Efficient Learning on Point Clouds with Basis Point Sets
With the increased availability of 3D scanning technology, point clouds are moving into the focus of computer vision as a rich representation of everyday scenes. However, they are hard to handle for machine learning algorithms due to their unordered structure. One common approach is to apply occupancy grid mapping, which dramatically increases the amount of data stored and at the same time loses details through discretization. Recently, deep learning models were proposed to handle point clouds directly and achieve input permutation invariance. However, these architectures often use an increased number of parameters and are computationally inefficient. In this work, we propose basis point sets (BPS) as a highly efficient and fully general way to process point clouds with machine learning algorithms. The basis point set representation is a residual representation that can be computed efficiently and can be used with standard neural network architectures and other machine learning algorithms. Using the proposed representation as the input to a simple fully connected network allows us to match the performance of PointNet on a shape classification task while using three orders of magnitude less floating-point operations. In a second experiment, we show how the proposed representation can be used for registering high-resolution meshes to noisy 3D scans. Here, we present the first method for single-pass high-resolution mesh registration, avoiding time-consuming per-scan optimization and allowing real-time execution.
PDF Abstract ICCV 2019 PDF ICCV 2019 Abstract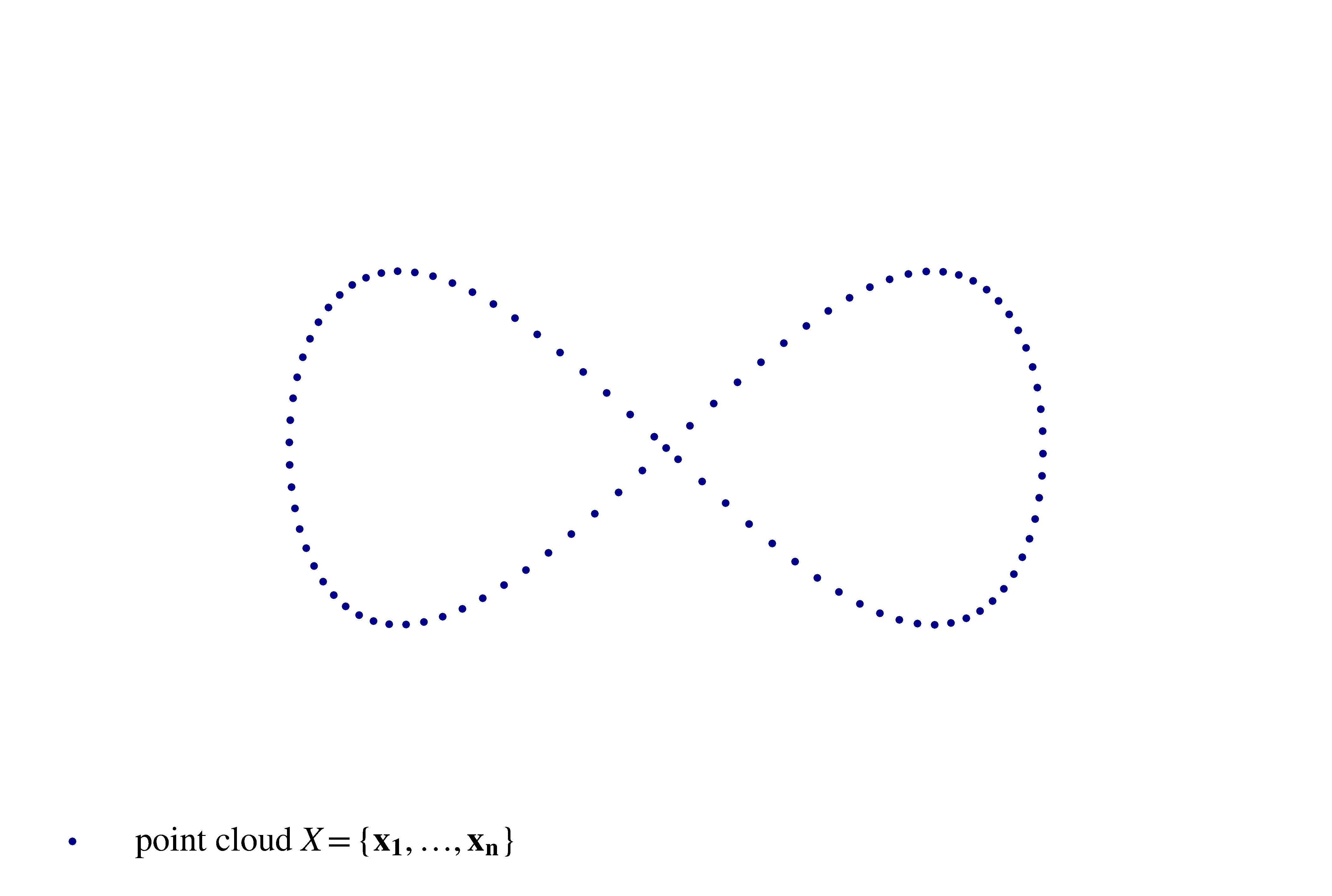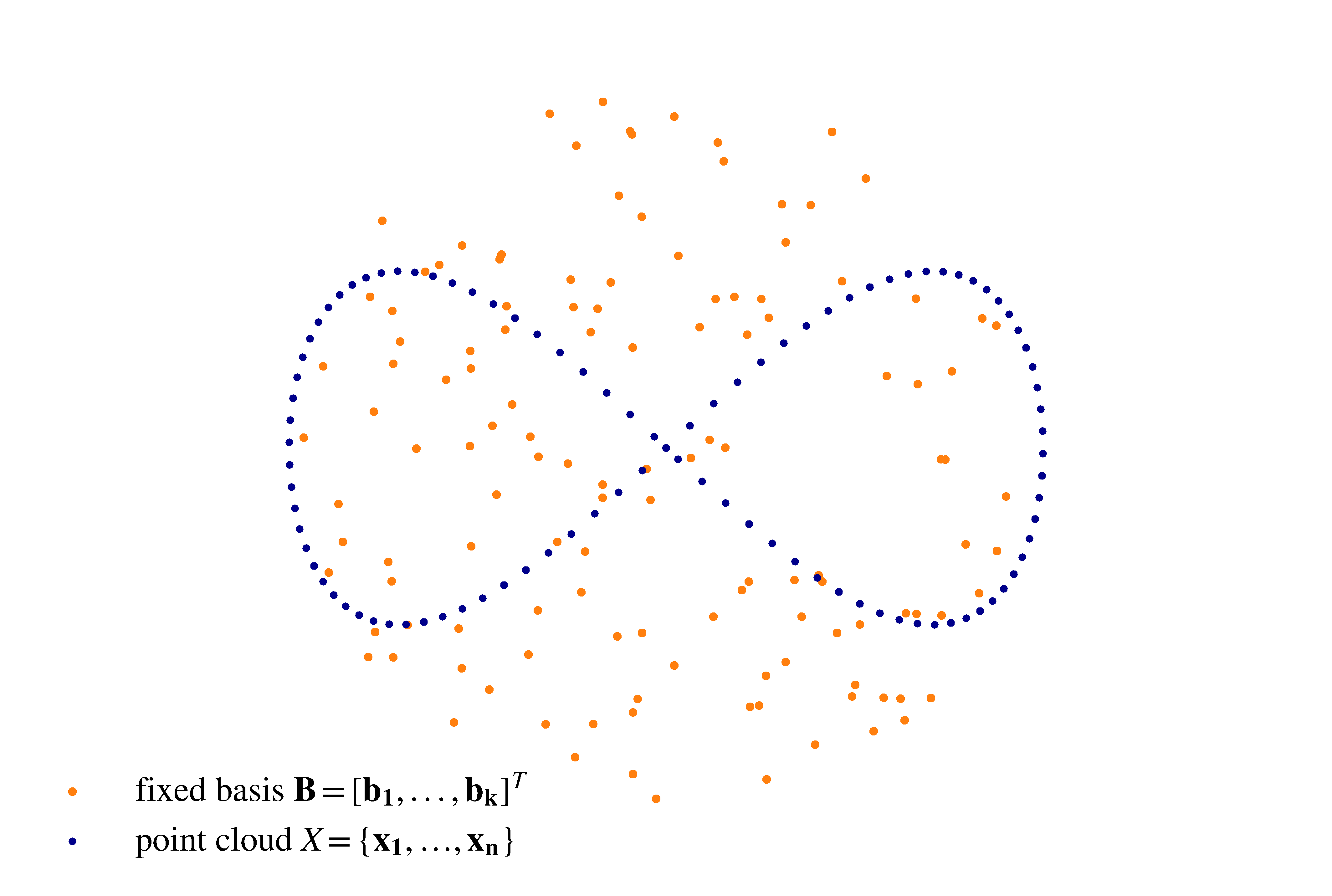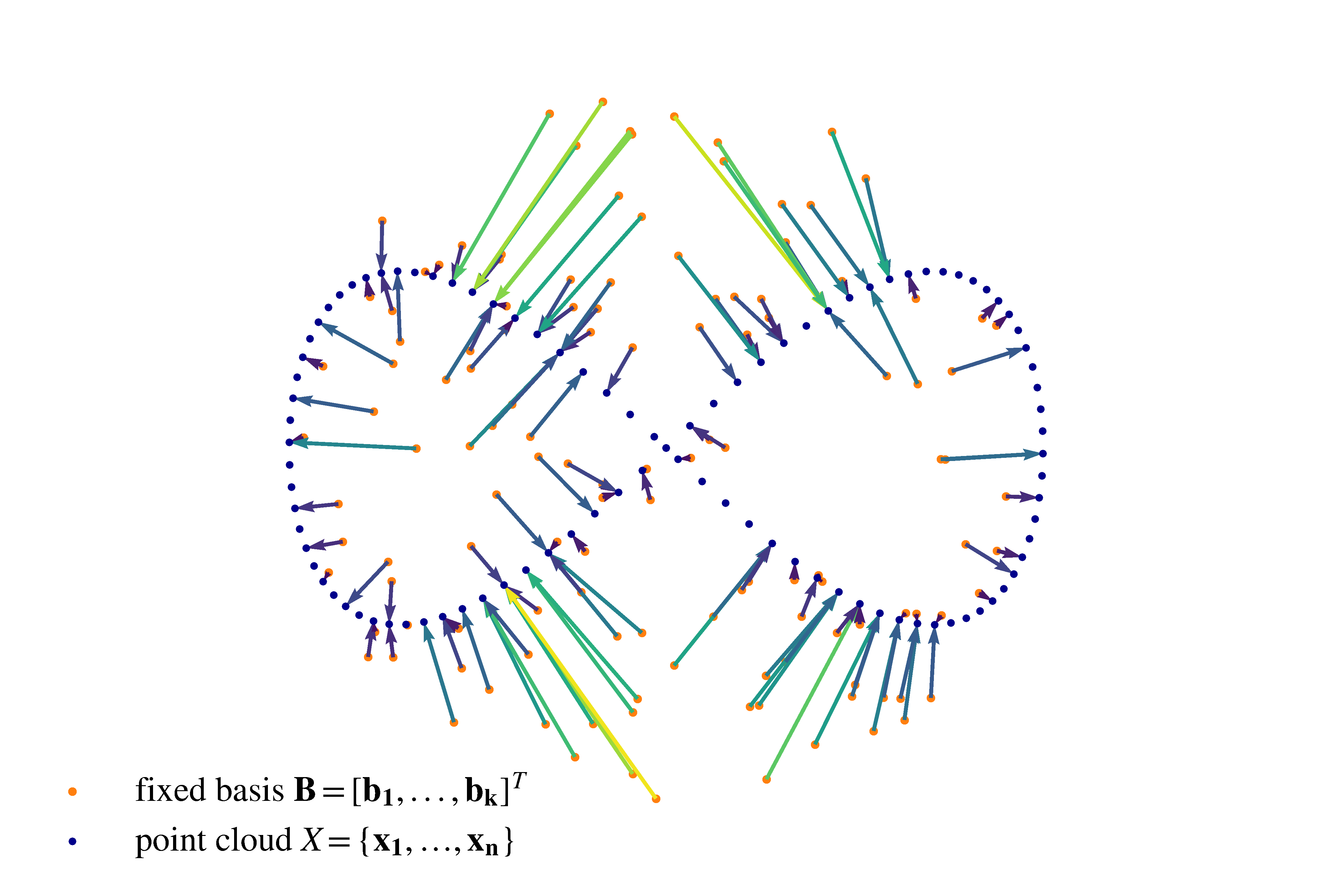


 ModelNet
ModelNet
 Dynamic FAUST
Dynamic FAUST