End-to-End Training of Multi-Document Reader and Retriever for Open-Domain Question Answering
We present an end-to-end differentiable training method for retrieval-augmented open-domain question answering systems that combine information from multiple retrieved documents when generating answers. We model retrieval decisions as latent variables over sets of relevant documents. Since marginalizing over sets of retrieved documents is computationally hard, we approximate this using an expectation-maximization algorithm. We iteratively estimate the value of our latent variable (the set of relevant documents for a given question) and then use this estimate to update the retriever and reader parameters. We hypothesize that such end-to-end training allows training signals to flow to the reader and then to the retriever better than staged-wise training. This results in a retriever that is able to select more relevant documents for a question and a reader that is trained on more accurate documents to generate an answer. Experiments on three benchmark datasets demonstrate that our proposed method outperforms all existing approaches of comparable size by 2-3% absolute exact match points, achieving new state-of-the-art results. Our results also demonstrate the feasibility of learning to retrieve to improve answer generation without explicit supervision of retrieval decisions.
PDF Abstract NeurIPS 2021 PDF NeurIPS 2021 Abstract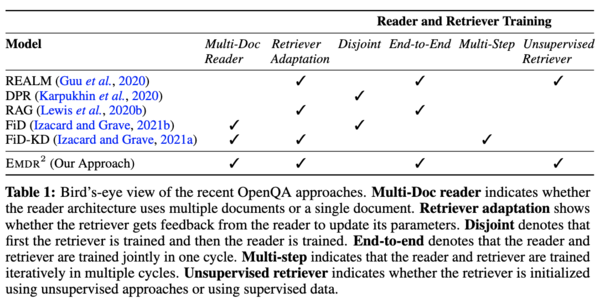








 Natural Questions
Natural Questions
 TriviaQA
TriviaQA
 WebQuestions
WebQuestions
