DoDNet: Learning to segment multi-organ and tumors from multiple partially labeled datasets
Due to the intensive cost of labor and expertise in annotating 3D medical images at a voxel level, most benchmark datasets are equipped with the annotations of only one type of organs and/or tumors, resulting in the so-called partially labeling issue. To address this, we propose a dynamic on-demand network (DoDNet) that learns to segment multiple organs and tumors on partially labeled datasets. DoDNet consists of a shared encoder-decoder architecture, a task encoding module, a controller for generating dynamic convolution filters, and a single but dynamic segmentation head. The information of the current segmentation task is encoded as a task-aware prior to tell the model what the task is expected to solve. Different from existing approaches which fix kernels after training, the kernels in dynamic head are generated adaptively by the controller, conditioned on both input image and assigned task. Thus, DoDNet is able to segment multiple organs and tumors, as done by multiple networks or a multi-head network, in a much efficient and flexible manner. We have created a large-scale partially labeled dataset, termed MOTS, and demonstrated the superior performance of our DoDNet over other competitors on seven organ and tumor segmentation tasks. We also transferred the weights pre-trained on MOTS to a downstream multi-organ segmentation task and achieved state-of-the-art performance. This study provides a general 3D medical image segmentation model that has been pre-trained on a large-scale partially labelled dataset and can be extended (after fine-tuning) to downstream volumetric medical data segmentation tasks. The dataset and code areavailableat: https://git.io/DoDNet
PDF Abstract CVPR 2021 PDF CVPR 2021 Abstract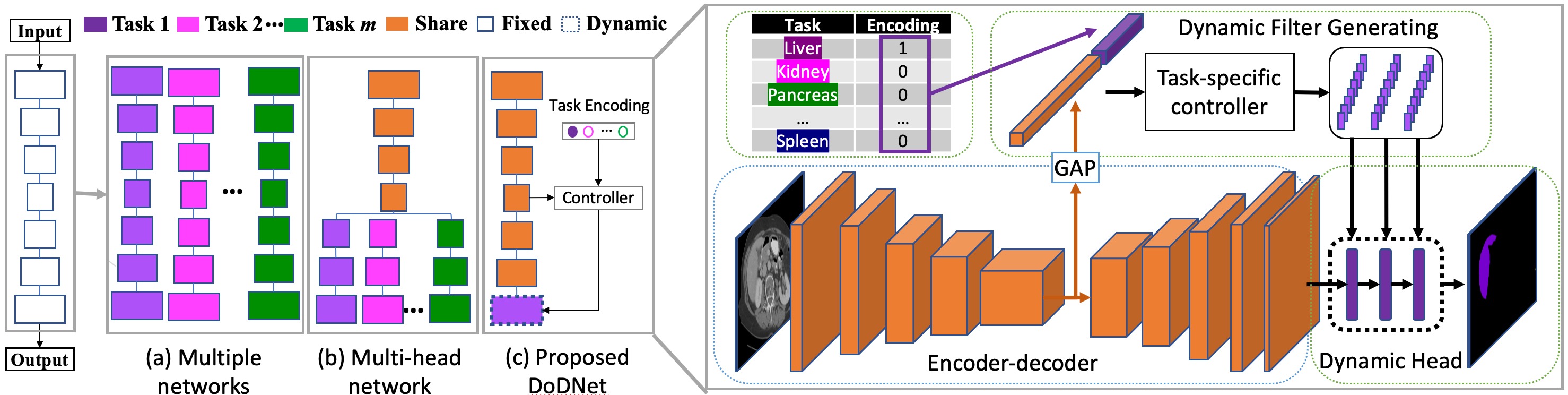





 Medical Segmentation Decathlon
Medical Segmentation Decathlon