Dynamic Routing Between Capsules
A capsule is a group of neurons whose activity vector represents the instantiation parameters of a specific type of entity such as an object or an object part. We use the length of the activity vector to represent the probability that the entity exists and its orientation to represent the instantiation parameters. Active capsules at one level make predictions, via transformation matrices, for the instantiation parameters of higher-level capsules. When multiple predictions agree, a higher level capsule becomes active. We show that a discrimininatively trained, multi-layer capsule system achieves state-of-the-art performance on MNIST and is considerably better than a convolutional net at recognizing highly overlapping digits. To achieve these results we use an iterative routing-by-agreement mechanism: A lower-level capsule prefers to send its output to higher level capsules whose activity vectors have a big scalar product with the prediction coming from the lower-level capsule.
PDF Abstract NeurIPS 2017 PDF NeurIPS 2017 Abstract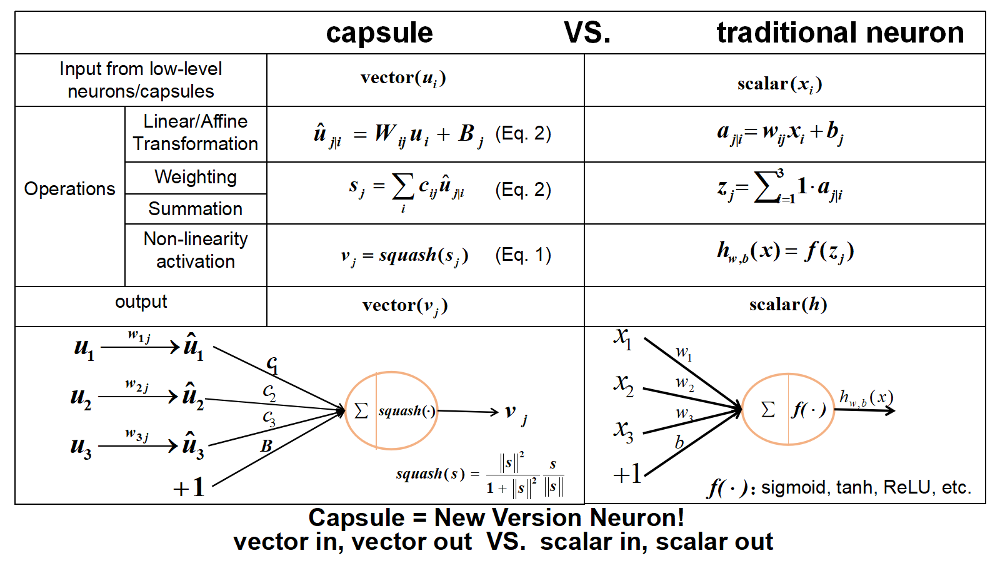









 MultiMNIST
MultiMNIST
 CIFAR-10
CIFAR-10
 MNIST
MNIST
 EMNIST
EMNIST
 smallNORB
smallNORB
