Generating Multiple Hypotheses for 3D Human Pose Estimation with Mixture Density Network
3D human pose estimation from a monocular image or 2D joints is an ill-posed problem because of depth ambiguity and occluded joints. We argue that 3D human pose estimation from a monocular input is an inverse problem where multiple feasible solutions can exist. In this paper, we propose a novel approach to generate multiple feasible hypotheses of the 3D pose from 2D joints.In contrast to existing deep learning approaches which minimize a mean square error based on an unimodal Gaussian distribution, our method is able to generate multiple feasible hypotheses of 3D pose based on a multimodal mixture density networks. Our experiments show that the 3D poses estimated by our approach from an input of 2D joints are consistent in 2D reprojections, which supports our argument that multiple solutions exist for the 2D-to-3D inverse problem. Furthermore, we show state-of-the-art performance on the Human3.6M dataset in both best hypothesis and multi-view settings, and we demonstrate the generalization capacity of our model by testing on the MPII and MPI-INF-3DHP datasets. Our code is available at the project website.
PDF Abstract CVPR 2019 PDF CVPR 2019 Abstract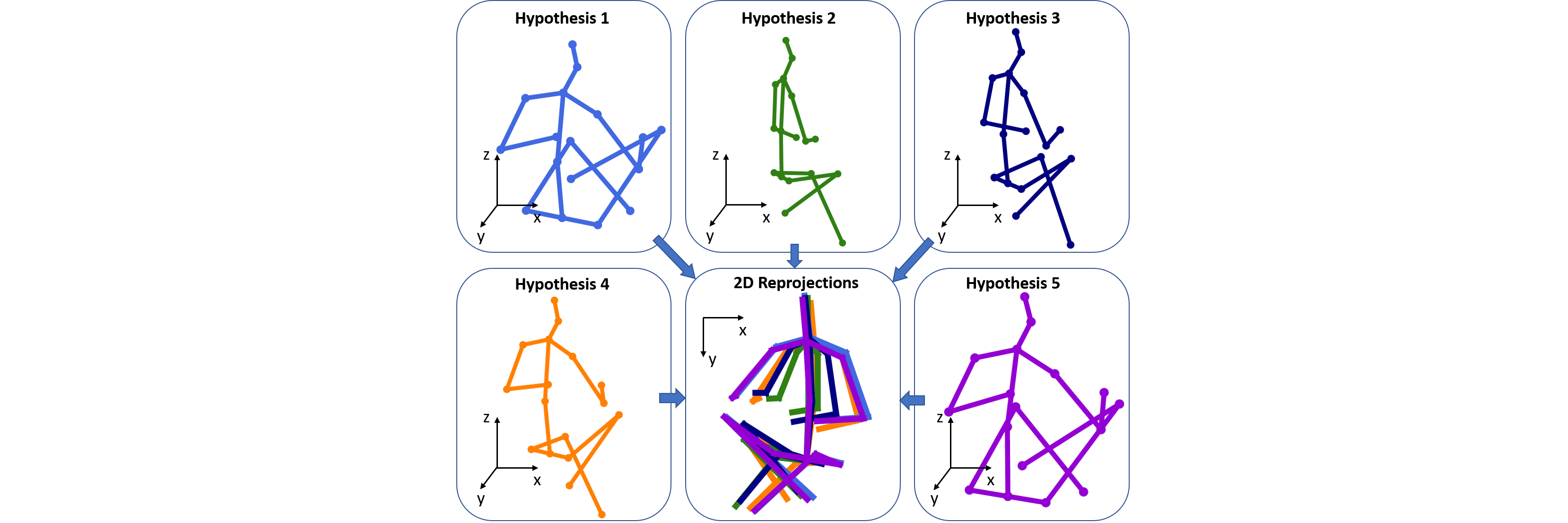








 Human3.6M
Human3.6M
 MPII
MPII
 MPI-INF-3DHP
MPI-INF-3DHP
