EnD: Entangling and Disentangling deep representations for bias correction
Artificial neural networks perform state-of-the-art in an ever-growing number of tasks, and nowadays they are used to solve an incredibly large variety of tasks. There are problems, like the presence of biases in the training data, which question the generalization capability of these models. In this work we propose EnD, a regularization strategy whose aim is to prevent deep models from learning unwanted biases. In particular, we insert an "information bottleneck" at a certain point of the deep neural network, where we disentangle the information about the bias, still letting the useful information for the training task forward-propagating in the rest of the model. One big advantage of EnD is that we do not require additional training complexity (like decoders or extra layers in the model), since it is a regularizer directly applied on the trained model. Our experiments show that EnD effectively improves the generalization on unbiased test sets, and it can be effectively applied on real-case scenarios, like removing hidden biases in the COVID-19 detection from radiographic images.
PDF Abstract CVPR 2021 PDF CVPR 2021 Abstract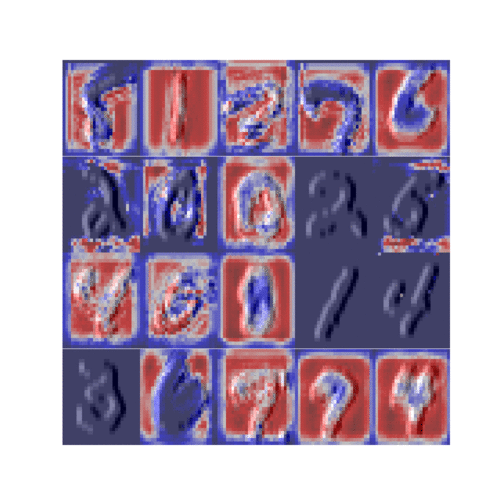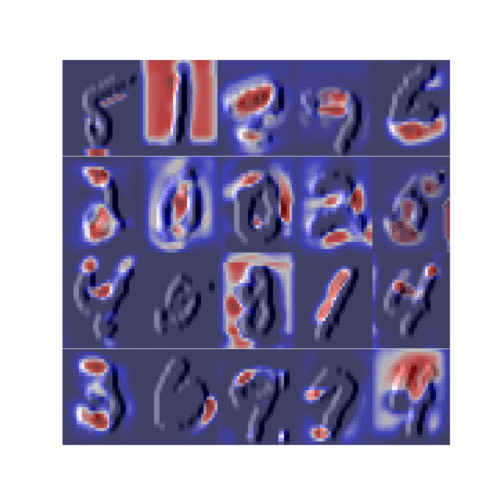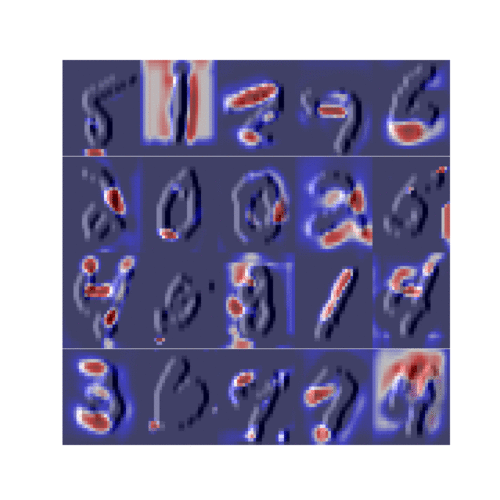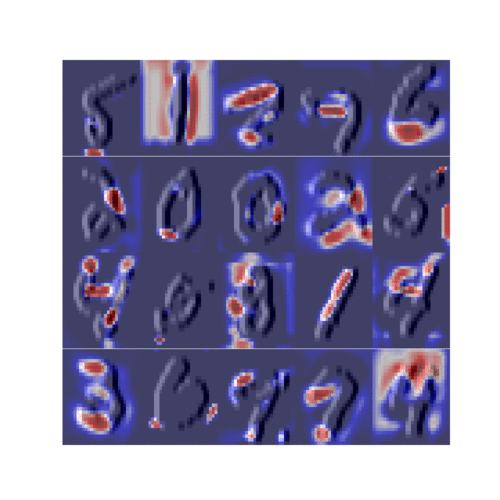










 CelebA
CelebA
