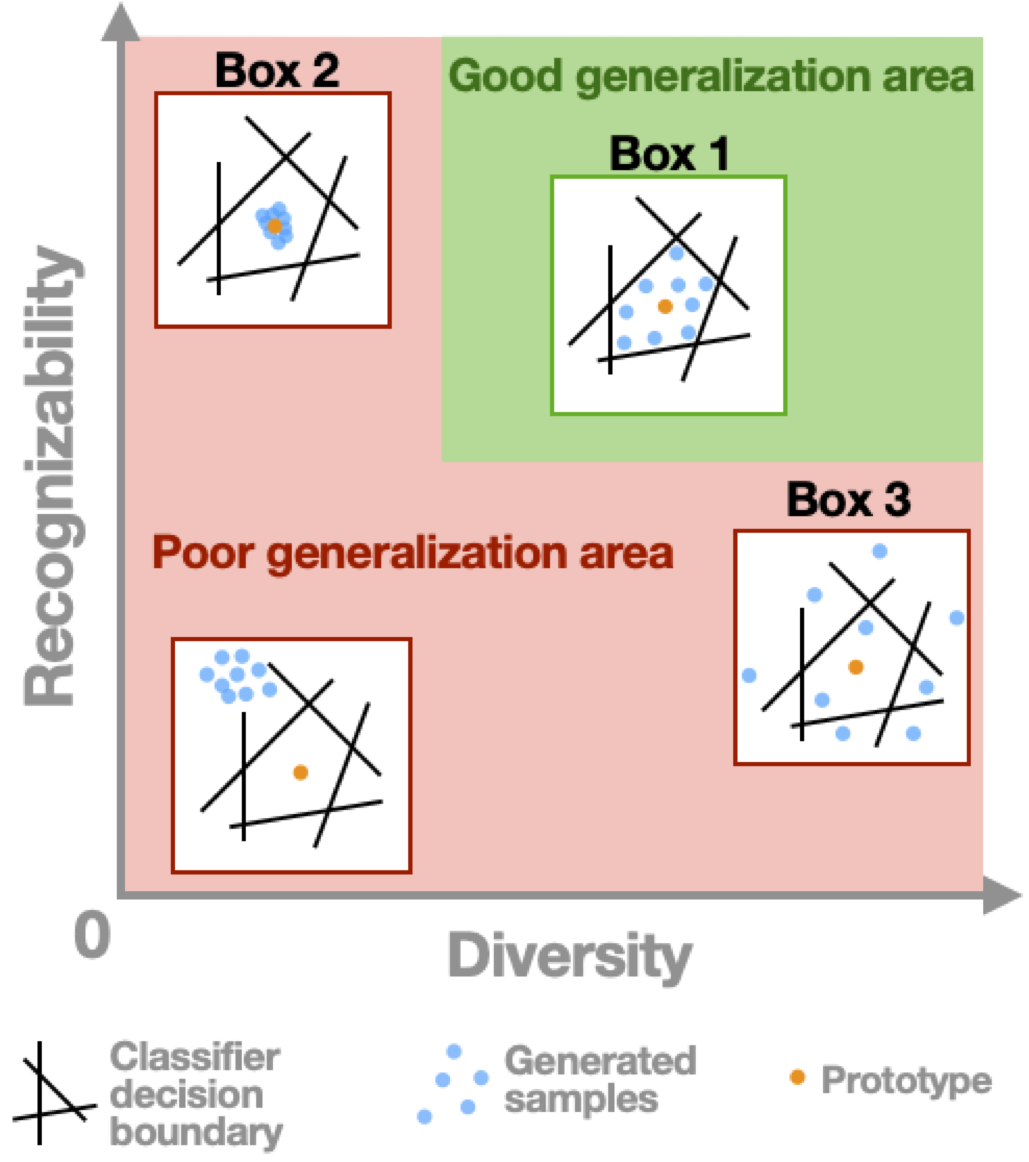
Diversity vs. Recognizability: Human-like generalization in one-shot generative models
Robust generalization to new concepts has long remained a distinctive feature of human intelligence. However, recent progress in deep generative models has now led to neural architectures capable of synthesizing novel instances of unknown visual concepts from a single training example. Yet, a more precise comparison between these models and humans is not possible because existing performance metrics for generative models (i.e., FID, IS, likelihood) are not appropriate for the one-shot generation scenario. Here, we propose a new framework to evaluate one-shot generative models along two axes: sample recognizability vs. diversity (i.e., intra-class variability). Using this framework, we perform a systematic evaluation of representative one-shot generative models on the Omniglot handwritten dataset. We first show that GAN-like and VAE-like models fall on opposite ends of the diversity-recognizability space. Extensive analyses of the effect of key model parameters further revealed that spatial attention and context integration have a linear contribution to the diversity-recognizability trade-off. In contrast, disentanglement transports the model along a parabolic curve that could be used to maximize recognizability. Using the diversity-recognizability framework, we were able to identify models and parameters that closely approximate human data.
PDF Abstract