Discriminative Clustering with Representation Learning with any Ratio of Labeled to Unlabeled Data
We present a discriminative clustering approach in which the feature representation can be learned from data and moreover leverage labeled data. Representation learning can give a similarity-based clustering method the ability to automatically adapt to an underlying, yet hidden, geometric structure of the data. The proposed approach augments the DIFFRAC method with a representation learning capability, using a gradient-based stochastic training algorithm and an optimal transport algorithm with entropic regularization to perform the cluster assignment step. The resulting method is evaluated on several real datasets when varying the ratio of labeled data to unlabeled data and thereby interpolating between the fully unsupervised regime and the fully supervised regime. The experimental results suggest that the proposed method can learn powerful feature representations even in the fully unsupervised regime and can leverage even small amounts of labeled data to improve the feature representations and to obtain better clusterings of complex datasets.
PDF Abstract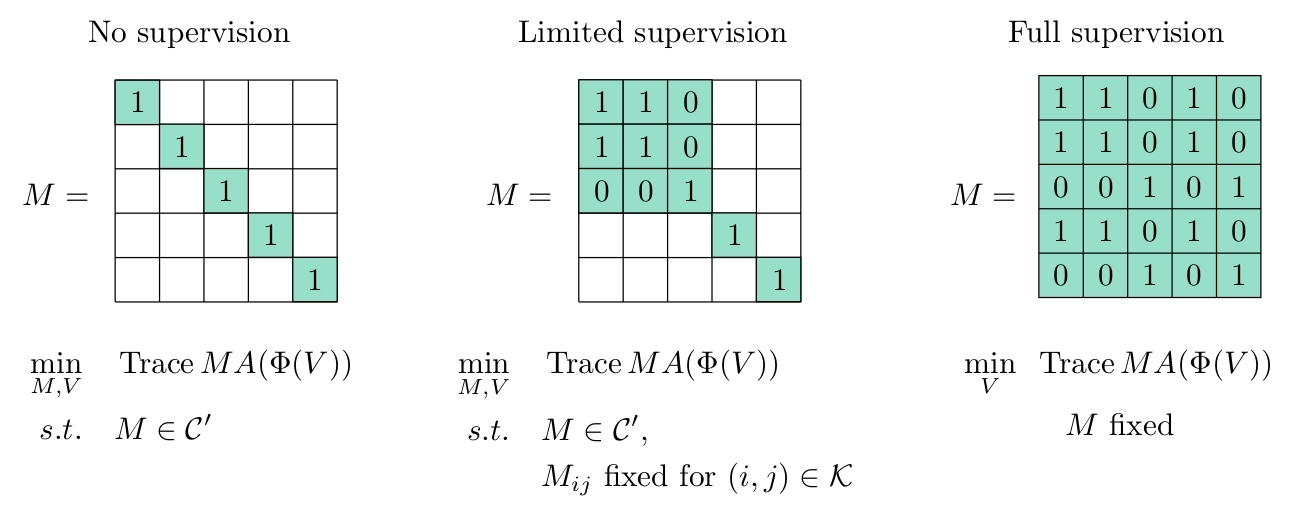



 CIFAR-10
CIFAR-10
 MNIST
MNIST